Abstract
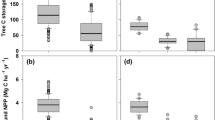
This study examined the biomass and carbon pools of the main ecosystem components in an age sequence of five Korean pine plantation forest stands in central Korea. The C contents in the tree and ground vegetation biomass, coarse woody debris, forest floor, and mineral soil were estimated by analyzing the C concentration of each component. The aboveground and total tree biomass increased with increasing stand age. The highest C concentration across this chronosequence was found in the tree branch while the lowest C concentration was found in the ground vegetation. The observed C contents for tree components, ground vegetation, and coarse woody debris were generally lower than the predicted C contents estimated from a biomass C factor of 0.5. Forest floor C content was age-independent. Total mineral soil C content appeared to decline initially after establishing Korean pine plantations and recover by the stand age of 35 years. Although aboveground tree biomass C content showed considerable accumulation with increasing age, the relative contribution of below ground C to total ecosystem C content varied substantially. These results suggest that successional development as temporal factor has a key role in estimating the C storage in Korean pine plantation forests.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avery TE, Burkhart HE (1983) Forest measurements, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Bert D, Danjon F (2006) Carbon concentration variations in the roots, stem and crown of mature Pinus pinaster (Ait.). For Ecol Manag 222:279–295
Cho Y-C, Shin H-C, Kim S-S, Lee C-S (2007) Dynamics and conservation of the Gwangneung National Forest in Central Korea: a national model for forest restoration. J Plant Biol 50:615–625
Choi S-D, Lee K, Chang Y-S (2002) Large rate of uptake of atmospheric carbon dioxide by planted forest biomass in Korea. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 16(4):1089. doi:10.1029/2002GB001914
Farley KA, Kelly EF, Hofstede RGM (2004) Soil organic carbon and water retention following conversion of grasslands to pine plantations in the Ecuadoran Andes. Ecosystems 7:729–739
Goodale CL, Apps MJ, Birdsey RA, Field CB, Heath LS, Houghton RA, Jenkins JC, Kohlmaier GH, Kurz W, Liu S, Nabuurs G-J, Nilsson S, Shvidenko AZ (2002) Forest carbon sinks in the Northern Hemisphere. Ecol Appl 12:891–899
Grünzweig JM, Gelfand I, Fried Y, Yakir D (2007) Biogeochemical factors contributing to enhanced carbon storage following afforestation of a semi-arid shrubland. Biogeosciences 4:891–904
Hooker TD, Compton JE (2003) Forest ecosystem carbon and nitrogen accumulation during the first century after agricultural abandonment. Ecol Appl 13:299–313
Houghton RA (2005) Aboveground forest biomass and the global carbon balance. Glob Chang Biol 11:945–958
Houghton RA (2007) Balancing the global carbon budget. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 35:313–347
Hwang JH, Bae SW, Lee KJ, Lee KS, Kim HS (2008) Short-term effect of thinning on aboveground carbon storage in Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) plantation. Jour Korean For Soc 97:605–610
Janssens IA, Sampson DA, Cermak J, Meiresonne L, Riguzzi F, Overloop S, Ceulemans R (1999) Above- and belowground phytomass and carbon storage in a Belgian Scots pine stand. Ann For Sci 56:81–90
Johnson DW, Todd DE Jr, Tolbert VR (2003) Changes in ecosystem carbon and nitrogen in a loblolly pine plantation over the first 18 years. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:1594–1601
Korea Forest Service (2007) Survey manual for forest biomass and soil carbon. Korea Forest Research Institute, Seoul
Korea Forest Service (2008) Statistical yearbook of forestry. Korea Forest Service, Seoul
Kwon K-C, Lee DK (2006) Biomass and energy content of Pinus koraiensis stand planted in Mt. Wolak. J Mokchae Konghak 34:66–75
Laganiere J, Angers DA, Pare D (2010) Carbon accumulation in agricultural soils after afforestation: a meta-analysis. Glob Chang Biol 16:439–453
Laiho R, Laine J (1997) Tree stand biomass and carbon content in an age sequence of drained pine mires in southern Finland. For Ecol Manag 93:161–169
Lamlom SH, Savidge RA (2003) A reassessment of carbon content in wood: variation within and between 41 North American species. Biomass Bioenergy 25:381–388
Lee DK, Kim GT (1997) Tree form and biomass allocation of Quercus, Larix leptolepis (Sieb. et Zucc.) Gordon and Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc. in Kwangju-gun, Kyunggi-do. Jour Korean For Soc 86:208–213
Lee KJ, Park IH (1987) Primary production and nutrients distribution in 22-year-old Pinus koraiensis and Quercus mongolica stands in Kwangju district. J Korean For En 7:11–21
Lee YJ, Seo YO, Park SM, Pyo JK, Kim RH, Son YM, Lee KH, Kim HH (2009) Estimation of biomass for 27 years old Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) plantation in Gangneung, Gangwon-Province. J Agr Life Sci 43:1–8
Lemma B, Kleja DB, Nilsson I, Olsson M (2006) Soil carbon sequestration under different exotic tree species in the southwestern highlands of Ethiopia. Geoderma 136:886–898
Li XD, Yi MJ, Son YH, ** GZ, Han SS (2010) Forest biomass carbon accumulation in Korea from 1954 to 2007. Scand J For Res. doi:10.1080/02827581.2010.524892
Martin JL, Gower ST, Plaut J, Holmes B (2005) Carbon pools in a boreal mixedwood logging chronosequence. Glob Chang Biol 11:1883–1894
Noh NJ, Son YH, Kim RH, Seo KY, Seo KW, Koo JW, Kyung JH, Kim JS, Lee YJ, Park IH, Lee KH, Son YM (2005) Biomass of Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) in Gapyeong area. Korean J For Meas 8:75–82
Noh NJ, Son YH, Lee KS, Yoon TK, Seo KW, Kim CS, Lee WK, Bae SW, Hwang JH (2010) Influence of stand density on soil CO2 efflux for a Pinus densiflora forest in Korea. J Plant Res 123:411–419
Oliver GR, Beets PN, Garrett LG, Pearce SH, Kimberly MO, Ford-Robertson JB, Robertson KA (2004) Variation in soil carbon in pine plantations and implications for monitoring soil carbon stocks in relation to land-use change and forest site management in New Zealand. For Ecol Manag 203:283–295
Paul KI, Polglase PJ, Nyakuengama JG, Khanna PK (2002) Change in soil carbon following afforestation. For Ecol Manag 168:241–257
Peichl M, Arain MA (2006) Above- and belowground ecosystem biomass and carbon pools in an age-sequence of temperate pine plantation forests. Agr For Meteorol 140:51–63
Peichl M, Arain MA (2007) Allometry and partitioning of above- and belowground tree biomass in an age-sequence of white pine forests. For Ecol Manag 253:68–80
Peltoniemi M, Makipaa R, Liski J, Tamminen P (2004) Changes in soil carbon with stand age—an evaluation of a modeling method with empirical data. Glob Chang Biol 10:2078–2091
Pregitzer KS, Euskirchen ES (2004) Carbon cycling and storage in world forests: biome patterns related to forest age. Glob Chang Biol 10:2052–2077
Son YH, Hwang JW, Kim ZS, Lee WK, Kim JS (2001) Allometry and biomass of Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) in central Korea. Bioresour Technol 78:251–255
Son YH, Seo KY, Kim RH, Koo JW, Yi MJ, Kim JH (2005) Biomass and nutrient distribution of Pinus Koraiensis seedlings invading a mixed forest dominated by Quercus mongolica. For Sci Technol 1:8–12
Son YH, Noh NJ, Kim RH, Koo JW, Yi MJ (2007) Biomass and nutrients of planted and naturally occurring Pinus koraiensis in Korea. Eurasian J For Res 10:41–50
Sprugel DG (1983) Correcting for bias in log-transformed allometric equations. Ecology 64:209–210
Sun OJ, Campbell J, Law BE, Wolf V (2004) Dynamics of carbon stocks in soils and detritus across chronosequences of different forest types in the Pacific Northwest, USA. Glob Chang Biol 10:1470–1481
Tak K, Chun Y, Wood PM (2007) The South Korean forest dilemma. Int For Rev 9:548–557
Tang JW, Bolstad PV, Martin JG (2009) Soil carbon fluxes and stocks in a Great Lakes forest—chronosequence. Glob Chang Biol 15:145–155
Taylor AR, Wang JR, Chen HYH (2007) Carbon storage in a chronosequence of red spruce (Picea rubens) forests in central Nova Scotia, Canada. Can J For Res 37:2260–2269
Yanai RD, Federer CA, Arthur MA, Siccama TG (2000) Challenges of measuring forest floor organic matter dynamics: repeated measures from a chronosequence. For Ecol Manag 138:273–283
Yi MJ (1998) Changes in aboveground biomass and nutrient accumulation of Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) Plantation by stand age at Kangwondo province. Jour Korean For Soc 87:276–285
Zheng H, Ouyang Z, Xu W, Wang X, Miao H, Li X, Tian Y (2008) Variation of carbon storage by different reforestation types in the hilly red soil region of southern China. For Ecol Manag 255:1113–1121
Acknowledgments
This study was carried out with the support of “Forest Science & Technology Projects (Project No. S1107L0101)” provided by Korea Forest Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Yi, M.J., Son, Y. et al. Biomass and Carbon Storage in an Age-Sequence of Korean Pine (Pinus koraiensis) Plantation Forests in Central Korea. J. Plant Biol. 54, 33–42 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-010-9140-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-010-9140-9