Abstract
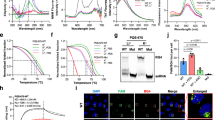
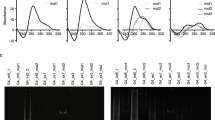
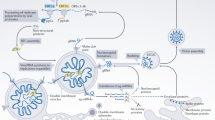
The G-quadruplex (G4) formed in single-stranded DNAs or RNAs plays a key role in diverse biological processes and is considered as a potential antiviral target. In the genome of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), 25 putative G4-forming sequences are predicted; however, the effects of G4-binding ligands on SARS-CoV-2 replication have not been studied in the context of viral infection. In this study, we investigated whether G4-ligands suppressed SARS-CoV-2 replication and whether their antiviral activity involved stabilization of viral RNA G4s and suppression of viral gene expression. We found that pyridostatin (PDS) suppressed viral gene expression and genome replication as effectively as the RNA polymerase inhibitor remdesivir. Biophysical analyses revealed that the 25 predicted G4s in the SARS-CoV-2 genome formed a parallel G4 structure. In particular, G4-644 and G4-3467 located in the 5′ region of ORF1a, formed a G4 structure that could be effectively stabilized by PDS. We also showed that PDS significantly suppressed translation of the reporter genes containing these G4s. Taken together, our results demonstrate that stabilization of RNA G4s by PDS in the SARS-CoV-2 genome inhibits viral infection via translational suppression, highlighting the therapeutic potential of G4-ligands in SARS-CoV-2 infection.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data published in this paper will be availlable upon request.
References
Abiri A, Lavigne M, Rezaei M et al (2021) Unlocking G-quadruplexes as antiviral targets. Pharmacol Rev 73(3):897–923. https://doi.org/10.1124/pharmrev.120.000230
Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF (2020) The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat Med 26(4):450–452. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9
Ariyo EO, Booy EP, Patel TR et al (2015) Biophysical characterization of G-quadruplex recognition in the PITX1 mRNA by the specificity domain of the helicase RHAU. PLoS ONE 10(12):e0144510. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144510
Bae JY, Lee GE, Park H et al (2021) Antiviral efficacy of pralatrexate against SARS-CoV-2. Biomol Ther (seoul) 29(3):268–272. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2021.032
Bao HL, Ishizuka T, Iwanami A, Oyoshi T, Xu Y (2017) A simple and sensitive 19F NMR approach for studying the interaction of RNA G-quadruplex with ligand molecule and protein. ChemistrySelect 2(15):4170–4175. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201700711
Berry SK, Fontana RJ (2020) Potential treatments for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin Liver Dis 15(5):181–186. https://doi.org/10.1002/cld.969
Bezzi G, Piga EJ, Binolfi A, Armas P (2021) CNBP binds and unfolds in vitro G-quadruplexes formed in the SARS-CoV-2 positive and negative genome strands. Int J Mol Sci 22(5):2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052614
Biffi G, Tannahill D, McCafferty J, Balasubramanian S (2013) Quantitative visualization of DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cells. Nat Chem 5(3):182–186. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1548
Biffi G, Di Antonio M, Tannahill D, Balasubramanian S (2014) Visualization and selective chemical targeting of RNA G-quadruplex structures in the cytoplasm of human cells. Nat Chem 6(1):75–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1805
Bohálová N, Cantara A, Bartas M et al (2021) Analyses of viral genomes for G-quadruplex forming sequences reveal their correlation with the type of infection. Biochimie 186:13–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2021.03.017
Burki TK (2022) The role of antiviral treatment in the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Respir Med 10(2):e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00011-X
Chen JS, Alfajaro MM, Chow RD et al (2021) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs dampen the cytokine and antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Virol 95(7):e00014-21. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00014-21
Cho HJ, Jeong SG, Park JE et al (2013) Antiviral activity of angelicin against gammaherpesviruses. Antiviral Res 100(1):75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.07.009
Corman VM, Landt O, Kaiser M et al (2020) Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill 25(3):2000045. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045
Creech CB, Walker SC, Samuels RJ (2021) SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. JAMA 325(13):1318–1320. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.3199
Cui H, Zhang L (2020) G-quadruplexes are present in human coronaviruses including SARS-CoV-2. Front Microbiol 11(2570):567317. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.567317
De Magis A, Manzo SG, Russo M et al (2019) DNA damage and genome instability by G-quadruplex ligands are mediated by R loops in human cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(3):816–825. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1810409116
Dhama K, Khan S, Tiwari R et al (2020) Coronavirus disease 2019-COVID-19. Clin Microbiol Rev 33(4):e00028-e120. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00028-20
Dolinnaya NG, Ogloblina AM, Yakubovskaya MG (2016) Structure, properties, and biological relevance of the DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes: overview 50 years after their discovery. Biochem Mosc 81(13):1602–1649. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297916130034
Dong Y, Dai T, Wang B et al (2021) The way of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development: success and challenges. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):387. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00796-w
Drygin D, Siddiqui-Jain A, O’Brien S et al (2009) Anticancer activity of CX-3543: a direct inhibitor of rRNA biogenesis. Can Res 69(19):7653–7661. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-1304
Fernandes Q, Inchakalody VP, Merhi M et al (2022) Emerging COVID-19 variants and their impact on SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, therapeutics and vaccines. Ann Med 54(1):524–540. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2022.2031274
Fischer WA, Eron JJ, Holman W et al (2022) A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus. Sci Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430
Groelly FJ, Porru M, Zimmer J et al (2022) Anti-tumoural activity of the G-quadruplex ligand pyridostatin against BRCA1/2-deficient tumours. EMBO Mol Med 14(3):e14501. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.202114501
Gussow AB, Auslander N, Faure G, Wolf YI, Zhang F, Koonin EV (2020) Genomic determinants of pathogenicity in SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci 117(26):15193–15199. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2008176117
Hansel-Hertsch R, Di Antonio M, Balasubramanian S (2017) DNA G-quadruplexes in the human genome: detection, functions and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(5):279–284. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.3
Hossain MU, Bhattacharjee A, Emon MTH et al (2021) Novel mutations in NSP-1 and PLPro of SARS-CoV-2 NIB-1 genome mount for effective therapeutics. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 19(1):52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-021-00152-z
Hu MH, Chen SB, Wang B et al (2017) Specific targeting of telomeric multimeric G-quadruplexes by a new triaryl-substituted imidazole. Nucleic Acids Res 45(4):1606–1618. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1195
Jeon S, Ko M, Lee J et al (2020) Identification of antiviral drug candidates against SARS-CoV-2 from FDA-approved drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00819-20
Ji D, Juhas M, Tsang CM, Kwok CK, Li Y, Zhang Y (2021) Discovery of G-quadruplex-forming sequences in SARS-CoV-2. Brief Bioinform 22(2):1150–1160. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa114
Katsuda Y, Sato SI, Asano L et al (2016) A small molecule that represses translation of G-quadruplex-containing mRNA. J Am Chem Soc 138(29):9037–9040. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b04506
Kim D, Lee JY, Yang JS, Kim JW, Kim VN, Chang H (2020) The architecture of SARS-CoV-2 transcriptome. Cell 181(4):914-921.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.011
Kosiol N, Juranek S, Brossart P, Heine A, Paeschke K (2021) G-quadruplexes: a promising target for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer 20(1):40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01328-4
Kumar S, Chandele A, Sharma A (2021) Current status of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. PLOS Pathog 17(9):e1009885. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1009885
Lavezzo E, Berselli M, Frasson I et al (2018) G-quadruplex forming sequences in the genome of all known human viruses: a comprehensive guide. PLOS Comput Biol 14(12):e1006675. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006675
Liu G, Du W, Sang X et al (2022) RNA G-quadruplex in TMPRSS2 reduces SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Commun 13(1):1444. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29135-5
Majee P, Kumar Mishra S, Pandya N et al (2020) Identification and characterization of two conserved G-quadruplex forming motifs in the Nipah virus genome and their interaction with G-quadruplex specific ligands. Sci Rep 10(1):1477. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58406-8
Majee P, Pattnaik A, Sahoo BR et al (2021) Inhibition of Zika virus replication by G-quadruplex-binding ligands. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 23:691–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.12.030
Ma-Lauer Y, Carbajo-Lozoya J, Hein MY et al (2016) p53 down-regulates SARS coronavirus replication and is targeted by the SARS-unique domain and PLpro via E3 ubiquitin ligase RCHY1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(35):E5192–E5201. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1603435113
Mergny JL, Li J, Lacroix L, Amrane S, Chaires JB (2005) Thermal difference spectra: a specific signature for nucleic acid structures. Nucleic Acids Res 33:e138–e138
Miglietta G, Russo M, Duardo RC, Capranico G (2021) G-quadruplex binders as cytostatic modulators of innate immune genes in cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 49(12):6673–6686. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab500
Mohanty J, Barooah N, Dhamodharan V, Harikrishna S, Pradeepkumar PI, Bhasikuttan AC (2013) Thioflavin T as an efficient inducer and selective fluorescent sensor for the human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA. J Am Chem Soc 135(1):367–376. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja309588h
Monchaud D, Teulade-Fichou MP (2008) A hitchhiker’s guide to G-quadruplex ligands. Org Biomol Chem 6(4):627–636. https://doi.org/10.1039/b714772b
Moruno-Manchon JF, Koellhoffer EC, Gopakumar J et al (2017) The G-quadruplex DNA stabilizing drug pyridostatin promotes DNA damage and downregulates transcription of Brca1 in neurons. Aging 9(9):1957–1970. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101282
Moruno-Manchon JF, Lejault P, Wang Y et al (2020) Small-molecule G-quadruplex stabilizers reveal a novel pathway of autophagy regulation in neurons. Elife 9:e52283. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.52283
Neckles C, Boer RE, Aboreden N et al (2019) HNRNPH1-dependent splicing of a fusion oncogene reveals a targetable RNA G-quadruplex interaction. RNA (new York, NY) 25(12):1731–1750. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.072454.119
Nijhuis M, van Maarseveen NM, Boucher CAB (2009) Antiviral resistance and impact on viral replication capacity: evolution of viruses under antiviral pressure occurs in three phases. In: Kräusslich HG, Bartenschlager R (eds) Antiviral strategies. Springer, Berlin, pp 299–320
Olivieri M, Cho T, Álvarez-Quilón A et al (2020) A genetic map of the response to DNA damage in human cells. Cell 182(2):481-496.e21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.040
Panera N, Tozzi AE, Alisi A (2020) The G-quadruplex/helicase world as a potential antiviral approach against COVID-19. Drugs 80(10):941–946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-020-01321-z
Qin G, Zhao C, Liu Y et al (2022) RNA G-quadruplex formed in SARS-CoV-2 used for COVID-19 treatment in animal models. Cell Discov 8(1):86. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41421-022-00450-x
Ravichandran S, Kim YE, Bansal V et al (2018) Genome-wide analysis of regulatory G-quadruplexes affecting gene expression in human cytomegalovirus. PLoS Pathog 14(9):e1007334. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1007334
Ravichandran S, Ahn JH, Kim KK (2019) Unraveling the regulatory G-quadruplex puzzle: lessons from genome and transcriptome-wide studies. Front Genet 10(1002):1002. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.01002
Ravichandran S, Razzaq M, Parveen N, Ghosh A, Kim KK (2021) The effect of hairpin loop on the structure and gene expression activity of the long-loop G-quadruplex. Nucleic Acids Res 49(18):10689–10706. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab739
Rubin D, Chan-Tack K, Farley J, Sherwat A (2020) FDA Approval of remdesivir—a step in the right direction. N Engl J Med 383(27):2598–2600. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp2032369
Ruggiero E, Richter SN (2018) G-quadruplexes and G-quadruplex ligands: targets and tools in antiviral therapy. Nucleic Acids Res 46(7):3270–3283. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky187
Ruggiero E, Richter SN (2020) Viral G-quadruplexes: new frontiers in virus pathogenesis and antiviral therapy. Annu Rep Med Chem 54:101–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.armc.2020.04.001
Ruggiero E, Richter SN (2023) Targeting G-quadruplexes to achieve antiviral activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 79:129085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.129085
Ruggiero E, Zanin I, Terreri M, Richter SN (2021) G-quadruplex targeting in the fight against viruses: an update. Int J Mol Sci 22(20):10984
Shamim A, Razzaq M, Kim KK (2020) MD-TSPC4: computational method for predicting the thermal stability of I-motif. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010061
Shen LW, Qian MQ, Yu K et al (2020) Inhibition of Influenza A virus propagation by benzoselenoxanthenes stabilizing TMPRSS2 Gene G-quadruplex and hence down-regulating TMPRSS2 expression. Sci Rep 10(1):7635. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64368-8
Su H, Xu J, Chen Y et al (2021) Photoactive G-quadruplex ligand identifies multiple G-quadruplex-related proteins with extensive sequence tolerance in the cellular environment. J Am Chem Soc 143(4):1917–1923. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c10792
Sun ZY, Wang XN, Cheng SQ, Su XX, Ou TM (2019) Develo** novel G-quadruplex ligands: from interaction with nucleic acids to interfering with nucleic acid(-)protein interaction. Molecules 24(3):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030396
Sun J, Wu G, Pastor F et al (2022) RNA helicase DDX5 enables STAT1 mRNA translation and interferon signalling in hepatitis B virus replicating hepatocytes. Gut 71(5):991–1005. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323126
Thakur S, Sasi S, Pillai SG et al (2022) SARS-CoV-2 mutations and their impact on diagnostics, therapeutics and vaccines. Front Med 9:815389–815389. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.815389
Tse WC, Boger DL (2005) A fluorescent intercalator displacement assay for establishing DNA binding selectivity and affinity. Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142700.nc0805s20
Tuesuwan B, Kern JT, Thomas PW et al (2008) Simian virus 40 large T-antigen G-quadruplex DNA helicase inhibition by G-quadruplex DNA-interactive agents. Biochemistry 47(7):1896–1909. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi701747d
V’Kovski P, Kratzel A, Steiner S, Stalder H, Thiel V (2021) Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Rev Microbiol 19(3):155–170. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6
Wang M, Cao R, Zhang L et al (2020) Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res 30(3):269–271. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
Wu J, Yuan X, Wang B et al (2020) Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2: from gene structure to pathogenic mechanisms and potential therapy. Front Microbiol 11(1576):1576. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01576
**e X, Muruato A, Lokugamage KG et al (2020a) An infectious cDNA clone of SARS-CoV-2. Cell Host Microbe 27(5):841-848.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2020.04.004
**e X, Muruato AE, Zhang X et al (2020b) A nanoluciferase SARS-CoV-2 for rapid neutralization testing and screening of anti-infective drugs for COVID-19. Nat Commun 11(1):5214. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19055-7
Xu S, Li Q, **ang J et al (2016) Thioflavin T as an efficient fluorescence sensor for selective recognition of RNA G-quadruplexes. Sci Rep 6(1):24793. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24793
Zhao C, Qin G, Niu J et al (2021) Targeting RNA G-quadruplex in SARS-CoV-2: a promising therapeutic target for COVID-19? Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 60(1):432–438. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202011419
Zhou Y, Hou Y, Shen J, Huang Y, Martin W, Cheng F (2020) Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2. Cell Discov 6(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41421-020-0153-3
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Pei-Yong Shi (University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX) for providing the recombinant SARS-CoV-2-Nluc and -mNG viruses. This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program (2021M3A9I2080487 and 2021M3A9I2080488), and the Basic Research Laboratory Program (2020R1A4A1018019) of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT). It was also supported by NRF (2021R1A2C3011644 and 2020R1A2C2013827).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12272_2023_1458_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 3375 kb)—Supplementary information accompanies the manuscript on the Archives of Pharmacal Research (https://www.springer.com/journal/12272)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Razzaq, M., Han, J.H., Ravichandran, S. et al. Stabilization of RNA G-quadruplexes in the SARS-CoV-2 genome inhibits viral infection via translational suppression. Arch. Pharm. Res. 46, 598–615 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01458-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01458-x