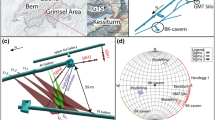
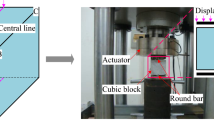
Abstract
The distinctive weathering profile and discontinuity of granites, dip** slightly at shallow depths and steeply in larger depths, are regarded as being due to their physical and geo-mechanical properties. This paper compares vertical stress (Sv) and overlain weight (γh) drawn from different kinds of in situ stress measurements, as well as coefficients of lateral stress. Stress trends are connected with discontinuities (joints and dykes), which reveal their relationships in space and dip angles of joints and dykes are compared in space, together with shear plane plunges and the strength of rocks from laboratory tests. As a result, it was found that the relict structural geostress contributes to maximum horizontal stress, especially at shallow depths. The most common feature is the high coefficient of lateral stress, which is mostly attributed to unloading in shallow depths and stress concentration at a certain depth after the erosion of overlain beds and the exposure of granites at the ground surface. Therefore, the weathering profiles and weathered capsule of granites could be interpreted from this viewpoint. One of the two main features of this paper is the connection of the extraordinary values of the lateral coefficient of in situ stress with unloading and the typical weathering profile at shallow depths. Another is the comparison of the shear stress and strength from in situ and laboratory tests, with a series of data from the same location and depth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AHH (Academy of Hydraulic Resources and Hydropower), 1991, Handbook on mechanical properties of rocks in China. Hydraulic Resources and Hydroelectric Power Press, Bei**g, 539 p. (in Chinese)
Brown, E.T. and Hoek, E., 1978, Trends in relationships between measured In-Situ stresses and depth. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstract, 15, 211–215.
CEA (Chinese Earthquake Administration), 2007, Basic database of geostress of continental crust of China. http:\\www.eq-icd.cn/webgis (accessed on Jan. 2008).
Choi, S.Y. and Park, H.D., 2002, Comparison among different criteria of RMR and Q-system for rock mass classification for tunneling in Korea. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 17, 391–401.
GGB (Guangdong Geological Bureau), 1965, Regional geological survey report: Huiyang Region and Baoan Region (1:200,000). Vol. 1/2, Guangzhou, 318 p. (in Chinese)
Haimson, B.C., 1978, The hydrofracturing stress measuring method and recent field results. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstract, 15, 167–178.
Hast, N., 1958, The measurement of rock pressure in mines. Årsbok Sveriges Geologiska Undersökning, Series C, 52, 1–183.
Hoek, E. and Brown, E.T., 1980, Underground excavations in rocks. Austin & Sons Ltd., Hertford, England, 532 p.
Hou, Y., Sun, W., Chen, Q., Wang, B., and Chen, S., 2006, In-situ stress measurement and its application in the pre-feasibility study of an underground oil reservoir in China. Journal of Geomechanics, 12, 197–202. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang, Z.G., Zhang, W.Q., and Chen, J.H., 1996, Red weathering crust in South China. Ocean Press, Bei**g, 312 p. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hubbert, M.K. and Willis, D.G., 1957, Mechanics of hydraulic fracturing. Transactions on American Institute of Mining Engineers, 153–156.
Kanagawa, T., Hibino, S., Ishide, T., Hagashi, M., and Ditahara, Y., 1986, In-situ stress measurements in the Japanese island: over-cording results from a multi-elements gauge used at 23 sites. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics, 23, 29–39.
Irfan, T.Y., 1996, Mineralogy, fabric properties and classification of weathered granites in Hong Kong. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology, 29, 5–35.
Linder, E.N. and Haipern, J.A., 1978, In-situ stress in North America: a compilation. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstract, 15, 1–14.
Liu, M., 2000, Alta of Chinese natural geography. China Map Press, Bei**g, 252 p. (in Chinese)
Liu, Y., Gong, B., **ao, B., and Luo, C., 1990, Analyses of ground stress field in underground excavation of Guangzhou Pumped Storage Power Station. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 4, 45–53. (in Chinese)
Liu, Y. and **ao, B., 1989, Preliminary analysis of ground stress field for the lock area of Three — Gorge Project. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2, 22–36. (in Chinese)
LNG (Liaoning Geological Exploration Bureau, Department of Geology), 1995, Geological map interpretation: 1:50,000 **ngshan Sheet, 23p. (in Chinese)
Ng, C.W.W., Guan, P., and Shang, Y.J., 2001, Weathering mechanisms and indices of the igneous rocks of Hong Kong. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 34, 133–151.
Pine, R.J., Tunbrdge, L.W., and Merrififld, C.M., 1983, In-situ stress measurement in Carnmenells Granite: overcoring tests at South Crofty mines at a depth of 790m. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics, 20, 54–72.
Shang, Y., Shi, Y., Yuan, G., and Sun, Y., 2007, Discontinuity distribution in granites and its effects on rock mass classification. In: Sousa, R. and Grossmann O. (eds.), Proceedings of the 11th Congress of the International Society for Rock Mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal. Taylor & Francis Group, London, 227–230.
Shi, Y., Shang, Y., Yuan, G., and Sun, Y., 2007, Site selection and evaluation of engineering geology for underground project at Daya Bay, China. Journal of Engineering Geology, 15, 328–337. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Thompson, P.M. and Chandler, N.A., 2004, In situ stress determinations in deep boreholes at the Underground Research Laboratory. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 41, 1305–1316.
Wang, J., 2007, Site selection for high nuclear waste disposal. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 25, 801–812. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wan, T., 1993, Structural geostress and intraplate deformation and application in East China. Geological Publishing House, Bei**g, 103 p. (in Chinese)
Yuan, G., Shang, Y., Shi, Y., and Guo, S., 2006, Engineering geological issues and measures for storage of oil and gas in underground rock caverns. Journal of Engineering Geology, 14, 792–799. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao, J., Hefny, A.M., and Zhou, Y.X., 2005, Hydrofracturing in situ stress measurements in Singapore granite. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 42, 577–583.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, Y., Park, HD., Yuan, G. et al. From in situ stress and discontinuities to the strength of granites: comparison and case study. Geosci J 12, 361–372 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-008-0036-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-008-0036-3