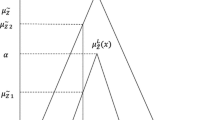
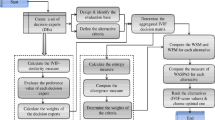
Abstract
Indians regard the River Ganga as religious because it sustains the ecosystem and ecology. Over the past few decades, human activities have caused significant changes in the Ganga river system. Ganga pollution’s leading cause is the need for more management of drainage and industrial design in the metropolitan cities of India. Therefore, in this paper, we have developed a \(\lambda \)-possibility-center based multi-criteria decision-making method under a fuzzy environment. With this decision-making technique, we have found which causes one of three leading causes of Ganga river pollution Disposal of industrial waste into the river, Human sewage and animal waste and Increasing population density. \(\lambda \)-possibility MCDM technique can deal the how to control the Ganga river pollution. Finally, we have Ganga river pollution with \(\lambda \)-possibility MCDM technique under a non-linear pentagonal fuzzy environment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Basu AK (1992) Ecological and Resource Study of the Ganga Delta. Bagchi, Calcutta, pp 25–36
Singh M, Singh AK (2007) Bibliography of environmental studies in natural characteristics and anthropogenic influences on the Ganga River. Environ Monit Assess 129(2007):421–432
Singh V, Ngpoore NK, Chand J, Lehri A (2020) Monitoring and assessment of pollution load in surface water of River Ganga around Kanpur, India: a study for suitability of this water for different uses. Environ Technol Innov 18(2):100676
Rai B (2013) Pollution and conservation of Ganga river in modern India. Int J Sci Res Publ 3(4):1–4
Sharmila S, Arockiarani I (2016) A pollution model of the river Ganges through inter criteria analysis. Int J Oceans Oceanogr 10(2):81–91
Shah ZU, Praveen S (2021) Pesticides pollution and risk assessment of river Ganga: a review. Heliyon 7:e07726
Paul D (2017) Research on heavy metal pollution of river Ganga: a review. Annal Agrar Sci 15(2017):278–286
Dwivedi S, Mishra S, Tripathi RD (2018) Ganga water pollution: a potential health threat to inhabitants of Ganga basin. Environ Int 117(2):327–338
Chaudhary M, Walker TR (2019) River Ganga pollution: causes and failed management plans. Environ Int 126(2019):202–206
Biswas P, Pramanik S, Giri BC (2016) Value and ambiguity index based ranking method of single valued trapezoidal neutrosophic numbers and its application to multi-attribute decision making. Neutrosophic Sets Systems 12(10):127–138
Appadoo SS, Bhatt SK, Bector CR (2008) Application of possibility theory to investment decisions. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 7(1):35–57
Wan SP, Dong JY (2013) Possibility method for triangular intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute group decision making with incomplete weight information. Int J Comput Intell Syst 7(1):65–79
Dutta P (2021) Multi-criteria decision making under uncertainty via the operations of generalized intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Granul Comput 6(1):321–337
Marimuthu D, Mahapatra GS (2020) Multi-criteria decision-making using a complete ranking of generalized trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Soft Comput 25(1):9859–9871
Nguyen NBT, Lin GH, Dang TT (2021) Fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making approach for on-line food delivery (OFD) companies evaluation and selection: a case study in vietnam. Processes 9(1):127
Garai T, Garg H, Roy TK (2020) A ranking method based on possibility mean for multi-attribute decision making with single valued neutrosophic numbers. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 11(1):5245–5258
Garai T, Garg H (2022) Multi-criteria decision making of water resource management problem (in Agriculture field, Purulia district) based on possibility measures under generalized single valued non-linear bipolar neutrosophic environment. Expert Syst Appl 205(1):117715
Mondal SP, Mandal M (2017) Pentagonal fuzzy number, its properties and application in fuzzy equation. Future Comput Inform J 2(1):110–117
Garai T, Garg H (2022) Possibilistic multi-attribute decision making for water resource management problem under single-valued bipolar neutrosophic environment. Int J Intell Syst 37(8):5031–5058
Panda M, Pal M (2016) A study on pentagonal fuzzy number and its corresponding matrices. Pacific Sci Rev B: Humanit Soc Sci 1(1):131–139
Chakraborty A, Mondal SP, Alam S, Ahmadian A, Senu N, De D, Salahshour S (2019) The pentagonal fuzzy number and its different representations, properties, ranking, defuzzification and application in Game problems. Symmetry 11(2):248
Garai T, Biswas G, Santra U (2022) A novel MCDM method based on possibility mean and its application to water resource management problem under bipolar fuzzy environment. Int Conf Intell Fuzzy Syst 1:405–412
Lin M, Huang C, Xu Z (2019) TOPSIS method based on correlation coefficient and entropy measure for linguistic pythagorean fuzzy sets and its application to multiple attribute decision making. Complexity 2019(1):1–16
Lin M, Wei J, Xu Z, Chen R (2018) Multi-attribute group decision-making based on linguistic pythagorean fuzzy interaction partitioned bonferroni mean aggregation operators. Complexity 1:1–24
Garai T (2022) A novel ranking method of the generalized intuitionistic fuzzy numbers based on possibility measures. Intelligent and Fuzzy Techniques for Emerging Conditions and Digital Transformation: Proceedings of the INFUS-2021 Conference 2:20–27
Wan SP, Xu JA (2016) Method for multi-attribute group decision-making with triangular intuitionistic fuzzy numbers application to trustworthy service selection. Sci Iran 24(1):794–807
Qiupeng G, Zuxing X (2017) A new approach for ranking fuzzy numbers based on possibility theory. J Comput Appl Math 309(1):674–682
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There have been no conflicting interests declared by the authors.
Ethical approval
This article doesn’t include animal experiments conducted by all the other authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Garai, T. \(\lambda \)-possibility-center based MCDM technique on the control of Ganga river pollution under non-linear pentagonal fuzzy environment. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 15, 3243–3253 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-024-04817-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-024-04817-8