Abstract
Neurodegenerative diseases such as stroke and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are two inter-related disorders that affect the neurons in the brain and central nervous system. Alzheimer’s is a disease by undefined origin and causes. Stroke and its most common type, ischemic stroke (IS), occurs due to the blockade of cerebral blood vessels. As an important feature, both of disorders are associated with irreversible damages to the brain and nervous system. In this regard, finding common signaling pathways and the same molecular origin between these two diseases may be a promising way for their solution. On the basis of literature appraisal, the most common signaling cascades implicated in the pathogenesis of AD and stroke including notch, autophagy, inflammatory, and insulin signaling pathways were reviewed. Furthermore, current therapeutic strategies including natural and synthetic pharmaceuticals aiming modulation of respective signaling factors were scrutinized to ameliorate neural deficits in AD and stroke. Taken together, digging deeper in the common connections and signal targeting can be greatly helpful in understanding and unified treating of these disorders.
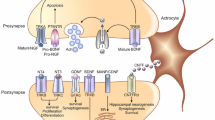
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Data and materials of this article are included within the article and there is no additional file or supporting information file.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- AGEs:
-
Advanced glycosylation end products
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- aPKC:
-
Atypical protein kinase C
- ApoE4:
-
Apolipoprotein E4
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant responsive element
- ASC:
-
Apoptosis associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- ceRNA:
-
Competitive endogenous RNA
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase
- CXCL8:
-
Chemokine (C–X–C motif) ligand 8
- DAMP:
-
DNA-binding/damage-associated molecular pattern
- DSL:
-
Delta/serrate/LAG2
- 4EBP1:
-
4E binding protein 1
- EPO:
-
Erythropoietin
- ERKs:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases
- GAS5:
-
Growth arrest-specific 5
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- FPRL1:
-
Formyl peptide receptor-like 1
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- HLJDD:
-
Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decotion
- HMGB-1:
-
High-mobility group protein 1
- IBA-1:
-
Ionized calcium binding adapter molecule 1
- IGFs:
-
Insulin-like growth factors
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- IS:
-
Ischemic stroke
- IRAKs:
-
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases
- JNKs:
-
C-Jun NH2-terminal kinases
- KKS:
-
Kallikrein-kinin system
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoproteins
- 5-LOX:
-
5-Lipoxygenase
- Lrrfip1:
-
Leucine-rich repeat flightless-1 interaction protein 1
- MAPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- MMP-9:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 9
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- MyD88:
-
Myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88
- NICD:
-
Notch intracellular domain
- NLRP3:
-
NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 protein
- NR4A2:
-
Nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2
- PAEs:
-
Purified anthocyanin extracts
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- p70S6K:
-
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1
- PPAR-α:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SAAT2:
-
Excitatory amino acid transporter subtype 2
- TCA:
-
Trans-cinnamaldehyde
- TK:
-
Tissue kallikrein
- TLRs:
-
Toll-like receptors
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- ULK1:
-
Unc-51-like kinase 1
- XIAP:
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis
References
2018 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures (2018) Alzheimer's & Dementia 14:367–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.001
Abd-Elrahman KS, Hamilton A, Vasefi M, Ferguson SSG (2018) Autophagy is increased following either pharmacological or genetic silencing of mGluR5 disease signaling in Alzheimer's mouse models. Mol Brain 11:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-018-0364-9
Abdul-Rahman O, Sasvari-Szekely M, Ver A, Rosta K, Szasz BK, Kereszturi E, Keszler G (2012) Altered gene expression profiles in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of type 2 diabetic rats. BMC Genomics 13:81–81. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-81
Abe T, Shimamura M, Jackman K, Kurinami H, Anrather J, Zhou P, Iadecola C (2010) Key role of CD36 in toll-like receptor 2 signaling in cerebral ischemia. Stroke 41:898–904. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.572552
Albright CF et al (2013) Pharmacodynamics of selective inhibition of γ-secretase by avagacestat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 344:686–695
Alzheimer’s A (2015) Alzheimer's disease facts and figures, Alzheimer's Dement J Alzheimer's Assoc 11
Andersson ER, Sandberg R, Lendahl U (2011) Notch signaling: simplicity in design, versatility in function. Development 138:3593–3612
Anrather J, Iadecola C (2016) Inflammation and Stroke: an Overview Neurotherapeutics 13:661–670
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ (1999) Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284:770–776
Arumugam TV et al (2006) Gamma secretase–mediated Notch signaling worsens brain damage and functional outcome in ischemic stroke. Nat Med 12:621
Arumugam TV et al (2011) Evidence that γ-secretase-mediated notch signaling induces neuronal cell death via the nuclear factor-κB-Bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell death pathway in ischemic stroke. Mol Pharm 80:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.111.071076
Baba T et al (2009) Electrical stimulation of the cerebral cortex exerts antiapoptotic, angiogenic, and anti-inflammatory effects in ischemic stroke rats through phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Stroke 40:e598–605. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.109.563627
Baek SH et al (2014) Modulation of mitochondrial function and autophagy mediates carnosine neuroprotection against ischemic brain damage. Stroke 45:2438–2443. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.005183
Balaganapathy P, Baik SH, Mallilankaraman K, Sobey CG, Jo DG, Arumugam TV (2018) Interplay between Notch and p53 promotes neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38:1781–1795. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17715956
Bao X et al (2015) Cell adhesion molecule pathway genes are regulated by cis-regulatory SNPs and show significantly altered expression in Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurobiol Aging 36:2904. e2901–2904. e2907
Barakat W, Safwet N, El-Maraghy NN, Zakaria MN (2014) Candesartan and glycyrrhizin ameliorate ischemic brain damage through downregulation of the TLR signaling cascade. Eur J Pharmacol 724:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.12.032
Batista AF et al (2018) The diabetes drug liraglutide reverses cognitive impairment in mice and attenuates insulin receptor and synaptic pathology in a non-human primate model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Pathol 245:85–100. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5056
Baynes JW, Thorpe SR (1999) Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: a new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes 48:1–9
Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P (2002) Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA 287:2570–2581
Benedito R, Roca C, Sörensen I, Adams S, Gossler A, Fruttiger M, Adams RH (2009) The notch ligands Dll4 and Jagged1 have opposing effects on angiogenesis. Cell 137:1124–1135
Benjamin EJ et al (2017) Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 update: a report from the American heart association circulation 135:e146-e603. https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000000485
Boehme AK, Esenwa C, Elkind MS (2017) Stroke risk factors, genetics, and prevention. Circ Res 120:472–495
Bomfim TR et al (2012a) An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer’s disease- associated Aβ oligomers. J Clin Invest 122:1339–1353. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI57256
Bomfim TR et al (2012b) An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer’s disease- associated Abeta oligomers. J Clin Invest 122:1339–1353. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci57256
Bonham LW et al (2018) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 is associated with biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease pathology and shows differential expression in transgenic mice. Front Neurosci 12:476. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00476
Booth R, Kim H (2014) Permeability analysis of neuroactive drugs through a dynamic microfluidic in vitro blood–brain barrier model. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 42:2379–2391
Brod S (2000) Unregulated inflammation shortens human functional longevity. Inflamm Res 49:561–570
Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG (2009) Apoptotic Mechanisms after Cerebral Ischemia Stroke 40:e331–e339
Burguete MC, Torregrosa Pérez-Asensio G, Fernando J, Castelló-Ruiz M, Salom Gil JB, José V, Alborch E (2006) Dietary phytoestrogens improve stroke outcome after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Eur J Neurosci 23:703–710
Caccamo A, Magrì A, Medina DX, Wisely EV, López-Aranda MF, Silva AJ, Oddo S (2013) mTOR regulates tau phosphorylation and degradation: implications for Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies. Aging Cell 12:370–380. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12057
Cameron B, Tse W, Lamb R, Li X, Lamb BT, Landreth GE (2012) Loss of interleukin receptor-associated kinase 4 signaling suppresses amyloid pathology and alters microglial phenotype in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 32:15112–15123. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1729-12.2012
Caso JR, Pradillo JM, Hurtado O, Leza JC, Moro MA, Lizasoain I (2008) Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in subacute stress-induced neuroinflammation and in the worsening of experimental stroke. Stroke 39:1314–1320. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.498212
Chan ES, Shetty MS, Sajikumar S, Chen C, Soong TW, Wong BS (2016) ApoE4 expression accelerates hippocampus-dependent cognitive deficits by enhancing Abeta impairment of insulin signaling in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Sci Rep 6:26119. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26119
Chen F, Zhang L, Wang E, Zhang C, Li X (2018) LncRNA GAS5 regulates ischemic stroke as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-137 to regulate the Notch1 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 496:184–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.022
Chen FZ, Zhao Y, Chen HZ (2019) MicroRNA-98 reduces amyloid β-protein production and improves oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction through the Notch signaling pathway via HEY2 in Alzheimer's disease mice. Int J Mol Med 43:91–102
Chen K et al (2006) Activation of Toll-like receptor 2 on microglia promotes cell uptake of Alzheimer disease-associated amyloid beta peptide. J Biol Chem 281:3651–3659. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M508125200
Chen K, Thomas SR, Keaney JF Jr (2003) Beyond LDL oxidation: ROS in vascular signal transduction. Free Radical Biol Med 35:117–132
Chen YF, Wang YW, Huang WS, Lee MM, Wood WG, Leung YM, Tsai HY (2016) Trans-cinnamaldehyde, an essential oil in cinnamon powder, ameliorates cerebral ischemia-induced brain injury via inhibition of neuroinflammation through attenuation of iNOS, COX-2 expression and NFkappa-B signaling pathway. Neuromolecular Med 18:322–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8395-9
Cheng YL et al (2014) Evidence that collaboration between HIF-1α and Notch-1 promotes neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke. Neurobiol Dis 62:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2013.10.009
Cheung N, Rogers S, Couper DJ, Klein R, Sharrett AR, Wong TY (2007) Is diabetic retinopathy an independent risk factor for ischemic stroke? Stroke 38:398–401
Chi N-F, Chien L-N, Ku H-L, Hu C-J, Chiou H-Y (2013a) Alzheimer disease and risk of stroke: a population-based cohort study. Neurology 80:705–711
Cisternas P, Zolezzi JM, Martinez M, Torres VI, Wong GW, Inestrosa NC (2019) Wnt-induced activation of glucose metabolism mediates the in vivo neuroprotective roles of Wnt signaling in Alzheimer disease. J Neurochem 149:54–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14608
Collino M et al (2006) Oxidative stress and inflammatory response evoked by transient cerebral ischemia/reperfusion: effects of the PPAR-alpha agonist WY14643. Free Radic Biol Med 41:579–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.04.030
Cook M, Baker N, Lanes S, Bullock R, Wentworth C, Arrighi HM (2015) Incidence of stroke and seizure in Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Age Ageing 44:695–699. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afv061
Corn PG (2008) Hypoxic regulation of miR-210: shrinking targets expand HIF-1’s influence. Cancer Biol Ther 7:265–267
Costa LG, Garrick JM, Roquè PJ, Pellacani C (2016) Mechanisms of neuroprotection by quercetin: counteracting oxidative stress and more. Oxid Med Cell Longev
Costa RM, Honjo T, Silva AJ (2003) Learning and memory deficits in Notch mutant mice. Curr Biol 13:1348–1354
Cristofaro B et al (2013) Dll4-Notch signaling determines the formation of native arterial collateral networks and arterial function in mouse ischemia models. Development 140:1720–1729. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.092304
Cui HX, Chen JH, Li JW, Cheng FR, Yuan K (2018) Protection of anthocyanin from Myrica rubra against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via modulation of the TLR4/NF-kappaB and NLRP3 pathways. Molecules 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071788
Cui JG, Li YY, Zhao Y, Bhattacharjee S, Lukiw WJ (2010) Differential regulation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1) and IRAK-2 by microRNA-146a and NF-kappaB in stressed human astroglial cells and in Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 285:38951–38960. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.178848
Cuyvers E, Sleegers K (2016) Genetic variations underlying Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from genome-wide association studies and beyond. The Lancet Neurology 15:857–868
de Bruijn RF, Ikram MA (2014) Cardiovascular risk factors and future risk of Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Med 12:130
de la Monte SM (2009) Insulin Resistance and Alzheimer’s Disease BMB Rep 42:475–481. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2009.42.8.475
de la Monte SM, Wands JR (2004) Alzheimer-associated neuronal thread protein mediated cell death is linked to impaired insulin signaling. J Alzheimers Dis 6:231–242
de Oliveira JS et al (2016) Berberine protects against memory impairment and anxiogenic-like behavior in rats submitted to sporadic Alzheimer's-like dementia: involvement of acetylcholinesterase and cell death. Neurotoxicology 57:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2016.10.008
Deng L, Pan J, Peng Q, Dong Z, Wang Y (2017) Toll-like receptor 3 and interferon β mRNA expressions were increased in peripheral blood of ischemic stroke patients with good outcome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 26:559–566
Dong S, Maniar S, Manole MD, Sun D (2018) Cerebral hypoperfusion and other shared brain pathologies in Ischemic Stroke and Alzheimer’s Disease. Transl Stroke Res 9:238–250
Donkor ES (2018) Stroke in the 21(st) century: a snapshot of the burden, epidemiology, and quality of life. Stroke Res Treat 2018:3238165. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3238165
Donnan GA, Baron J-C, Ma H, Davis SM (2009) Penumbral selection of patients for trials of acute stroke therapy. The Lancet Neurology 8:261–269
Doody RS et al (2013) A phase 3 trial of semagacestat for treatment of Alzheimer's disease New England. J Med 369:341–350
Ethell DW (2010) An amyloid-notch hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscientist 16:614–617
Fann DY et al (2018) Evidence that NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling promotes NLRP inflammasome activation in neurons following ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol 55:1082–1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0394-9
Farkhondeh T, Samarghandian S, Pourbagher-Shahri AM, Sedaghat M (2019) The impact of curcumin and its modified formulations on Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Physiol 234:16953–16965
Fasanaro P et al (2008) MicroRNA-210 modulates endothelial cell response to hypoxia and inhibits the receptor tyrosine kinase ligand Ephrin-A3. J Biol Chem 283:15878–15883
Friedman T (2015) The Effect of Rosmarinic Acid on Immunological and Neurological Systems. Journal of Restorative Medicine 4:50–59
Furlong LI (2013) Human Diseases through the Lens of Network Biology. Trends Genet 29:150–159
Gabbouj S et al (2019) Intranasal insulin activates Akt2 signaling pathway in the hippocampus of wild-type but not in APP/PS1 Alzheimer model mice. Neurobiol Aging 75:98–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.11.008
Gæde P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving H-H, Pedersen O (2008) Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes New England. J Med 358:580–591
Gamaldo A, Moghekar A, Kilada S, Resnick S, Zonderman A, O’brien R (2006) Effect of a clinical stroke on the risk of dementia in a prospective cohort. Neurology 67:1363–1369
Gontier G, George C, Chaker Z, Holzenberger M, Aid S (2015) Blocking IGF signaling in adult neurons alleviates Alzheimer’s disease pathology through amyloid-beta clearance. J Neuro Off J Soc Neurosci 35:11500–11513. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0343-15.2015
Griffin SJ et al (2011) Effect of early intensive multifactorial therapy on 5-year cardiovascular outcomes in individuals with type 2 diabetes detected by screening (ADDITION-Europe): a cluster-randomised trial. The Lancet 378:156–167
Gu J et al (2016) Combination of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Radix Paeoniae ameliorate focal cerebral ischemic in MCAO rats via endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent apoptotic signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 187:313–324
Gu J, Su S, Guo J, Zhu Y, Zhao M, Duan JA (2018) Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of the combination of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Radix Paeoniae against focal cerebral ischaemia via TLR4/MyD88/MAPK/NF-kappaB signalling pathway in MCAO rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 70:268–277. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12841
Guan J, Wei X, Qu S, Lv T, Fu Q, Yuan Y (2017) Osthole prevents cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via the Notch signaling pathway. Biochem Cell Biol 95:459–467. https://doi.org/10.1139/bcb-2016-0233
Guan T, Liu Q, Qian Y, Yang H, Kong J, Kou J, Yu B (2013a) Ruscogenin reduces cerebral ischemic injury via NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory pathway in the mouse model of experimental stroke. Eur J Pharmacol 714:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.07.036
Guan T, Liu Q, Qian Y, Yang H, Kong J, Kou J, Yu B (2013b) Ruscogenin reduces cerebral ischemic injury via NF-κB-mediated inflammatory pathway in the mouse model of experimental stroke. Eur J Pharmacol 714:303–311
Gubern C et al (2014) Characterization of Gcf2/Lrrfip1 in experimental cerebral ischemia and its role as a modulator of Akt, mTOR and beta-catenin signaling pathways. Neurosci 268:48–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.02.051
Guerrero-Romero F, Rodríguez-Morán M (1999) Proteinuria is an independent risk factor for ischemic stroke in non–insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Stroke 30:1787–1791
Guo RB, Wang GF, Zhao AP, Gu J, Sun XL, Hu G (2012) Paeoniflorin protects against ischemia-induced brain damages in rats via inhibiting MAPKs/NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory responses. PLoS One 7:e49701. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049701
Guo T, Zhang D, Zeng Y, Huang TY, Xu H, Zhao Y (2020) Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 15:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-020-00391-7
Hall A et al (2010) Piperidine-Derived γ-Secretase Modulators Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 20:1306–1311
He P, Shen Y (2009) Interruption of beta-catenin signaling reduces neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 29:6545–6557. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0421-09.2009
Hebert LE, Weuve J, Scherr PA, Evans DA (2013) Alzheimer disease in the United States (2010–2050) estimated using the 2010 census. Neurology 80:1778–1783. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31828726f5
Hellström M et al. (2007) Dll4 signalling through Notch1 regulates formation of tip cells during angiogenesis. Nature 445:776–780
Henley DB, May PC, Dean RA, Siemers ER (2009) Development of semagacestat (LY450139), a functional γ-secretase inhibitor, for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother 10:1657–1664
Hennes MM, O’Shaughnessy IM, Kelly TM, LaBelle P, Egan BM, Kissebah AH (1996) Insulin-resistant lipolysis in abdominally obese hypertensive individuals: role of the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension 28:120–126
Hölttä M et al (2016) A Single Dose of the γ-Secretase Inhibitor Semagacestat Alters the Cerebrospinal Fluid Peptidome in Humans. Alzheimer’s Res Ther 8:11
Huang G, Cao X, Zhang X, Chang H, Yang Y, Du W, Wilson JX (2009) Effects of soybean isoflavone on the notch signal pathway of the brain in rats with cerebral ischemia. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 55:326–331. https://doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.55.326
Huang H, Zhong R, **a Z, Song J, Feng L (2014) Neuroprotective effects of rhynchophylline against ischemic brain injury via regulation of the Akt/mTOR and TLRs signaling pathways. Molecules 19:11196–11210. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811196
Hubbs JL et al (2012) Optimization of a natural product-based class of γ-secretase modulators. J Med Chem 55:9270–9282
Idris I, Gray S, Donnelly R (2001) Protein kinase C activation: isozyme-specific effects on metabolism and cardiovascular complications in diabetes. Diabetologia 44:659–673
Ishii H et al (1996) Amelioration of vascular dysfunctions in diabetic rats by an oral PKC β inhibitor. Science 272:728–731
Jiang M et al (2014) Neuroprotective effects of bilobalide on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury are associated with inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediator production and down-regulation of JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation. J Neuroinflammation 11:167. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-014-0167-6
** L et al (2014) Pathway-based analysis tools for complex diseases: a review genomics, proteomics & bioinformatics 12:210–220
Josien H et al (2007) Small Conformationally Restricted Piperidine N-Arylsulfonamides as Orally Active γ-Secretase Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:5330–5335
Kaminari A, Giannakas N, Tzinia A, Tsilibary EC (2017) Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) rescues insulin-mediated impairment in the 5XFAD model of Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep 7:683. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00794-5
Katsel P, Roussos P, Beeri MS, Gama-Sosa MA, Gandy S, Khan S, Haroutunian V (2018) Parahippocampal gyrus expression of endothelial and insulin receptor signaling pathway genes is modulated by Alzheimer’s disease and normalized by treatment with anti-diabetic agents. PLoS One 13:e0206547. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206547
Kitazawa M et al (2011) Blocking IL-1 signaling rescues cognition, attenuates tau pathology, and restores neuronal beta-catenin pathway function in an Alzheimer's disease model. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 187:6539–6549. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1100620
Kumar D, Ganeshpurkar A, Kumar D, Modi G, Gupta SK, Singh SK (2018) Secretase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: long road ahead. Eur J Med Chem 148:436–452
Lesnick TG et al (2007) A genomic pathway approach to a complex disease: axon guidance and Parkinson disease. PLoS Genet 3:e98
Li L, Chen Y, Gibson SB (2013) Starvation-induced autophagy is regulated by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species leading to AMPK activation. Cell Signal 25:50–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.09.020
Li S, Zhang X, Wang Y, Ji H, Du Y, Liu H (2012) DAPT protects brain against cerebral ischemia by down-regulating the expression of Notch 1 and Nuclear factor kappa B in rats. Neurol Sci 33:1257–1264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-0948-6
Li X, Wang MH, Qin C, Fan WH, Tian DS, Liu JL (2017) Fingolimod suppresses neuronal autophagy through the mTOR/p70S6K pathway and alleviates ischemic brain damage in mice. PLoS One 12:e0188748. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188748
Li YH et al (2016) Neuron-derived FGF10 ameliorates cerebral ischemia injury via inhibiting NF-kappaB-dependent neuroinflammation and activating PI3K/Akt survival signaling pathway in mice. Sci Rep 6:19869. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19869
Liang K, Zhu L, Tan J, Shi W, He Q, Yu B (2015) Identification of autophagy signaling network that contributes to stroke in the ischemic rodent brain via gene expression. Neurosci Bull 31:480–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-015-1547-3
Liu G et al (2012) Cell adhesion molecules contribute to Alzheimer’s disease: multiple pathway analyses of two genome-wide association studies. J Neurochem 120:190–198
Liu G et al (2014) Cardiovascular disease contributes to Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from large-scale genome-wide association studies. Neurobiol Aging 35:786–792
Liu S et al (2016a) Curcumin protects against stroke and increases levels of Notch intracellular domain. Neurol Res 38:553–559
Liu W et al (2016b) Electroacupuncture protects against ischemic stroke by reducing autophagosome formation and inhibiting autophagy through the mTORC1-ULK1 complex-Beclin1 pathway. Int J Mol Med 37:309–318
Liu XL, Wang G, Song W, Yang WX, Hua J, Lyu L (2018a) MicroRNA-137 promotes endothelial progenitor cell proliferation and angiogenesis in cerebral ischemic stroke mice by targeting NR4A2 through the Notch pathway. J Cell Physiol 233:5255–5266. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26312
Liu XL, Wang G, Song W, Yang WX, Hua J, Lyu L (2018b) MicroRNA‐137 promotes endothelial progenitor cell proliferation and angiogenesis in cerebral ischemic stroke mice by targeting NR4A2 through the Notch pathway. J Cell Physiol 233:5255–5266
Liu Y-H, Zeng F, Wang Y-R, Zhou H-D, Giunta B, Tan J, Wang Y-J (2013) Immunity and Alzheimer’s disease: immunological perspectives on the development of novel therapies. Drug Discovery Today 18:1212–1220
Lleó A et al (2004) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs lower Aβ 42 and change presenilin 1 conformation. Nat Med 10:1065–1066
Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ (2006) Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet 367:1747–1757. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(06)68770-9
Lou YL et al (2012) MiR-210 activates notch signaling pathway in angiogenesis induced by cerebral ischemia. Mol Cell Biochem 370:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1396-6
Luchsinger JA, Tang M-X, Stern Y, Shea S, Mayeux R (2001) Diabetes mellitus and risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with stroke in a multiethnic cohort. Am J Epidemiol 154:635–641
Luo L, Peng G, Zhu Y, Dong H, Amos CI, **ong M (2010) Genome-wide gene and pathway analysis. Eur J Hum Genet 18:1045
Lv H, Li J, Che YQ (2019) CXCL8 gene silencing promotes neuroglial cells activation while inhibiting neuroinflammation through the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB-signaling pathway in mice with ischemic stroke. J Cell Physiol 234:7341–7355. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27493
Lv H et al (2015) Salvianolic acid B attenuates apoptosis and inflammation via SIRT1 activation in experimental stroke rats. Brain Res Bull 115:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.05.002
Ma T et al (2010) Dysregulation of the mTOR pathway mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One 5. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012845
Mehta M, Adem A, Sabbagh M (2012) New acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease. Int J Alzheimer's Dis
Mesquita RF (2014) Protein kinase Cε-calcineurin cosignaling downstream of toll-like receptor 4 downregulates fibrosis and induces wound healing gene expression in cardiac myofibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 34:574–594
Meyer EP, Ulmann-Schuler A, Staufenbiel M, Krucker T (2008) Altered morphology and 3D architecture of brain vasculature in a mouse model for Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:3587–3592
Nakano-Ito K et al (2014) E2012-induced cataract and its predictive biomarkers. Toxicol Sci 137:249–258
Norrving B, Kissela B (2013) The global burden of stroke and need for a continuum of care. Neurology 80:S5–S12
Panza F et al (2010) γ‐Secretase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: The current state CNS neuroscience & therapeutics 16:272–284
Pendlebury ST, Rothwell PM (2009) Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 8:1006–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(09)70236-4
Pham N, Dhar A, Khalaj S, Desai K, Taghibiglou C (2014) Down regulation of brain cellular prion protein in an animal model of insulin resistance: possible implication in increased prevalence of stroke in pre-diabetics/diabetics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 448:151–156
Phng L-K, Gerhardt H (2009) Angiogenesis: a team effort coordinated by notch. Dev Cell 16:196–208
Pinti M et al (2014) Circulating mitochondrial DNA increases with age and is a familiar trait: Implications for “inflamm‐aging”. Eur J Immunol 44:1552–1562
Pluta R, Bogucka-Kocka A, Ułamek-Kozioł M, Bogucki J, Januszewski S, Kocki J, Czuczwar SJ (2018) Ischemic tau protein gene induction as an additional key factor driving development of Alzheimer’s phenotype changes in CA1 area of hippocampus in an ischemic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Rep 70:881–884
Purkayastha S, Cai D (2013) Neuroinflammatory basis of metabolic syndrome. Mol Metab 2 (4): 356–63. Epub 2013/12/12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2013.09.005
Rahman M et al (2019) Discovering biomarkers and pathways shared by Alzheimer’s disease and ischemic stroke to identify novel therapeutic targets. Medicina 55:191
Ray WJ et al (1999) Evidence for a physical interaction between presenilin and Notch. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:3263–3268
Ren C et al (2018a) Cerebral ischemia induces angiogenesis in the peri-infarct regions via Notch1 signaling activation. Exp Neurol 304:30–40
Ren C et al (2018b) Cerebral ischemia induces angiogenesis in the peri-infarct regions via Notch1 signaling activation. Exp Neurol 304:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.02.013
Roizen M (2009) Association of dietary intake of soy, beans, and isoflavones with risk of cerebral and myocardial infarctions in Japanese populations: the Japan Public Health Center–Based (JPHC) Study Cohort I Kokubo Y, Iso H, Ishihara J, et al (Natl Cardiovascular Ctr, Osaka, Japan; Osaka Univ, Japan; Natl Cancer Ctr, Tokyo, Japan; et al) Circulation 116: 2553–2562, 2007 Year Book of Anesthesiology and Pain Management 2009:166–167
Roncarati R et al (2002) The γ-secretase-generated intracellular domain of β-amyloid precursor protein binds Numb and inhibits Notch signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:7102–7107
Rösen P, Nawroth P, King G, Möller W, Tritschler HJ, Packer L (2001) The role of oxidative stress in the onset and progression of diabetes and its complications: asummary of a Congress Series sponsored byUNESCO‐MCBN, the American Diabetes Association and the German Diabetes Society Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews 17:189–212
Sajan M et al (2016) Brain insulin signaling is increased in insulin-resistant states and decreases in FOXOs and PGC-1alpha and increases in Abeta1–40/42 and Phospho-Tau may abet Alzheimer development. Diabetes 65:1892–1903. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-1428
Salminen A, Kauppinen A, Kaarniranta K (2017) Hypoxia/ischemia activate processing of amyloid precursor protein: impact of vascular dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 140:536–549
Sarwar N, Gao P, Seshasai S (2010) Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease [published correction appears in Lancet. 2010; 376 (9745): 958] Lancet 375:2215–2222
Saura CA et al (2004) Loss of presenilin function causes impairments of memory and synaptic plasticity followed by age-dependent neurodegeneration. Neuron 42:23–36
Saxena A et al (2016) Prognostic significance of hyperglycemia in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: the INTERACT2 study. Stroke 47:682–688
Schmidt AM, Yan SD, Wautier J-L, Stern D (1999) Activation of receptor for advanced glycation end products: a mechanism for chronic vascular dysfunction in diabetic vasculopathy and atherosclerosis. Circ Res 84:489–497
Schneider A et al (2014) Forced arm use is superior to voluntary training for motor recovery and brain plasticity after cortical ischemia in rats. Exp Transl Stroke Med 6:3
Schreihofer DA, Do KD, Schreihofer AM (2005) High-soy diet decreases infarct size after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in female rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 289:R103–R108
Shi F, Dong Z, Li H, Liu X, Liu H, Dong R (2017) MicroRNA-137 protects neurons against ischemia/reperfusion injury through regulation of the Notch signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 352:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.01.015
Shi R, Weng J, Zhao L, Li XM, Gao TM, Kong J (2012) Excessive Autophagy Contributes to Neuron Death in Cerebral Ischemia. CNS Neurosci Ther 18:250–260. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00295.x
Shi S et al (2016) Gx-50 reduces beta-amyloid-induced TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, NO, and PGE2 expression and inhibits NF-kappaB signaling in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Immunol 46:665–676. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201545855
Shimamura M et al (2014) OPG/RANKL/RANK axis is a critical inflammatory signaling system in ischemic brain in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:8191–8196. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1400544111
Shutter JR et al (2000) Dll4, a novel Notch ligand expressed in arterial endothelium. Genes Dev 14:1313–1318
Sims NR, Muyderman H (2010) Mitochondria, oxidative metabolism and cell death in stroke. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis 1802:80–91
Stead LG et al (2009) Hyperglycemia as an independent predictor of worse outcome in non-diabetic patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke. Neurocrit Care 10:181–186
Suchting S, Freitas C, le Noble F, Benedito R, Bréant C, Duarte A, Eichmann A (2007) The Notch ligand Delta-like 4 negatively regulates endothelial tip cell formation and vessel branching. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:3225–3230
Tagami S et al (2017) Semagacestat is a Pseudo-Inhibitor of γ-Secretase. Cell Rep 21:259–273
Takeo K et al (2014) Allosteric regulation of γ-secretase activity by a phenylimidazole-type γ-secretase modulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:10544–10549
Tao X et al (2015) Dioscin ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through the downregulation of TLR4 signaling via HMGB-1 inhibition. Free Radic Biol Med 84:103–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.03.003
Tolppanen A-M, Lavikainen P, Solomon A, Kivipelto M, Soininen H, Hartikainen S (2013a) Incidence of stroke in people with Alzheimer disease: a national register–based approach. Neurology 80:353–358
Tolppanen AM, Lavikainen P, Solomon A, Kivipelto M, Soininen H, Hartikainen S (2013b) Incidence of stroke in people with Alzheimer disease: a national register-based approach. Neurology 80:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31827f08c5
Töyry JP, Niskanen LK, Länsimies EA, Partanen KP, Uusitupa MI (1996) Autonomic neuropathy predicts the development of stroke in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Stroke 27:1316–1318
Tu XK, Zhang HB, Shi SS, Liang RS, Wang CH, Chen CM, Yang WZ (2016) 5-LOX inhibitor zileuton reduces inflammatory reaction and ischemic brain damage through the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 41:2779–2787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1994-x
Tuo Q et al (2017) Tau-mediated iron export prevents ferroptotic damage after ischemic stroke. Mol Psychiatry 22:1520
Vemuri P et al (2017) Age, vascular health, and Alzheimer disease biomarkers in an elderly sample. Annals of Neurology 82:706–718
Vijayan M, Reddy PH (2016) Stroke, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer's disease: molecular links. J Alzheimers Dis : JAD 54:427–443. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-160527
Walker KA et al (2021) Neuronal insulin signaling and brain structure in nondemented older adults: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Neurobiol Aging 97:65–72
Wang PR, Wang JS, Zhang C, Song XF, Tian N, Kong LY (2013) Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-decotion induced protective autophagy against the injury of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via MAPK-mTOR signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 149:270–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.035
Wang R, Tang XC (2005) Neuroprotective Effects of Huperzine A Neuro-Signals 14:71–82
Wei H et al (2016) cPKCgamma-modulated autophagy in neurons alleviates ischemic injury in brain of mice with ischemic stroke through Akt-mTOR pathway. Transl Stroke Res 7:497–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-016-0484-4
Wei Y et al (2017) Salidroside inhibits inflammation through PI3K/Akt/HIF signaling after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Inflammation 40:1297–1309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0573-x
Wei Z, Chigurupati S, Arumugam TV, Jo DG, Li H, Chan SL (2011) Notch activation enhances the microglia-mediated inflammatory response associated with focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 42:2589–2594. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.614834
Willis CL, Meske DS, Davis TP (2010) Protein kinase C activation modulates reversible increase in cortical blood–brain barrier permeability and tight junction protein expression during hypoxia and posthypoxic reoxygenation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1847–1859
Wolfe MS et al (1999) Peptidomimetic probes and molecular modeling suggest that Alzheimer’s γ-secretase is an intramembrane-cleaving aspartyl protease. Biochemistry 38:4720–4727
Woodling NS et al (2014) Suppression of Alzheimer-associated inflammation by microglial prostaglandin-E2 EP4 receptor signaling. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 34:5882–5894. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0410-14.2014
Wu L-R et al (2017) Vinpocetine alleviate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by down-regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling. Oncotarget 8:80315–80324. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20699
**ang Z et al (2015) Integrating genome-wide association study and brain expression data highlights cell adhesion molecules and purine metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 52:514–521
Xu Y, Gao L, Shi L, Li J, Liu W, Du Y (2012) Effect of electroacupuncture intervention on expression of vascular PKC in the ischemic cerebral tissue in rats with cerebral infarction Zhen ci yan jiu=. Acupuncture Research 37:218–223
Yang J et al (2017) Tissue kallikrein protects against ischemic stroke by suppressing TLR4/NF-κB and activating Nrf2 signaling pathway in rats. Exp Ther Med 14:1163–1170
Yang L, Shah K, Wang H, Karamyan VT, Abbruscato TJ (2011) Characterization of neuroprotective effects of biphalin, an opioid receptor agonist, in a model of focal brain ischemia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 339:499–508
Yang X-s, Liu M-y, Zhang H-m, Xue B-z, Shi H, Liu D-x (2014) Protein kinase C-δ mediates sepsis-induced activation of complement 5a and urokinase-type plasminogen activator signaling in macrophages. Inflamm Res 63:581–589
Yang X et al (2019) The diabetes drug semaglutide reduces infarct size, inflammation, and apoptosis, and normalizes neurogenesis in a rat model of stroke. Neuropharmacology 158:107748
Yang Y et al (2013) Primary prevention of macroangiopathy in patients with short-duration type 2 diabetes by intensified multifactorial intervention: seven-year follow-up of diabetes complications in Chinese. Diabetes Care 36:978–984
Yates SC et al (2013) Dysfunction of the mTOR pathway is a risk factor for Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun 1:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/2051-5960-1-3
Zhang D, Han S, Wang S, Luo Y, Zhao L, Li J (2017) cPKC γ‐mediated down‐regulation of UCHL 1 alleviates ischaemic neuronal injuries by decreasing autophagy via ERK‐mTOR pathway. J Cell Mol Med 21:3641–3657
Zhang H-y (2012) New insights into huperzine A for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33:1170–1175
Zhang Y, Miao JM (2018) Ginkgolide K promotes astrocyte proliferation and migration after oxygen-glucose deprivation via inducing protective autophagy through the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 832:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.05.029
Zhu L, Ye T, Tang Q, Wang Y, Wu X, Li H, Jiang Y (2016) Exercise preconditioning regulates the toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappab signaling pathway and reduces cerebral ischemia/reperfusion Inflammatory injury: a study in rats. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 25:2770–2779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.07.033
Funding
This study was funded by Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Kermanshah, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eskandari, S., Sajadimajd, S., Alaei, L. et al. Targeting Common Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Stroke and Alzheimer’s: a Comprehensive Review. Neurotox Res 39, 1589–1612 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00381-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00381-7