Abstract
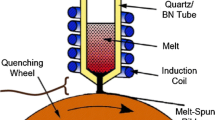
The numerical simulation model of single roller melt spinning for rapid quenching process of NdFeB alloy was built, and the vacuum chamber, cooling roller and sample were taken into account as a system. The existing mature technology was in order to verify the correctness of simulation. The rapid quenching ribbons with different roll speeds were used as the simulation objects. The results of the numerical simulation and experiments show that the validity of the model has been testified and the reasons of the formation of complete quenching ribbons and by-product have been explained. The experimental thickness of the ribbons is proportional to the theoretical thickness. In the same spray condition, with the roll speed increasing, the thickness decreases linearly. At the speed range of 25–30 m·s−1, the simulated calculation date is close to the experimental date, which can be considered as an ideal technological parameter.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu WQ, Chang C, Yue M, Yang JS, Zhang DT, Zhang JX, Liu YQ. Coercivity, microstructure, and thermal stability of sintered Nd–Fe–B magnets by grain boundary diffusion with TbH3 nanoparticles. Rare Met. 2017;36(9):718.
Zheng ZG, Zhong XC, Su KP, Yu HY, Liu ZW, Zeng DC. Magnetic properties and large magnetocaloric effects in amorphous Gd–Al–Fe alloys for magnetic refrigeration. Sci China Phys Mech Astron. 2011;54(7):1267.
Zhao W, Liu Y, Li J, Wang RQ, Qiu YC. Microstructure and magnetic properties of hot-deformed anisotropic NdFeB magnets prepared from amorphous precursors with different crystallization proportions. Rare Met. 2017;36(4):268.
Liu WQ, Chang C, Yue M, Yang JS, Zhang DT, Zhang JX, Liu YQ. Coercivity, microstructure, and thermal stability of sintered Nd–Fe–B magnets by grain boundary diffusion with TbH3 nanoparticles. Rare Met. 2017;36(9):718.
Li JJ, Li AH, Zhu MG, Pan W, Li W. Study on corrosion behaviors of sintered Nd–Fe–B magnets in different environ mental conditions. J Appl Phys. 2011;109(7):07A744.
Zhang X, Ma YT, Zhang B, Li Y, Lei MK, Wang FH, Zhu MG, Wang XC. Corrosion behavior of hot-pressed nanocrystalline NdFeB magnet in a simulated marine atmosphere. Corros Sci. 2014;87:156.
Betancourt I, Davies HA. Exchange coupled nanocomposite hard magnetic alloys. Mater Sci Technol. 2010;26:5.
El-Moneim AA, Gutfleisch O, Plotnikov A, Gebert A. Corrosion behaviour of hot-pressed and die-upset nanocrystalline NdFeB-based magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 2002;248(1):121.
Lee RW, Brewer EG, Schaffel NA. Processing of Neodymium–iron–boron melt-spun ribbons to fully dense magnets. IEEE Trans Magn. 1985;21(5):1958.
Yi PP, Lin M, Chen RJ, Lee D, Yan AR. Enhanced magnetic properties and bending strength of hot deformed Nd–Fe–B magnets with Cu additions. J Alloys Compd. 2010;491(1–2):605.
Chen WH, Li W, Li CJ. The role of Nb addition in Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets with high performance. J Alloys Compd. 2001;319(1–2):280.
Dou YW. Progress of magnetic materials. J Funct Mater. 2014;45(10):10001.
Chang WC, Wu SH, Ma BM, Bounds CO. The effects of La-substitution on the microstructure and magnetic properties of nanocomposite NdFeB melt spun ribbons. J Magn Magn Mater. 1997;167(1–2):65.
Yoshida Y, Kasai Y, Watanabe T. Hot workability of melt-spun NdFe–Co–B magnets. J Appl Phys. 1991;69(8):5841.
Liu Y, Tu MS, Mao XZ. Effect of plastic on the properties of bonded NdFeB permanent magnet. J Funct Mater. 1995;26(2):170.
Brown DN, Chen Z, Guschl P, Campbell P. Developments with melt spun RE–Fe–B powder for bonded magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 2006;303:e371.
Li W, Zhu MG. Research progress of high performance metallic permanent magnetic materials. Mater China. 2009;28(9–10):62.
Hu ZH, Qu HJ, Zhao JQ, Luo C, Li J, Liu Y. Enhanced mechanical properties in die-upset Nd-Fe-B magnets via die-upsetting process. J Rare Earths. 2012;30(11):1112.
Li AH, Li W, Lai B, Wang HJ, Zhu MG. Investigation on microstructure, texture, and magnetic properties of hot deformed Nd-Fe-B ring magnets. Journal of Applied Physics. 2010; 107 (9): 09A7251.
Lai B, Li YF, Wang HJ, Li AH, Zhu MG, Li W. Quasiperiodic layer structure of die-upset NdFeB magnets. J Rare Earths. 2013;31(7):679.
Saito T, Fujita M, Kuji T, Fukuoka K, Syono Y. The development of high performance Nd–Fe–Co–Ga–B die upset magnets. J Appl Phys. 1998;83(11):6390.
Li W, Zhu MG. High property rare-earth permanent magnetic materials and its pivotal preparation technique. Chin J Nonferrous Met. 2004;14(Z1):332.
Zhu MG, Li W, Li XM. Exchange coupling and coercivity of nanocrystalline Nd4.5(Fe, Ga, Co)77.5B18 bonded magnets. Acta Metall Sin. 2003;39(2):217.
Yue M, Tian M, Zhang JX, Zhang DT, Niu PL, Yang F. Microstructure and magnetic properties of anisotropic Nd–Fe–B magnets produced by spark plasma sintering technique. Mater Sci Eng B. 2006;131(1–3):18.
Song J, Yue M, Zuo JH, Zhang ZR, Liu WQ, Zhang DT, Zhang JX, Guo ZH, Li W. Structure and magnetic properties of bulk nanocrystalline Nd–Fe–B permanent magnets prepared by hot pressing and hot deformation. J Rare Earths. 2013;31(7):674.
Yue M, Niu PL, Li YL, Zhang DT, Liu WQ, Zhang JX, Chen CH, Liu S, Lee D, Higgins A. Structure and magnetic properties of bulk isotropic and anisotropic Nd2Fe14B/α-Fe nanocomposite permanent magnets with different α-Fe contents. J Appl Phys. 2008;103(7):07E1011.
Lai B, Li YF, Wang HJ, Wang XC, Li AH, Zhu MG, Li W, Zhang Y. Effect of wheel speed and pressure difference on melt-spun NdFeB powders and die-upset magnets. J Funct Mater. 2014;45(3):03083.
Yoshida Y, Kasai Y, Watanabe T, Shibata S, Panchanathan V, Croat JJ. Hot workability of melt-spun NdFe–Co–B magnets. J Appl Phys. 1991;69(8):5841.
Brown DN, Smith B, Ma BM, Campbell P. The dependence of magnetic properties and hot workability of rare earth-ironboride magnets upon composition. IEEE Trans Magn. 2004;40(4):2895.
Lai B, Li YF, Wang HJ, Li AH, Zhu MG, Wei L, Zhang Y. Model of temperature field for the preparation process of melt-spun NdFeB powders. J Rare Earths. 2014;32(6):514.
Yang YS, Dong WH, Chen XM. Transient heat transfer model for rapid solidification of metals. Acta Metall Sin. 2003;39(3):249.
Andreev SV, Bartashevich MI, Pushkarsky VI, Maltsev VN, Pamyatnykh LA, Tarasov EN, Kudrevatykh NV, Goto T. Law of approach to saturation in highly anisotropic ferromagnets Application to NdFeB melt-spun ribbons. J Alloys Compd. 1997;260(1–2):196.
Pollard RJ, Parker SFH, Grundy PJ. The effect of quench rate on the microstructure and coercivity of some Nd–Fe–B ribbons. J Magn Magn Mater. 1988;75(3):239.
Wang XC, Zhu MG, Li W, Zheng LY, Zhao DL, Du X, Du A. The microstructure and magnetic properties of melt-spun CeFeB ribbons with varying Ce content. Electron Mater Lett. 2015;11(1):109.
Gu M, Li L, Sun H, Dong PY. Electric processing research on temperature field and thermal stress of NdFeB material. Mach Des Manuf. 2014;02:106.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51571064) and the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2014CB643701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XC., Yue, M., Zhang, DT. et al. Numerical simulation of single roller melt spinning for NdFeB alloy based on finite element method. Rare Met. 39, 1145–1150 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01229-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01229-y