Abstract
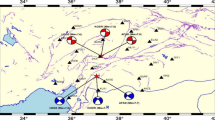
Indian map** agency, Survey of India (SOI), is ambitiously implementing nation-wide network of Continuously Operating Reference Stations (CORS) to improve the accuracy of derived three-dimensional relative positions of the Global Navigational Satellite System (GNSS) over the regions. However, it does not only improve the accuracy but also reduce the cost of reliable data acquisition. Recently, SOI has established a number of CORS networks and continues to cover the entire India for its suitability in the infrastructure projects and in the generation and updating of revenue maps. The present article attempts to measure the accuracy of a single baseline static survey carried out using the CORS network by studying fifteen stations established in different parts of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. To study the accuracy using the established CORS network, 7 days of continuous observed data from fifteen stations of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh have been processed. The study has been done taking a base–rover combination with varying distance (D) from 30 to 160 km and the time duration (T) at 20 min, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, and 24 h using observational CORS data (including both GPS and GLONASS). The present study shows that (i) dependence of accuracy on distance (D) up to 160 km is almost negligible when final ephemeris data of GPS satellite orbit (International GPS Service) have been used and (ii) the positional accuracy improved with an increase in observation duration. Finally, regression analysis has been done to establish the relationship between distance (D), duration (T), and accuracy for the given CORS network.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altiner, Y., Söhne, W., Güney, C., Perlt, J., Wang, R., & Muzli, M. (2013). A geodetic study of the 23 October 2011 Van, Turkey earthquake. Tectonophysics, 588, 118–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2012.12.005
Bruyninx, C. H. W. A. G. C. S., Habrich, H., Söhne, W., Kenyeres, A., Stangl, G., & Völksen, C. (2012). Enhancement of the EUREF permanent network services and products. In Geodesy for Planet Earth. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20338-1_4
Cefalo, R., & Gatti, M. (2000). Dual frequency GPS + GLONASS measurements in the static relative positioning. Bollettino Di Geodesia e Scienze Affini, 59(4), 391–403.
Dardanelli, G., Brutto, M. L., & Pipitone, C. (2020). GNSS CORS network of the university of Palermo: Design and first analysis of data. Geographia Technica, 15(1), 43–69. https://doi.org/10.21163/GT_2020.151.05
Dawidowicz, K., Lamparski, J., & Świątek, K. (2008). The height differences appointment using satellite leveling. Acta Scientiarum Polonorum. Geodesia Et Descriptio Terrarum, 7(1), 29–34.
Eckl, M. C., Snay, R. A., Soler, T., Cline, M. W., & Mader, G. L. (2001). Accuracy of GPS-derived relative positions as a function of interstation distance and observing-session duration. Journal of Geodesy, 75(12), 633–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900100204
Geng, J., Meng, X., Dodson, A. H., & Teferle, F. N. (2010). Integer ambiguity resolution in precise point positioning: Method comparison. Journal of Geodesy, 84(9), 569–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-010-0399-x
Geng, J., Teferle, F. N., Shi, C., Meng, X., Dodson, A. H., & Liu, J. (2009). Ambiguity resolution in precise point positioning with hourly data. GPS Solutions, 13(4), 263–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-009-0119-2
Grejner-Brzezinska, D. A., Kashani, I., & Wielgosz, P. (2005). On accuracy and reliability of instantaneous network RTK as a function of network geometry, station separation, and data processing strategy. GPS Solutions, 9(3), 212–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-005-0130-1
Hernández-Andrade, D., Romero-Andrade, R., Sharma, G., Trejo-Soto, M. E., & Cabanillas-Zavala, J. L. (2022). Quality assessment of continuous operating reference stations (CORS)-GPS stations in Mexico. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 13(3), 275–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geog.2021.12.003
Hilla, S., & Cline, M. (2004). Evaluating pseudorange multipath effects at stations in the National CORS Network. GPS Solutions, 7(4), 253–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-003-0073-3
Huang, F., Dou, X., Lei, J., Lin, J., Ding, F., & Zhong, J. (2016). Statistical analysis of nighttime medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances using airglow images and GPS observations over central China. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 121(9), 8887–8899. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JA022760
Ji, S., Zheng, Q., Weng, D., Chen, W., Wang, Z., & He, K. (2021). Single epoch ambiguity resolution of small-scale CORS with multi-frequency GNSS. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010013
**g-nan, L., & Mao-Rong, G. E. (2003). PANDA software and its preliminary result of positioning and orbit determination. Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences, 8(2), 603–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02899825
Kenyeres, A., & Bruyninx, C. (2004). EPN coordinate time series monitoring for reference frame maintenance. GPS Solutions, 8(4), 200–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-004-0104-8
Krzan, G., Dawidowicz, K., & Krzysztof, S. (2013). Analysis of current position determination accuracy in natural resources canada precise point positioning service. Artificial Satellites, 48(3), 111–124. https://doi.org/10.2478/arsa-2013-0010
Kun, S., & Yong, W. (2007). The development and application of CORS technology and its value in the solution for environment protect in the GMS. GMSARN International Journal, 1(2), 69–74.
Liu, T., Yu, Z., Ding, Z., Nie, W., & Xu, G. (2021). Observation of ionospheric gravity waves introduced by thunderstorms in low latitudes China by GNSS. Remote Sensing, 13(20), 4131. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204131
Moudrý, V., Urban, R., Štroner, M., Komárek, J., Brouček, J., & Prošek, J. (2019). Comparison of a commercial and home-assembled fixed-wing UAV for terrain map** of a post-mining site under leaf-off conditions. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40(2), 555–572. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1516311
Musa, T. A. (2007). Analysis of residual atmospheric delay in the low latitude regions using network-based GPS positioning Doctoral dissertation. Sydney, Australia: University of New South Wales.
Osório, I., & Cunha, M. (2013). The role of the TRS in precision agriculture: DGPS with EGNOS and RTK Positioning using data from NTRIP streams. Reference frames for applications in geosciences (pp. 277–282). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32998-2_40
Seier, G., Sulzer, W., Lindbichler, P., Gspurning, J., Hermann, S., Konrad, H. M., & Adelwöhrer, R. (2018). Contribution of UAS to the monitoring at the Lärchberg-Galgenwald landslide (Austria). International Journal of Remote Sensing, 39(15–16), 5522–5549. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1454627
Shi, C., Geng, J., Liu, J., & Ge, M. (2006, September). Integrated adjustment of LEO and GPS with PANDA in precision orbit determination. In Proceedings of the 19th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2006), 2579–2586.
Shiokawa, K., Ihara, C., Otsuka, Y., & Ogawa, T. (2003). Statistical study of nighttime medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances using midlatitude airglow images. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JA009491
Shoab, M., Singh, V. K., & Ravibabu, M. V. (2021). High-precise true digital orthoimage generation and accuracy assessment based on UAV images. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-021-01364-z
Zeybek, M. (2021). Accuracy assessment of direct georeferencing UAV images with onboard global navigation satellite system and comparison of CORS/RTK surveying methods. Measurement Science and Technology, 32(6), 065402. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6501/abf25d
Zhang, J., & Lachapelle, G. (2001). Precise estimation of residual tropospheric delays using a regional GPS network for real-time kinematic applications. Journal of Geodesy, 75(5), 255–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900100171
Acknowledgements
We are sincerely thankful to the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and Survey of India (SOI) for their utmost help to perform this academic research and provide the relevant data over the period.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Gond, A.K., Ohri, A., Maurya, S.P. et al. Accuracy Assessment of Relative GPS as a Function of Distance and Duration for CORS Network. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 51, 1267–1277 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-023-01701-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-023-01701-4