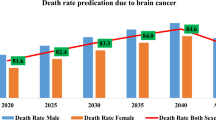
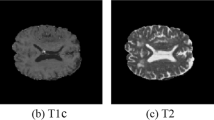
Abstract
Predictive models in radiology can now be constructed with remarkable accuracy using an amalgamation of radiomics and artificial intelligence. To effectively prepare for surgical procedures and assess the progression of the tumor, accurate segmentation of gliomas is essential. The current study aims to address a segmentation of the whole tumor (WT), tumor core (TC), and enhancing tumor (ET), three partially overlap** regions of interest within the glioma with two variants, high-graded glioma (HGG) and low-graded glioma (LGG), made available through the BraTS 2019, 2020, and 2021 challenges. The traditional approach has been bypassed by focusing only on the network architecture, but rather the proposed research work is also concentrating on data pre-processing, augmentation, training, and testing strategies to improve the performance of the automatic brain tumor segmentation. UNet and its variants have recently been shown to be effective in automatically segmenting brain tumors from volumetric multi-modal magnetic resonance (MR) images. Motivated from the literature, an improved UNet + + framework (ResUNet + +) is proposed to segment multi-modal volumetric MR images of brain tumor. The ResUNet + + is a 3D (three-dimensional) encoder-decoder model where the encoder path is replaced with the pre-trained backbone of the ResNet50 model. Moreover, the standard convolutional blocks of the traditional UNet architecture are substituted with the 3D dense convolutional blocks, and in the decoder phase, convolutional layers are replaced by the convolutional transpose layers (ConvTranspose), outperforming the existing models in terms of segmenting the WT, TC, and ET in both HGG and LGG. The performance of the ResUNet + + framework is evaluated using five different performance parameters, and when compared with the state-of-the-art models, the results demonstrate the effectiveness of the framework.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Brain Tumor Datasets are publicly available. BraTS 2019, BraTS 2020: https://www.med.upenn.edu/cbica/BraTS2019/data.html. BraTS 2021: http://braintumorsegmentation.org/.
References
Abualigah LM, Ekinci S, Izci D, Zitar RA (2023) Modified elite opposition-based artificial hummingbird algorithm for designing FOPID controlled cruise control system. Intell Autom Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2023.040291
Adaloglou N (2021) An overview of unet architectures for semantic segmentation and biomedical image segmentation. AI Summer. https://theaisummer.com/unet-architectures/. Accessed 15 Apr 2021
Agushaka JO, Ezugwu AE, Abualigah LM (2022) Gazelle optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired metaheuristic optimizer. Neural Comput Appl 35:4099–4131
Alali AZ, Hussein Ali K (2022) Segmentation of human brain gliomas tumour images using U-Net architecture with transfer learning. Diyala J Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.24237/djes.2022.15102
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R (2015) SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39:2481–2495
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby JS, Freymann JB, Farahani K, Davatzikos C (2017) Advancing the cancer genome atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci Data. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2017.117
Bakas S, Reyes M, Jakab A, Bauer S, Rempfler M, Crimi A, Shinohara RT, Berger C, Ha SM, Rozycki M, Prastawa M, Alberts E, Lipková J, Freymann JB, Kirby JS, Bilello M, Fathallah-Shaykh HM, Wiest R, Kirschke JS, Wiestler B, Colen RR, Kotrotsou A, LaMontagne PJ, Marcus DS, Milchenko M, Nazeri A, Weber M, Mahajan A, Baid U, Kwon D, Agarwal M, Alam M, Albiol A, Albiol A, Varghese A, Tuan TA, Arbel T, Avery A, Pranjal B, Banerjee S, Batchelder T, Batmanghelich NK, Battistella E, Bendszus M, Benson E, Bernal J, Biros G, Cabezas M, Chandra S, Chang Y, Al E (2018) Identifying the best machine learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation, progression assessment, and overall survival prediction in the BRATS challenge. Ar**v, abs/1811.02629
Bhalerao MM, Thakur SP (2019) Brain tumor segmentation based on 3D residual U-Net. BrainLes@MICCAI
Cai C, Gou B, Khishe M, Mohammadi M, Rashidi S, Moradpour R, Mirjalili SM (2022) Improved deep convolutional neural networks using chimp optimization algorithm for Covid-19 diagnosis from the X-ray images. Expert Syst Appl 213:119206–119206
Cao T, Wang G, Ren L, Li Y, Wang H (2022) Brain tumor magnetic resonance image segmentation by a multiscale contextual attention module combined with a deep residual UNet (MCA-ResUNet). Phys Med Biol 67(9):095007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/ac5e5c
Chen L, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H (2017) Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. Ar**v, abs/1706.05587
Chen F, Yang CL, Khishe M (2022) Diagnose Parkinson’s disease and cleft lip and palate using deep convolutional neural networks evolved by IP-based chimp optimization algorithm. Biomed Signal Process Control 77:103688
Çiçek Ö, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O (2016) 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention
Gu Z, Cheng J, Fu H, Zhou K, Hao H, Zhao Y, Zhang T, Gao S, Liu J (2019) CE-Net: context encoder network for 2D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38:2281–2292
Hatamizadeh A, Yang D, Roth HR, Xu D (2021) UNETR: transformers for 3D medical image segmentation. IEEE/CVF Winter Conf Appl Comput vis (WACV) 2022:1748–1758
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Deep residual learning for image recognition. IEEE Conf Comput vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR) 2016:770–778
Honari S, Yosinski J, Vincent P, Pal CJ (2015) Recombinator networks: learning coarse-to-fine feature aggregation. IEEE Conf Comput vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR) 2016:5743–5752
Hu G, Zheng Y, Abualigah LM, Hussien AG (2023) DETDO: an adaptive hybrid dandelion optimizer for engineering optimization. Adv Eng Inf 57:102004
Huang H, Lin L, Tong R, Hu H, Zhang Q, Iwamoto Y, Han X, Chen Y, Wu J (2020) UNet 3+: a full-scale connected UNet for medical image segmentation. ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 1055–1059
Isensee F, Jaeger PF, Full PM, Vollmuth P, Maier-Hein, K (2020) nnU-Net for brain tumor segmentation. Ar**v, abs/2011.00848
Jiang Z, Ding C, Liu M, Tao D (2019) Two-stage cascaded U-Net: 1st place solution to BraTS challenge 2019 segmentation Task. BrainLes@MICCAI
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Lin X, Dong J, Cheng T, Liang J (2022) SwinBTS: a method for 3D multimodal brain tumor segmentation using swin transformer. Brain Sci 12(6):797. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060797
Kaushik A (2020) Understanding Resnet50 architecture. OpenGenus IQ: computing expertise & legacy. https://iq.opengenus.org/resnet50-architecture/
Khasawneh N, Fraiwan M, Fraiwan L, Khassawneh B, Ibnian A (2021) Detection of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images using deep convolutional neural networks. Sensors (basel) 21(17):5940. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21175940.PMID:34502829;PMCID:PMC8434649
Khishe M, Caraffini F, Kuhn S (2021) Evolving deep learning convolutional neural networks for early COVID-19 detection in chest X-ray images. Mathematics 9:1002
Lee J, Shin D, Oh SH, Kim H (2022) Method to minimize the errors of AI: quantifying and exploiting uncertainty of deep learning in brain tumor segmentation. Sensors (Basel) 22(6):2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22062406
Lin G, Milan A, Shen C, Reid ID (2016) RefineNet: multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. IEEE Conf Comput vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR) 2017:5168–5177
Lin C, Hong Y, Liu J (2021) Aggregation-and-attention network for brain tumor segmentation. BMC Med Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-021-00639-8
Liu P, Dou Q, Wang Q, Heng P (2020a) An encoder-decoder neural network with 3d squeeze-and-excitation and deep supervision for brain tumor segmentation. IEEE Access 8:34029–34037
Liu L, Cheng J, Quan Q, Wu F, Wang Y, Wang J (2020b) A survey on U-shaped networks in medical image segmentations. Neurocomputing 409:244–258
Liu D, Sheng N, He T, Wang W, Zhang J, Zhang J (2022) SGEResU-Net for brain tumor segmentation. Math Biosci Eng: MBE 19(6):5576–5590
Liu H, Wang C, Jiang X, Khishe M (2023) A few-shot learning approach for Covid-19 diagnosis using Quasi-configured topological spaces. J Artif Intell Soft Comput Res 14:77–95
Maram B, Rana P (2021) Brain tumour detection on BraTS 2020 using U-Net. 2021 9th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO), 1–5
McKinley R, Meier R, Wiest R (2018) Ensembles of densely-connected CNNs with label-uncertainty for brain tumor segmentation. BrainLes@MICCAI
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Farahani K, Kirby JS, Burren Y, Porz N, Slotboom J, Wiest R, Lanczi L, Gerstner ER, Weber M, Arbel T, Avants BB, Ayache N, Buendia P, Collins DL, Cordier N, Corso JJ, Criminisi A, Das T, Delingette H, Demiralp Ç, Durst CR, Dojat M, Doyle S, Festa J, Forbes F, Geremia E, Glocker B, Golland P, Guo X, Hamamci A, Iftekharuddin KM, Jena R, John NM, Konukoglu E, Lashkari D, Mariz JA, Meier R, Pereira S, Precup D, Price SJ, Riklin-Raviv T, Reza SM, Ryan MT, Sarikaya D, Schwartz LH, Shin H, Shotton J, Silva CA, Sousa N, Subbanna NK, Székely G, Taylor TJ, Thomas OM, Tustison N, Ünal GB, Vasseur F, Wintermark M, Ye D, Zhao L, Zhao B, Zikic D, Prastawa M, Reyes M, Leemput KV (2015) The multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34:1993–2024
Miotto R, Wang F, Wang S, Jiang X, Dudley JT (2018) Deep learning for healthcare: review, opportunities and challenges. Brief Bioinform 19(6):1236–1246
Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc LL, Lee MJ, Heinrich MP, Misawa K, Mori K, McDonagh SG, Hammerla NY, Kainz B, Glocker B, Rueckert D (2018) Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas. Ar**v, abs/1804.03999
Ostrom QT, Gittleman HR, Xu JC, Kromer C, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2016) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro Oncol 18(suppl_5):v1–v75
Peiris H, Hayat M, Chen Z, Egan GF, Harandi M (2021) A volumetric transformer for accurate 3D tumor segmentation. Ar**v, abs/2111.13300
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells W, Frangi A (eds) Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention – MICCAI 2015. MICCAI 2015. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 9351. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Saffari A, Khishe M, Mohammadi M, Hussein Mohammed A, Rashidi S (2022) DCNN-FuzzyWOA: artificial intelligence solution for automatic detection of COVID-19 using X-Ray images. Comput Intell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5677961
Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T (2014) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Conf Comput vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR) 2015:3431–3440
Tianqing H, Khishe M, Mohammadi M, Parvizi GR, Karim SH, Rashid TA (2021) Real-time COVID-19 diagnosis from X-Ray images using deep CNN and extreme learning machines stabilized by chimp optimization algorithm. Biomed Signal Process Control 68:102764–102764
Valanarasu JM, Sindagi VA, Hacihaliloglu I, Patel VM (2020) KiU-Net: overcomplete convolutional architectures for biomedical image and volumetric segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 41:965–976
Wang F, Jiang R, Zheng L, Meng C, Biswal B (2019) 3D U-Net based brain tumor segmentation and survival days prediction. BrainLes@MICCAI
Wang X, Gong C, Khishe M, Mohammadi M, Rashid TA (2021a) Pulmonary diffuse airspace opacities diagnosis from chest X-Ray images using deep convolutional neural networks fine-tuned by whale optimizer. Wirel Pers Commun 124:1355–1374
Wang W, Chen C, Ding M, Li J, Yu H, Zha S (2021b) TransBTS: multimodal brain tumor segmentation using transfoRmer. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention
**ao Z, Tong H, Qu R, **ng H, Luo S, Zhu Z, Song F, Feng L (2023) CapMatch: semi-supervised contrastive transformer capsule with feature-based knowledge distillation for human activity recognition. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3344294
**ao Z, **ng H, Zhao B, Qu R, Luo S, Dai P, Li K, Zhu Z (2024a) Deep contrastive representation learning with self-distillation. IEEE Trans Emerg Topics Comput Intell 8:3–15
**ao Z, **ng H, Qu R, Feng L, Luo S, Dai P, Zhao B, Dai Y (2024b) Densely knowledge-aware network for multivariate time series classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 54:2192–2204
Xu B, Martín D, Khishe M, Boostani R (2022) COVID-19 diagnosis using chest CT scans and deep convolutional neural networks evolved by IP-based sine-cosine algorithm. Med Biol Eng Comput 60:2931–2949
Yao D, Chi W, Khishe M (2022) Parkinson’s disease and cleft lip and palate of pathological speech diagnosis using deep convolutional neural networks evolved by IPWOA. Appl Acoust. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2022.109003
Zare M, Ghasemi M, Zahedi A, Golalipour K, Mohammadi SK, Mirjalili SM, Abualigah LM (2023) A global best-guided firefly algorithm for engineering problems. J Bionic Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42235-023-00386-2
Zeineldin RA, Karar M, Coburger J, Wirtz CR, Burgert O (2020) DeepSeg: deep neural network framework for automatic brain tumor segmentation using magnetic resonance FLAIR images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 15:909–920
Zeineldin RA, Karar M, Burgert O, Mathis-Ullrich F (2022) Multimodal CNN networks for brain tumor segmentation in MRI: a BraTS 2022 challenge solution. Ar**v, abs/2212.09310
Zhang Z, Liu Q, Wang Y (2017) Road extraction by deep residual U-Net. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 15:749–753
Zhang Y, Zhong P, Jie D, Wu J, Zeng S, Chu J, Liu Y, Wu EX, Tang X (2021) Brain tumor segmentation from multi-modal MR images via ensembling UNets. Front Radiol 1:1–11
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, Wang X, Jia J (2016) Pyramid scene parsing network. IEEE Conf Comput vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR) 2017:6230–6239
Zhou Z, Siddiquee MM, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J (2019) UNet++: redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39:1856–1867
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, A., Singh, Y. & Chinagundi, B. ResUNet + + : a comprehensive improved UNet + + framework for volumetric semantic segmentation of brain tumor MR images. Evolving Systems (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12530-024-09579-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12530-024-09579-4