Abstract
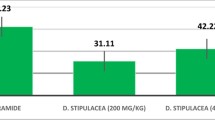
The aim of this study was to investigate the in vitro and in vivo anticestodal effects of methanol extract of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L. (Malvaceae) leaf against Hymenolepis diminuta (Rudolphi, 1819), a zoonotic tapeworm. Under the in vitro study, H. diminuta worms were exposed to 10, 20 and 40 mg/ml concentrations of methanol leaf extract and the effects were judged on the basis of physical motility/mortality of worms. On the other hand, in the case of in vivo study, H. diminuta infected rats were treated individually with 200, 400 and 800 mg/kg doses of leaf extract for 5 days. The effects were judged on the basis of reduction in eggs per gram (EPG) of faeces and worm counts. In case of in vitro test, the treatment with 40 mg/ml concentration of extract revealed prominent anticestodal effect and caused paralysis of worms in 3.00 ± 0.53 h and mortality in 4.08 ± 0.21 h. However, under in vivo study, the 800 mg/kg dose of extract revealed the highest anticestodal effect and caused 66.55 % reduction in EPG count and 75.00 % reduction in worm count in the treated animals. The results of this study indicated that H. rosa-sinesis leaf extract possesses concentration-dependent anticestodal effect against H. diminuta, indicating that the plant possesses promising active principle for the control of intestinal helminthic infections.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akendengué B (1992) Medicinal plants used by the Fang traditional healers in Equatorial Guinea. J Ethnopharmacol 37:165–173
Akhtar MS, Ahmad I (1992) Comparative efficacy of Mallotus philippinensis fruit (Kamala) or Nilzan® drug against gastrointestinal cestodes in Beetal goats. Small Rumin Res 8:121–128
Anonymous (1977) Manual of veterinary parasitological techniques. Technical Bulletin No. 18. Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, her Majesty’s Stationery Office, London, pp 1–57
Anonymous (2004) Thinking beyond deworming. Lancet 364:1993–1994
Cos P, Vlietinck AJ, Berghe DV, Maes L (2006) Anti-infective potential of natural products: how to develop a stronger in vitro ‘proof-of-concept’. J Ethnopharmacol 106:290–302
de Silva NR, Brooker S, Hotez PJ, Montresor A, Engels D, Savioli L (2003) Soil-transmitted helminth infections: updating the global picture. Trends Parasitol 12:547–551
Gauthaman KK, Saleem MT, Thanislas PT, Prabhu VV, Krishnamoorthy KK, Devaraj NS, Somasundaram JS (2006) Cardioprotective effect of the Hibiscus rosa sinensis flowers in an oxidative stress model of myocardial ischemic reperfusion injury in rat. BMC Complement Altern Med 20:32
Jadhav VM, Thorat RM, Kadam VJ, Sathe NS (2009) Traditional medicinal uses of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis. J Pharm Res 2:1220–1222
Kurup PNV, Ramdas VNK, Joshi P (1979) Handbook of medicinal plants. Central Council of Research in Ayurveda and Siddha, New Delhi, p 86
Lahlou M (2002) Potential of Origanum compactum as a cercaricide in Morocco. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 96:587–593
Nath P (2014) Evaluation of anthelmintic activity of some medicinal plants used in the folk-lore medicine system of Riang tribe in Tripura. Ph.D. thesis, North Eastern Hill University, Shillong
Qadri SM (2008) Soil transmitted helminthic infections (STH) in children and its impact on their health in India. Master of Public Health Dissertation, KIT (Royal Tropical Institute), Amsterdam
Ruban P, Gajalakshmi K (2012) In vitro antibacterial activity of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis flower extract against human pathogens. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2:399–403
Sarkar B, Kumar D, Sasmal D, Mukhopadhyay K (2014) Antioxidant and DNA damage protective properties of anthocyanin-rich extracts from Hibiscus and Ocimum: a comparative study. Nat Prod Res 28:1393–1398
Satou T, Koga M, Matsuhashi R, Koike K, Tada I, Nikaido T (2002) Assay of nematocidal activity of isoquinoline alkaloids using third-stage larvae of Strongyloides ratti and S. venezuelensis. Vet Parasitol 104:131–138
Tandon V, Yadav AK, Roy B, Das B (2011) Phytochemicals as cure of worm infections in traditional medicine systems. In: Srivastava UC, Kumar S (eds) Emerging trends in zoology. Narendra Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 351–378
Vijaya, Yadav AK (2014) In vitro anthelmintic assessment of selected phytochemicals against Hymenolepis diminuta, a zoonotic tapeworm. J Parasit Dis. doi:10.1007/s12639-014-0560-1
WHO (2002) WHO Country cooperation strategy 2006–2011, Supplement on Traditional Medicine. World Health Organization, Country Office for India, New Delhi
WHO (2006) Preventive chemotherapy in human helminthiasis. Coordinated use of anthelminthic drugs in control interventions: a manual for health professionals and programme managers. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241547103_eng.pdf. Accessed on 20 Oct 2014
Yadav AK, Tangpu V (2008) Anticestodal activity of Adhatoda vasica extract against Hymenolepis diminuta infections in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 119:322–324
Yadav AK, Temjenmongla (2011) Anticestodal activity of Houttuynia cordata leaf extract against Hymenolepis diminuta in experimentally infected rats. J Parasit Dis 35:190–194
Yadav AK, Tangpu V (2012) Anthelmintic activity of ripe fruit extract of Solanum myriacanthum Dunal (Solanaceae) against experimentally induced Hymenolepis diminuta (Cestoda) infections in rats. Parasitol Res 110:1047–1053
Acknowledgments
PN was recipient of a Research Fellowship in Science for Meritorious Students by the UGC, New Delhi. The study was also supported, in part, by a Grant under the DSA Programme of the UGC, New Delhi in the Department of Zoology, NEHU, Shillong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nath, P., Yadav, A.K. Anticestodal properties of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L. (Malvaceae): an in vitro and in vivo study against Hymenolepis diminuta (Rudolphi, 1819), a zoonotic tapeworm. J Parasit Dis 40, 1261–1265 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-015-0664-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-015-0664-2