Abstract
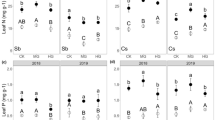
Seasonal variations in foliar stable carbon composition (δ13C) and nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) concentrations of Populus euphratica Olivier and Tamarix ramosissima Ledeb, as well as correlations between foliar δ13C values and N, P and K concentrations were studied in the E**a oasis in the lower reaches of the Heihe River, northwestern China. Foliar δ13C values, and P and K concentrations significantly differed between species. Foliar δ13C signatures in T. ramosissima were significantly more enriched than those in P. euphratica, but P and K concentrations of P. euphratica were higher. The seasonal variations and patterns of these were similar. The total foliar δ13C values and N, P and K concentrations in both P. euphratica and T. ramosissima showed a descending trend. There were significantly positive correlations between foliar δ13C values and N and P concentration of both P. euphratica and T. ramosissima. For the relationship between foliar δ13C and K concentration, there appeared oppositely positive and negative correlations in P. euphratica and T. ramosissima, respectively, but they were not significant. The simple positive correlations of δ13C–P% and δ13C–N% suggested that N and P in P. euphratica and T. ramosissima behave in a similar manner. This study also showed that there were nutrient deficiencies; N and P nutriments were the co-limiting factors in P. euphratica, while it was P nutriment in T. ramosissima.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R, Chapin FS III (2000) The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: a re-evaluation of processes and patterns. Adv Ecol Res 30:1–67
Alifragis D, Smiris P, Maris F, Kavvadias FV (2001) The effect of stand age on the accumulation of nutrients in the aboveground components of an Aleppo pine ecosystem. For Ecol Manag 141:259–269
Bei**g Agricultural University (1994) Agricultural chemistry (pandect). Agricultural Press, Bei**g (in Chinese)
Boerner REJ (1985) Foliar nutrient dynamics, growth and nutrient use efficiency of Hammamelis virginiana in three forest microsites. Can J Bot 63:1476–1481
Bollmark L, Sennerby-Forsse L, Ericsson T (1999) Seasonal dynamics and effects of nitrogen supply rate on nitrogen and carbohydrate reserves in cutting-derived willow (Salix viminalis L.) plants. Can J For Res 29:85–94
Brooks JR, Flanagan LB, Buchmann N, Ehleringer JR (1997) Carbon isotope composition of boreal plants: functional grou** of life forms. Oecologia 110:301–311
Cerling DC, Wang Y, Quade J (1993) Expansion of C4 ecosystems as an indicator of global ecological change in the late Miocene. Nature 361:344–345
Chen T, Qin DH, Ren JW, Sun WZ, Chen X (2000) The altitudinal and temporal variation of δ13C values in leaves of Plantago medial. Acta Bot Boreal Occident Sin 20(4):672–675 (in Chinese)
Chen SP, Bai YF, Han XG (2002) Applications of stable carbon isotope techniques to ecological research. Acta Phytoecol Sin 26(5):549–560 (in Chinese)
Chen SL, Li JK, Wang SS, Fritz E, Hüttermann A, Altman A (2003) Effects of NaCl on shoot growth, transpiration, ion compartmentation, and transport in regenerated plants of P. euphratica and Populus tomentosa. Can J For Res 33(6):967–975
Chen GS, Zeng DH, Chen FS (2004a) Concentration of tree foliar and soil nutrients in Pinus spp. plantations in relation to species and stand age in Zhanggutai sandy land, northeast China. J For Res 15(1):11–18
Chen YH, Hu J, Li YS, Xu B, Yan CL (2004b) Application of stable carbon isotope techniques to research into water stress. Acta Ecol Sin 24(5):1027–1033 (in Chinese)
Choi WJ, Chang SX, Allen HL, Kelting DL, Ro HM (2005) Irrigation and fertilization effects on foliar and soil carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios in a loblolly pine stand. For Ecol Manag 213:90–101
Condon AG, Farquhar GD, Richards RA (1990) Genotypic variation in carbon isotope discrimination and transpiration efficiency in wheat. Leaf gas exchange and whole plant studies. Aust J Plant Physiol 17:9–22
Cunningham SA, Summerhayes B, Westoby M (1999) Evolutionary divergences in leaf structure and chemistry, comparing rainfall and soil nutrient gradients. Ecol Monogr 69:569–588
DaMatta FM, Loos RA, Silva EA, Loureiro ME, Ducatti C (2002) Effects of soil water deficit and nitrogen nutrition on water relations and photosynthesis of pot-grown Coffea canephora Pierre. Trees Struct Funct 16:555–558
Damesin C, Rambal S, Joffre R (1997) Between-tree variations in leaf δ13C of Quercus pubescens and Quercus ilex among Mediterranean habitats with different water availability. Oecologia 111:26–35
Deng X, Li XM, Zhang XM, Ye WH (2002) A study of the gas exchange characteristics of four desert plants. Acta Phytoecol Sin 26:605–612 (in Chinese)
Deng X, Li XM, Zhang XM, Ye WH, Foezki A, Runge M (2003) The studies about the photosynthetic response of the four desert plants. Acta Ecol Sin 23(3):598–605 (in Chinese)
Devitt DA, Salal A, Mace KA, Smith SD (1997) The effect of applied water on the water use of saltcedar in a desert riparian environment. J Hydrol 192:233–246
Duquesnay A, Breda N, Stievenard M, Dupouey JL (1998) Changes of tree-ring δ13C and water use efficiency of beech in north-eastern France during the past century. Plant Cell Environ 21:565–572
Elumalai RP, Nagpal P, Reed JW (2002) A mutation in the Arabidopsis KT2/KUP2 potassium transporter gene affects shoot cell expansion. Plant Cell 14:119–131
Evans JR (1989) Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants. Oecologia 78:9–19
Evans RD (2001) Physiological mechanisms influencing plant nitrogen isotope composition. Trends Plant Sci 6:121–126
Farquhar GD, Ehleringer JR, Hubick KT (1989a) Carbon isotope discrimination and photosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 40:503–537
Farquhar GD, Hubick KT, Condon AG et al (1989b) Carbon isotope fractionation and plant water use efficiency [A] stable isotopes in ecological research [C]. Springer, Berlin, pp 21–40
Fay MF, Lledó MD, Kornblum MM, Crespo MB (1999) From the waters of Babylon? Populus euphratica in Spain is clonal and probably introduced. Biodivers Conserv 8(6):768–778
Feng Q, Cheng GD (1998) Current situation, problems and rational utilization of water resources in arid northwestern China. J Arid Environ 40:373–382
Foulds W (1993) Nutrient concentration of foliage and soil in south-west Australia. New Phytol 125:529–546
Garten CT, Taylor GE (1992) Foliar δ13C with in a temperate deciduous forest: spatial, temporal, and species source of variation. Oecologia 90:1–7
Gnansiri S, Hirohumi S (1990) Cell membrane stability and leaf water relation as affected by phosphorus nutrition under water stress in maize. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 36(4):661–666
Gu RS, Liu QL, Pei D, Jiang XN (2004) Understanding saline and osmotic tolerance of P. euphratica suspended cells. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 78:261–265
Güsewell S, Koerselman W (2002) Variation in nitrogen and phosphorus concentration of wetland plants. Perspect Plant Ecol 5:37–61
Han WX, Fang JY, Guo DL, Zhang Y (2005) Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol 168:377–385
He ZB, Zhao WZ (2006) Characterizing the spatial structures of riparian plant communities in the lower reaches of the Heihe River in China using geostatistical techniques. Ecol Res 21:551–559
Holtum JAM, Winter K (2005) Carbon isotope composition of canopy leaves in a tropical forest in Panama throughout a seasonal cycle. Trees Struct Funct 19:545–551
Huang JH, Lin GH, Zhao W, Han XG (2005) Application of stable isotope technique in the study of plant water use. Acta Ecol Sin 25(9):2362–2371 (in Chinese)
Iqbal MM, Akhter J, Mohammad W, Shah SM, Nawaz H, Mahmood K (2005) Effect of tillage and fertilizer levels on wheat yield, nitrogen uptake and their correlation with carbon isotope discrimination under rainfed conditions in north-west Pakistan. Soil Tillage Res 80:47–57
Ismail AM, Hall AE, Bray EA (1994) Drought and pot size effects on transpiration efficiency and carbon isotope discrimination of cowpea accessions and hybrids. Aust J Plant Physiol 21:23–35
Kayahare GJ, Carter RE, Klinka K (1995) Site index of western hemlock (Tsuga heterophylla) in relation to soil nutrient and foliar chemical measures. For Ecol Manag 74:161–169
Koerselman W, Meuleman AFM (1996) The vegetation N:P ratio: a new tool to detect the nature of nutrients limitation. J Appl Ecol 33:1441–1450
Körner CH, Farquhar GD, Wong SC (1991) Carbon isotope discrimination by plants follows latitudinal and altitudinal trends. Oecologia 88:30–40
Korol RL, Kirschbaum MUF, Farquhar GD, Jeffreys M (1999) Effects of water status and soil fertility on the C-isotope signature in Pinus radiata. Tree Physiol 19:551–562
Lawlor DW (2002) Carbon and nitrogen assimilation in relation to yield: mechanisms are the key to understanding production systems. J Exp Bot 53:773–787
Li ZJ, Lu CX, Duan HJ (1996) Anatomical studies on the vegetative organs of P. euphratica Oliv. and Populus pruinosa Schrenk. J Talimu Univ Agric Reclam 8(2):21–33 (in Chinese)
Ma HC, Wang SS, Jiang XN (1998) The diurnal pattern of gas exchange in P. euphratica. J Southwest For Coll 18(1):24–32 (in Chinese)
Máguas C, Griffiths H (2003) Applications of stable isotopes in plant ecology. Prog Bot 64:473–505
McKee KL (1993) Soil physicochemical patterns and mangrove species distribution: reciprocal effects. J Ecol 81:477–487
McNulty SG, Swank WT (1995) Wood δ13C as a measure of annual basal area growth and soil water stress in a Pinus strobes forest. Ecology 76:1581–1586
Monneveux P, Reynolds MP, Trethowan R, González-Santoyo H, Peña RJ, Zapata F (2005) Relationship between grain yield and carbon isotope discrimination in bread wheat under four water regimes. Eur J Agron 22:231–242
Parolin P (2001) Morphological and physiological adjustments to waterlogging and drought in seedlings of Amazonian floodplain trees. Oecologia 128:326–335
Qu CM, Han XG, Su B, Huang JH, Jiang GM (2001) The characteristics of foliar δ13C values of plants and plant water use efficiency indicated by δ13C values in two fragmented rainforests in **shuangbanna, Yunnan. Acta Bot Sin 43(2):186–192 (in Chinese)
Raeini-Sarjaz M, Barthakur NN, Arnold NP, Jones PJH (1998) Water stress, water use efficiency, carbon isotope discrimination and leaf gas exchange relationships of the Bush Bean. J Agron Crop Sci 180:173–179
Reich PB, Kloeppel BD, Ellsworth DS, Walters MB (1995) Different photosynthesis–nitrogen relations in deciduous hardwood and evergreen coniferous tree species. Oecologia 104:24–30
Reich PB, Ellsworth DS, Walters MB (1998) Leaf structure (specific leaf area) modulates photosynthesis–nitrogen relations: evidence from within and across species and functional groups. Funct Ecol 12:948–958
Rottenberg A, Nevo E, Zohary D (2000) Genetic variability in sexually dimorphic and monomorphic populations of P. euphratica (Salicaceae). Can J For Res 30(3):482–486
Saito Y, Shiraishi S, Tanimoto T, Yin L, Watanabe S, Ide Y (2002) Genetic diversity of P. euphratica populations in northwestern China determined by RAPD DNA analysis. New For 23:97–103
Sauter JJ, van Cleve B, Apel K (1988) Protein bodies in ray cells of Populus × canadensis Moench ‘Robusta’. Planta 173:31–34
Schwinning S, Ehleringer JR (2001) Water use trade-off and optimal adaptations to pulse-driven arid ecosystems. J Ecol 89:464–480
Shaheen R, Hood-Nowotny RC (2005) Effect of drought and salinity on carbon isotope discrimination in wheat cultivars. Plant Sci 168:901–909
Shangguan ZP, Shao MA, Dyckmans J (2000) Nitrogen nutrition and water stress effects on leaf photosynthetic gas exchange and water use efficiency in winter wheat. Environ Exp Bot 44:141–149
Si JH, Chang ZQ, Su YH, ** HY, Feng Q (2008) Stomatal conductance characteristics of P. euphratica leaves and response to environmental factors in the extreme arid region. Acta Bot Boreal Occident Sin 28(1):125–130 (in Chinese)
Smith SD, Nowak RS (1990) Ecophysiology of plants in the inter-mountain lowlands. In: Osmond CB, Pitelka LF, Hidy GM (eds) Plant biology of the basin and range. Ecological studies, vol 80. Springer, Berlin, pp 179–241
Sparks JP, Ehleringer JR (1997) Leaf carbon isotope discrimination and nitrogen content for riparian trees along elevational transects. Oecologia 109:362–367
Su YH (2007) Study on the soil organic carbon dynamics of typical vegetation communities in E** Banner. PhD, Cold and Arid Region Environmental and Engineering Research Institute, CAS, China (in Chinese)
Su PX, Yan QD, Chen HS (2005) δ13C values and water use efficiency of the leaves and assimilating shoots of desert plants. Acta Bot Boreal Occident Sin 25(4):727–732 (in Chinese)
Tausz M, Trummer W, Wonisch A, Goessler W (2004) A survey of foliar mineral nutrient concentration of Pinus canariensis at field plots in Tenerife. For Ecol Manag 189:49–55
Tessier JT, Raynal DJ (2003) Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation. J Appl Ecol 40:523–534
Thumma BR, Naidu BP, Cameron DF, Bahnisch LM (1998) Transpiration efficiency and its relationship with carbon isotope discrimination under well-watered and water-stressed conditions in Stylosanthes scarab. Aust J Agric Res 49:1039–1045
Tognetti R, Peñuelas J (2003) Nitrogen and carbon concentration, and stable isotope ratios in Mediterranean shrubs growing in the proximity of a CO2 spring. Biol Plant 46(3):411–418
Turner NC (1997) Further progress in crop water relations. Adv Agron 58:293–337
Vitousek PM, Aplet G, Turner D et al (1992) The Mauna Loa environmental matrix: foliar and soil nutrients. Oecologia 89:372–382
Von Fircks Y, Sennerby-Forsse L (1998) Seasonal fluctuations of starch in root and stem tissues of coppiced Salix viminalis plants grown under two nitrogen regimes. Tree Physiol 18:243–249
von Fircksa YH, Tom E, Lisa SF (2001) Seasonal variation of macronutrients in leaves, stems and roots of Salix dasyclados Wimm. grown at two nutrient levels. Biomass Bioenergy 21:321–334
Wang SM, Wan CG, Wang YR et al (2004) The characteristics of Na+, K+ and free proline distribution in several drought-resistant plants of the Alxa Desert, China. J Arid Environ 56:525–539
Wassen MJ, Olde Venterink HGM, de Swart EOAM (1995) Nutrient concentration in mire vegetation as a measure of nutrient limitation in mire ecosystems. J Veg Sci 6:5–16
Watanabe S, Kojima K, Ide YJ, Sasaki S (2000) Effects of osmotic stress on praline and sugar accumulation in Populus euphratlca in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 63:199–206
Xu SJ, An LZ, Feng HY (2002) The seasonal effects of water stress on Ammopiptanthus mongolicus in a desert environment. J Arid Environ 51:437–447
Yan CR, Han XG, Chen LZ et al (1998) Foliar δ13C with in temperate deciduous forest: its spatial change and interspecies variation. Acta Bot Sin 40(9):853–859 (in Chinese)
Yan CR, Han XG, Chen LZ (2001) Water use efficiency of six woody species in relation to micro-environmental factors of different habitats. Acta Ecol Sin 21(11):1952–1956 (in Chinese)
Zhang XY, Gong JD, Zhou MX, Si JH (2003) A study on the stem sap flow of P. euphratica and Tamarix ramosissima by heat pulse technique. J Glaciol Geocryol 25(5):585–590 (in Chinese)
Zhang F, Yang YL, He WL (2004) Effect of salinity on growth and compatible solutes of callus induced from P. euphratica. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 40(5):491–495
Zhao LJ, **ao HL, Liu XH (2006) Variations of foliar carbon isotope discrimination and nutrient concentration in Artemisia ordosica and Caragana korshinskii at the southeastern margin of China’s Tengger Desert. Environ Geol 50:285–294
Zheng SX, Shangguan ZP (2005) Studies on variety in the δ13C value of typical plants in Loess plateau over the last 70 years. Acta Phytoecol Sin 29(2):289–295 (in Chinese)
Zheng SX, Shangguan ZP (2007) Spatial patterns of foliar stable carbon isotope compositions of C3 plant species in the Loess Plateau of China. Ecol Res 22:342–353
Ziegler H (1995) Stable isotopes in plant physiology and ecology. Prog Bot 56:1–2
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (40901048, 40725001, 40671010, and 40701054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, S.K., Feng, Q., Su, Y.H. et al. Research on the water use efficiency and foliar nutrient status of Populus euphratica and Tamarix ramosissima in the extreme arid region of China. Environ Earth Sci 62, 1597–1607 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0643-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0643-y