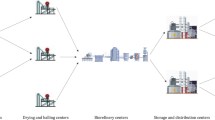
Abstract
As a major agricultural country, China’s straw energy has received extensive attention in the context of green development. However, the uncoordinated supply chain hinders the utilization of straw energy. To improve the current situation caused by insufficient fuel supply of power plants and declining state subsidies. This paper takes the straw direct combustion power generation supply chain as the research object. Considering the economic cost of each stage and the carbon emission reduction in the whole life cycle of straw power generation. A decentralized decision model based on the Stackelberg game and a centralized decision model considering the overall revenue is constructed. By comparing the optimal solution of the model, we found that in the centralized decision model, the amount of straw flowing into the supply chain increased significantly and the total revenue was improved. Then, the revenue-sharing contract is introduced for coordination. The results indicate that the appropriate combination of the straw purchase price and revenue sharing coefficient can Pareto improve the revenue of each participating member, and achieve a win–win situation.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
IEA.: An energy sector roadmap to carbon neutrality in China. IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/an-energy-sector-roadmap-to-carbon-neutrality-in-china. (2021). Accessed 19 September 2022.
**ao, J., Li, G.H., **e, L., Wang, S.Y., Yu, L.A.: Decarbonizing China’s power sector by 2030 with consideration of technological progress and cross-regional power transmission. Energy Policy 150, 112150 (2021)
Huang, M., Zhu, L., Zhang, W.B., Zhu, L.J., Ma, Z.Q., Chen, D.Y.: Insight into the synergistic reaction mechanism of biomass pseudo components and low-density polyethylene for the production of light aromatics through co-catalytic fast pyrolysis over hierarchical HZSM-5. Fuel 324, 124699 (2022)
Lehtveer, M., Fridahl, M.: Managing variable renewables with biomass in the European electricity system: emission targets and investment preferences. Energy 213, 118786 (2020)
Emenike, O., Michailos, S., Finney, K.N., Hughes, K.J., Ingham, D., Pourkashanian, M.: Initial techno-economic screening of BECCS technologies in power generation for a range of biomass feedstock. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 40, 100743 (2020)
Wang, Z.W., Wang, Z.F., Xu, G.Y., Ren, J.Z., Wang, H., Li, J.: Sustainability assessment of straw direct combustion power generation in China: from the environmental and economic perspectives of straw substitute to coal. J. Clean. Prod. 273, 122890 (2020)
Zhao, Z.Y., Yan, H.: Assessment of the biomass power generation industry in China. Renew. Energy 37(1), 53–60 (2012)
Fan, K., Mao, W.J., Qu, H., Li, X.N., Wang, M.: Study on government subsidy in a two-level supply chain of direct-fired biomass power generation based on contract coordination. J. Indus. Manage. Optimiz. (2022). https://doi.org/10.3934/jimo.2022049
Zhang, X.P., Luo, K.Y., Tan, Q.L.: A feedstock supply model integrating the official organization for China’s biomass generation plants. Energy Policy 97, 276–290 (2016)
Le, H.A., Thu, D.H., Khoi, N.Q.: Rice straw-base power generation: a potential and economic cost-benefit analysis for a small power plant (10 MWe) in Vietnam. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manage. 23(6), 2232–2241 (2021)
Logeswaran, J., Shamsuddin, A.H, Silitonga, A.S., Mahlia, T.M.I.: Prospect of using rice straw for power generation: a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27(21), 25956–25969 (2020)
Kashif, M., Awan, M.B., Nawaz, S., Amjad, M., Talib, B., Farooq, M., Nizami, A.S., Rehan, M.: Untapped renewable energy potential of crop residues in Pakistan: challenges and future directions. J. Environ. Manage. 256, 109924 (2020)
Zhang, M.M., Zhou, D.Q., Ding, H., **, J.L.: Biomass power generation investment in China: a real options evaluation. Sustainability 8(6), 563 (2016)
Wang, L.L., Watanabe, T.: A Stackelberg game theoretic analysis of incentive effects under perceived risk for China’s straw-based power plant supply chain. Energies 9(6), 455 (2016)
Wu, J.J., Zhang, J., Yi, W.M., Cai, H.Z., Li, Y., Su, Z.P.: A game-theoretic analysis of incentive effects for agribiomass power generation supply chain in China. Energies 14(3), 546 (2021)
Mou, H.W., Li, H., Zhou, Y.G., Zheng, Y.J., Dong, R.J., Cao, J.X.: Estimating winter wheat straw amount and spatial distribution in Qihe County, China, using GF-1 satellite images. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 13(1), 013102 (2021)
Wu, Y.N., Li, L.W.Y., Xu, R.H., Chen, K.F., Hu, Y., Lin, X.S.: Risk assessment in straw-based power generation public-private partnership projects in China: a fuzzy synthetic evaluation analysis. J. Cleaner Prod. 161, 977–990 (2017)
Nagel, J.: Determination of an economic energy supply structure based on biomass using a mixed-integer linear optimization model. Ecol. Eng. 16(1), 91–102 (2000)
Wen, W.: Game analysis on feedstock supply chain of straw power industry in China. Dissertation, Nan**g University of Aeronautics and Astronautics. (2015). (in Chinese)
Mafakheri, F., Nasiri, F.: Modeling of biomass-to-energy supply chain operations: applications, challenges and research directions. Energy Policy 67, 116–126 (2014)
Tan, Q.L., Wang, T.R., Zhang, Y.M., Miao, X.Y., Zhu, J.: Nonlinear multi-objective optimization model for a biomass direct-fired power generation supply chain using a case study in China. Energy 139, 1066–1079 (2017)
Wu, J.J., Zhang, J., Yi, W.M., Cai, H.Z., Su, Z.P., Li, Y.: Economic analysis of different straw supply modes in China. Energy 237, 121594 (2021)
Xu, X.L., Chen, Y.J.: A comprehensive model to analyze straw recycling logistics costs for sustainable development: evidence from biomass power generation. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 39(4), e13394 (2020)
Cao, J., Pang, B., Mo, X.P., Xu, F.Y.: A new model that using transfer stations for straw collection and transportation in the rural areas of China: a case of **ghai, Tian**. Renew. Energy 99, 911–918 (2016)
Sun, Y.F., Cai, W.C., Chen, B., Guo, X.Y., Hu, J.J., Jiao, Y.Z.: Economic analysis of fuel collection, storage, and transportation in straw power generation in China. Energy 132, 194–203 (2017)
Zhang, Q., Zhou, D.Q., Zhou, P., Ding, H.: Cost analysis of straw-based power generation in Jiangsu Province. China. Appl. Energy. 102, 785–793 (2013)
Wang, Z.W., Wang, Z.F., Tahir, N., Wang, H., Li, J., Xu, G.Y.: Study of synergetic development in straw power supply chain: straw price and government subsidy as incentive. Energy Policy 146, 111788 (2020)
Wen, W., Zhou, P.: Impacts of regional governmental incentives on the straw power industry in China: a game-theoretic analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 203, 1095–1105 (2018)
Iakovou, E., Karagiannidis, A., Vlachos, D., Toka, A., Malamakis, A.: Waste biomass-to-energy supply chain management: a critical synthesis. Waste Manage. 30(10), 1860–1870 (2010)
Wen, W., Zhang, Q.: A design of straw acquisition mode for China’s straw power plant based on supply chain coordination. Renewable Energy 76, 369–374 (2015)
Wang, L.L., Watanabe, T.: Factors affecting farmers’ risk perceptions regarding biomass supply: a case study of the national bioenergy industry in northeast China. J. Clean. Prod. 139, 517–526 (2016)
Lin, B.Q., He, J.X.: Is biomass power a good choice for governments in China? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 73, 1218–1230 (2017)
He, N., Jiang, Z.Z., Huang, S., Li, K.Y.: Evolutionary game analysis for government regulations in a straw-based bioenergy supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2022.2030067
Sun, D.Q., Ge, Y., Zhou, Y.H.: Punishing and rewarding: how do policy measures affect crop straw use by farmers? An empirical analysis of Jiangsu Province of China. Energy Policy 134, 110882 (2019)
Singh, J.: Overview of electric power potential of surplus agricultural biomass from economic, social, environmental and technical perspective—a case study of Punjab. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 42, 286–297 (2015)
Wang, X.W., Cai, Y.P., Dai, C.: Evaluating China’s biomass power production investment based on a policy benefit real options model. Energy 73, 751–761 (2014)
Zhang, C.Y., Ho, S.H., Chen, W.H., **e, Y.P., Liu, Z.Q., Chang, J.S.: Torrefaction performance and energy usage of biomass wastes and their correlations with torrefaction severity index. Appl. Energy 220, 598–604 (2018)
Shafie, S.M., Masjuki, H.H., Mahlia, T.M.I.: Life cycle assessment of rice straw-based power generation in Malaysia. Energy 70, 401–410 (2014)
Suramaythangkoor, T., Gheewala, S.H.: Implementability of rice straw utilization and greenhouse gas emission reductions for heat and power in Thailand. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2(2), 133–147 (2011)
Nasiri, F., Zaccour, G.: An exploratory game-theoretic analysis of biomass electricity generation supply chain. Energy Policy 37(11), 4514–4522 (2009)
Canbulut, G., Kose, E., Arik, O.A.: Handling of revenue sharing contracts within the scope of game theory. Soft. Comput. 25(1), 321–329 (2021)
Bart, N., Chernonog, T., Avinadav, T.: Revenue-sharing contracts in supply chains: a comprehensive literature review. Int. J. Prod. Res. 59(21), 6633–6658 (2020)
Yan, B., Fan, J., Wu, J.W.: Channel choice and coordination of fresh agricultural product supply chain. RAIRO Op. Research. 55(2), 679–699 (2021)
Liu, F., Wang, J.J., Liu, J.G., Kong, Y.D.: Coordination of port service chain with an integrated contract. Soft. Comput. 24(9), 6245–6258 (2020)
Chen, Y.H., Kung, L.C., Yu, J.Y., Tsai, H.J., Wang, Y.J.: Impact of management models on revenue sharing for signaling medical equipment reliability. J. Op. Res. Soc. 73(6), 1379–1392 (2021)
Fan, K., Li, X.N., Wang, L., Wang, M.: Two-stage supply chain contract coordination of solid biomass fuel involving multiple suppliers. Comput. Ind. Eng. 135, 1167–1174 (2019)
Song, H.H., Gao, X.X.: Green supply chain game model and analysis under revenue-sharing contract. J. Clean. Prod. 170, 183–192 (2018)
El Ouardighi, F.: Supply quality management with optimal wholesale price and revenue sharing contracts: a two-stage game approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 156, 260–268 (2014)
Mao, H.Y., Guo, Y.X., Zhang, Y.Y., Zhou, S.L., Liu, C.H.: Low-carbon technology service mode with revenue-sharing contract considering advance funding risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20121-4
Sun, N., Wang, Y.J., Gao, C.Y., Wang, H.Y., Qin, C., Bi, Y.Y.: Cost analysis of straw collection, storage and transportation—a case study of Henan Province. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Regional Plan. 39(05), 91–96+230 (2018). (in Chinese)
Zong, X.Y.: Study on transportation cost model and acquisition path of straw direct combustion power generation. Dissertation, North China Electric Power University. (2017). (in Chinese)
Sun, Y.F., Wang, Y.P., Yang, B., Zheng, Z.P., Wang, C., Chen, B., Li, S.L., Ying, J.L., Liu, X.P., Chen, L., Mu, W.L.: Emergy evaluation of straw collection, transportation and storage system for power generation in China. Energy 231, 120792 (2021)
Chang C.Y.: Research on biomass-fired power generation fuel supply chain inventory system optimization. Dissertation, Nan**g University of Aeronautics and Astronautics. (2014). (in Chinese)
Wei, Y.M., Zhang, X.P., Luo, K.Y., Liu, Y.: External performance of biomass power generation in china based on life cycle analysis. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 10(5), 385–396 (2016)
Wang, P.G.: Emission analysis of air and PM pollution on straw power plant supply chain based on life cycle assessment. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 33(14), 229–237 (2017). (in Chinese)
Chao, R., Guo, J.Q., Feng, X.X., Gu, G.L.: Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of parameters calculated by inference formula method. Pearl River. 36(04), 29–31 (2015). (in Chinese)
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Department of Henan Province (Grant No. 212102110212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZW: Writing—original draft, Investigation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Funding acquisition. TH: Methodology, Investigation, Software, Formal analysis, Writing—review & editing, Visualization. ZW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Data curation, Writing-review &editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Hou, T. & Wang, Z. Revenue Coordination of Straw Power Generation Supply Chain Under Carbon Trading Environment. Waste Biomass Valor 14, 1769–1785 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01960-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01960-1