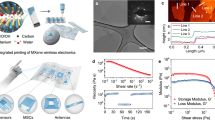
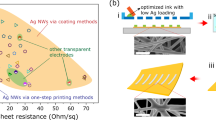
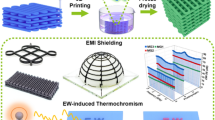
Abstract
Facile preparation of additive-free inks with both high viscosity and high conductivity is critical for scalable screen printing of wireless electronics, yet very challenging. MXene materials exhibit excellent conductivity and hydrophilicity, showing great potential in the field of additive-free inks for screen printing. Here, we demonstrate the synthesis of additive-free two-dimensional (2D) titanium carbide MXene inks, and realize screen-printed MXene wireless electronics for the first time. The viscosity of MXene ink is solely regulated by tuning the size of MXene nanosheet without any additives, hence rendering the printed MXene film extremely high conductivity of 1.67 × 105 S/m and fine printing resolution down to 0.05 mm on various flexible substrates. Moreover, radio frequency identification (RFID) tags fabricated using the additive-free MXene ink via screen printing exhibit stable antenna reading performance and superb flexibility. This article, thus offers a new route for the efficient, low-cost and pollution-free manufacture of printable electronics based on additive-free MXene inks.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang, C.; Qiu, K. F.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. Z.; Hu, J. J. Towards robust and stealthy communication for wireless intelligent terminals. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 11791–11814.
Oteafy, S. M. A.; Hassanein, H. S. IoT in the fog: A roadmap for data-centric IoT development. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 157–163.
Xu, L. Q.; Tang, Y. Z.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F. H.; Chen, J. K.; Xuan, W. P.; **, H.; Ye, Z.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y. B. et al. Fully self-powered instantaneous wireless liquid level sensor system based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2022, 75, 5425–5434.
Wang, W. T.; Lu, L. S.; Lu, X. Y.; Liang, Z. B.; Lin, H. H.; Li, Z. H.; Wu, X. H.; Lin, L. H.; **e, Y. X. Scorpion-inspired dual-bionic, microcrack-assisted wrinkle based laser induced graphene-silver strain sensor with high sensitivity and broad working range for wireless health monitoring system. Nano Res. 2023, 75, 1228–1241.
Khan, Y.; Thielens, A.; Muin, S.; Ting, J.; Baumbauer, C.; Arias, A. C. A new frontier of printed electronics: Flexible hybrid electronics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905279.
Li, D. D.; Lai, W. Y.; Zhang, Y. Z.; Huang, W. Printable transparent conductive films for flexible electronics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704738.
Shao, Y. Z.; Wei, L. S.; Wu, X. Y.; Jiang, C. M.; Yao, Y.; Peng, B.; Chen, H.; Huangfu, J. T.; Ying, Y. B.; Zhang, C. J. et al. Room-temperature high-precision printing of flexible wireless electronics based on MXene inks. Nat. Commun. 2022, 73, 3223.
Zhu, H. W.; Gao, H. L.; Zhao, H. Y.; Ge, J.; Hu, B. C.; Huang, J.; Yu, S. H. Printable elastic silver nanowire-based conductor for washable electronic textiles. Nano Res. 2020, 70, 2879–2884.
Zhang, Y. F.; Wang, C.; Dong, X. Y.; Jiang, H. M.; Hu, T.; Meng, C. G.; Huang, C. Alkali etching metal silicates derived from bamboo leaves with enhanced electrochemical properties for solid-state hybrid supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 417, 127964.
Lin, Y.; Li, Q. S.; Ding, C., Wang, J. Y.; Yuan, W.; Liu, Z. Y.; Su, W. M.; Cui, Z. High-resolution and large-size stretchable electrodes based on patterned silver nanowires composites. Nano Res. 2022, 75, 4590–4598.
Wang, G. D.; Adil, M. A.; Zhang, J. Q.; Wei, Z. X. Large-area organic solar cells: Material requirements, modular designs, and printing methods. Adv. Mater. 2009, 37, 1805089.
Ma, R. H.; Wang, C. F.; Yan, W.; Sun, M. Z.; Zhao, J. X.; Zheng, Y. T.; Li, X.; Huang, L. B.; Chen, B.; Wang, F. et al. Interface synergistic effects induced multi-mode luminescence. Nano Res. 2022, 75, 4457–4465.
Kokkonen, M.; Talebi, P.; Zhou, J.; Asgari, S.; Soomro, S. A.; Elsehrawy, F.; Halme, J.; Ahmad, S.; Hagfeldt, A.; Hashmi, S. G. Advanced research trends in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 9, 10527–10545.
Liang, J. J.; Tong, K.; Pei, Q. B. A water-based silver-nanowire screen-print ink for the fabrication of stretchable conductors and wearable thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5986–5996.
Jun, H. Y.; Lee, E. J.; Ryu, S. O. Synthesis and characterization of copper ink and direct printing of copper patterns by inkjet printing for electronic devices. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2020, 20, 853–861.
Gemeiner, P.; Pavličková, M.; Hatala, M.; Hvojnik, M.; Homola, T.; Mikula, M. The effect of secondary dopants on screen-printed PEDOT: PSS counter-electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51929.
Pan, K. W.; Fan, Y. Y.; Leng, T.; Li, J. S.; **n, Z. Y.; Zhang, J. W.; Hao, L.; Gallop, J.; Novoselov, K. S.; Hu, Z. R. Sustainable production of highly conductive multilayer graphene ink for wireless connectivity and IoT applications. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5197.
Chen, K.; Gao, W.; Emaminejad, S.; Kiriya, D.; Ota, H.; Nyein, H. Y. Y.; Takei, K.; Javey, A. Printed carbon nanotube electronics and sensor systems. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4397–4414.
Goh, Y.; Lauro, S.; Barber, S. T.; Williams, S. A.; Trabold, T. A. Cleaner production of flexographic ink by substituting carbon black with biochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 324, 129262.
Ding, H.; He, P.; Yang, J. X.; Liu, C. G.; Zhao, H.; Derby, B. Water-based highly conductive graphene inks for fully printed humidity sensors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 455304.
Liu, L. X.; Shen, Z. G.; Zhang, X. J.; Ma, H. Highly conductive graphene/carbon black screen printing inks for flexible electronics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 12–21.
Mohammadi, A. V.; Rosen, J.; Gogotsi, Y. The world of two-dimensional carbides and nitrides (MXenes). Science 2021, 372, eabf1581.
Jiang, J. Z.; Bai, S. S.; Zou, J.; Liu, S.; Hsu, J. P.; Li, N.; Zhu, G. Y.; Zhuang, Z. C.; Kang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Z. Improving stability of MXenes. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6551–6567.
Yu, L. H.; Fan, Z. D.; Shao, Y. L.; Tian, Z. N.; Sun, J. Y.; Liu, Z. F. Versatile N-doped MXene ink for printed electrochemical energy storage application. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901839.
Wu, H.; **e, Y. M.; Ma, Y. A.; Zhang, B. B.; **a, B.; Zhang, P. X.; Qian, W.; He, D. P.; Zhang, X.; Li, B. W. et al. Aqueous MXene/xanthan gum hybrid inks for screen-printing electromagnetic shielding, joule heater, and piezoresistive sensor. Small 2022, 18, 2107087.
Li, X.; Sun, R. J.; Pan, J. Y.; Shi, Z. H.; Lv, J. J.; An, Z. J.; He, Y.; Chen, Q. M.; Han, R. P. S.; Zhang, F. N. et al. All-MXene-printed RF resonators as wireless plant wearable sensors for in situ ethylene detection. Small, in press, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202207889.
Chen, Y. A.; Li, Y. H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, C. Z.; Qi, H. S. Holocellulose nanofibril-assisted intercalation and stabilization of Ti3C2Tx MXene inks for multifunctional sensing and EMI shielding applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 36221–36231.
Deng, Z. M.; Li, L. L.; Tang, P. P.; Jiao, C. Y.; Yu, Z. Z.; Koo, C. M.; Zhang, H. B. Controllable surface-grafted MXene inks for electromagnetic wave modulation and infrared anti-counterfeiting applications. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 16976–16986.
Abdolhosseinzadeh, S.; Schneider, R.; Verma, A.; Heier, J.; Nüesch, F.; Zhang, C. F. Turning trash into treasure: Additive free MXene sediment inks for screen-printed micro-supercapacitors. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000716.
Sarycheva, A.; Polemi, A.; Liu, Y. Q.; Dandekar, K.; Anasori, B.; Gogotsi, Y. 2D titanium carbide (MXene) for wireless communication. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau0920.
Huang, L.; Huang, Y.; Liang, J. J.; Wan, X. J.; Chen, Y. S. Graphene-based conducting inks for direct inkjet printing of flexible conductive patterns and their applications in electric circuits and chemical sensors. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 675–684.
Zhang, J. Z.; Uzun, S.; Seyedin, S.; Lynch, P. A.; Akuzum, B.; Wang, Z. Y.; Qin, S.; Alhabeb, M.; Shuck, C. E.; Lei, W. W. et al. Additive-free MXene liquid crystals and fibers. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 254–265.
Onsager, L. The effects of shape on the interaction of colloidal particles. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1949, 51, 627–659.
Tezel, G. B.; Arole, K.; Holta, D. E.; Radovic, M.; Green, M. J. Interparticle interactions and rheological signatures of Ti3C2Tz MXene dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 605, 120–128.
Leng, T.; Pan, K. W.; Zhang, Y. W.; Li, J. S.; Afroj, S. L.; Novoselov, K. S.; Hu, Z. R. Screen-printed graphite nanoplate conductive ink for machine learning enabled wireless radiofrequency-identification sensors. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 6197–6208.
Lin, M. Y.; Gai, Y. Z.; **ao, D.; Tan, H. J.; Zhao, Y. P. Preparation of pristine graphene paste for screen printing patterns with high conductivity. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 713, 98–104.
Xu, L. Y.; Wang, H. P.; Wu, Y. D.; Wang, Z. A.; Wu, L. X.; Zheng, L. H. A one-step approach to green and scalable production of graphene inks for printed flexible film heaters. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 1895–1905.
Wang, J. J.; Du, Y.; Qin, J.; Wang, L.; Meng, Q. F.; Li, Z. Y.; Shen, S. Z. Flexible thermoelectric reduced graphene oxide/Ag2S/methyl cellulose composite film prepared by screen printing process. Polymers 2022, 14, 5437.
Zheng, S. H.; Wang, H.; Das, P.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y. X.; Ma, J. X.; Liu, S. Z.; Wu, Z. S. Multitasking MXene inks enable high-performance printable microelectrochemical energy storage devices for all-flexible self-powered integrated systems. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005449.
Wan, S. J.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, N. N.; Wang, S. J.; Du, Y.; Xu, Z. P.; Deng, X. L.; Dou, S. X.; Jiang, L. et al. Ultrastrong MXene films via the synergy of intercalating small flakes and interfacial bridging. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7340.
Arapov, K.; Jaakkola, K.; Ermolov, V.; Bex, G.; Rubingh, E.; Haque, S.; Sandberg, H.; Abbel, R.; De With, G.; Friedrich, H. Graphene screen-printed radio-frequency identification devices on flexible substrates. Phys. Status Solidi. Rapid Res. Lett. 2016, 10, 812–818.
Zhang, B. H.; Wang, Z.; Song, R. G.; Fu, H. Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.; He, D. P.; Wu, Z. P. Passive UHF RFID tags made with graphene assembly film-based antennas. Carbon 2021, 178, 803–809.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22279097), the Hainan Provincial Joint Project of Sanya Yazhou Bay Science and Technology City (No. 520LH054), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WUT: 2021IVA66).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Fu, H., Si, Y. et al. Size effect enabling additive-free MXene ink with ultrahigh conductivity for screen printing of wireless electronics. Nano Res. 16, 11012–11017 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5762-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5762-3