Abstract
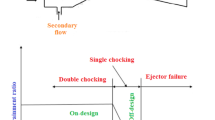
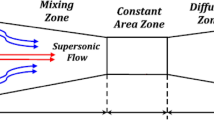
A numerical simulation of the internal flow structure of a steam ejector is conducted in a jet refrigeration system. The previous studies widely used traditional performance curves for assessment of ejector performance. However, a critical performance curve which is obtained by connecting each critical point at various generator temperatures has been rarely studied. In this paper, we design a range of primary nozzles with same or different area ratio by varying the nozzle’s throat and exit diameters, and the impact of nozzle geometries on the critical performance curve is mainly explored. Moreover, we proposed a linear fractional fitting function of generator temperature to predict the critical entrainment ratio and compression ratio for different nozzles. It is found that the nozzle throat diameter is a key parameter affecting the ejector performance and shock wave structure, and the hot source may provide some guidance for the adjustment of nozzle size.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a, b, c :
-
Coefficients
- A :
-
Cross sectional area
- c cr :
-
Critical sound velocity
- c 1, c 2, c 3 :
-
Coefficients
- COP :
-
Coefficient of performance
- CR :
-
Compression ratio
- D :
-
Diameter
- k :
-
Specific heat ratio
- m :
-
Mass flow rate
- Ma :
-
Mach number
- NPX :
-
Nozzle exit position
- P :
-
Pressure
- R :
-
Gas constant
- Rm :
-
Entrainment ratio
- T :
-
Temperature
- V :
-
Velocity
- β :
-
Momentum correction coefficient
- λ :
-
Velocity coefficient
- δ :
-
Flow turning angle at the primary nozzle exit
- c :
-
Condenser
- cr :
-
Critical
- e :
-
Exit
- evap :
-
Evaporator
- gen :
-
Generator
- m :
-
The mixing fluid
- p :
-
The primary fluid
- s :
-
The secondary fluid
- t :
-
Throat
- w :
-
Wall
References
X. Guo, Z. Jiang, X. Chen and T. Wang, Experimental investigation on aerodynamic performance of hypersonic wind tunnel two-stage ejector, Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 32(4) (2018) 99–103.
J. Chen, S. Jarall, H. Havtun and B. Palm, A review on versatile ejector applications in refrigeration systems, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 49 (2015) 67–90.
J. Dong, W. Wang, Z. Han, H. Ma, Y. Deng, F. Su and X. Pan, Experimental investigation of the steam ejector in a single-effect thermal vapor compression desalination system driven by a low-temperature heat source, Energies, 11 (9) (2018).
G. Singhal, Mainuddin, R. K. Tyagi, A. L. Dawar and P. M. V. Subbarao, Pressure recovery studies on a supersonic COIL with central ejector configuration, Optics and Laser Technology, 42(7) (2010) 1145–1153.
J. H. Keenan and E. P. Neumann, A simple air ejector, ASME Journal of Applied Mechanics, 64 (1942) 75–81.
I. W. Eames, S. Aphornratana and H. Haider, A theoretical and experimental-study of a small-scale steam jet refrigerator, International Journal of Refrigeration-Revue Internationale Du Froid, 18(6) (1995) 378–386.
B. J. Huang, J. M. Chang, C. P. Wang and V. A. Petrenko, A 1-D analysis of ejector performance, International Journal of Refrigeration-Revue Internationale Du Froid, 22(5) (1999) 354–364.
T. Sriveerakul, S. Aphornratana and K. Chunnanond, Performance prediction of steam ejector using computational fluid dynamics: part 1, validation of the CFD results, International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 46(8) (2007) 812–822.
S. Varga, A. C. Oliveira and B. Diaconu, Numerical assessment of steam ejector efficiencies using CFD, International Journal of Refrigeration-Revue Internationale Du Froid, 32(6) (2009) 1203–1211.
S. H. Kang, J. G. Kim and H.-J. Namkoung, Effects of component geometries and inflow conditions on ejector operational mode, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 33(10) (2019) 5003–5008.
S. Baek and S. Song, Numerical study for the design optimization of a two-phase ejector with R134a refrigerant, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 32(9) (2018) 4231–4236.
T. Thongtip and S. Aphornratana, An experimental analysis of the impact of primary nozzle geometries on the ejector performance used in R141b ejector refrigerator, Applied Thermal Engineering, 110 (2017) 89–101.
R. Yapici, Experimental investigation of performance of vapor ejector refrigeration system using refrigerant R123, Energy Conversion and Management, 49(5) (2008) 953–961.
K. O. Shestopalov, B. J. Huang, V. O. Petrenko and O. S. Volovyk, Investigation of an experimental ejector refrigeration machine operating with refrigerant R245fa at design and offdesign working conditions, part 1, theoretical analysis, International Journal of Refrigeration-Revue Internationale Du Froid, 55 (201) 201–211.
Y. H. Zhu, W. J. Cai, C. Y. Wen and Y. Z. Li, Numerical investigation of geometry parameters for design of high performance ejectors, Applied Thermal Engineering, 29(5–6) (2009) 898–905.
W. X. Chen, D. T. Chong, J. J. Yan and J. P. Liu, The numerical analysis of the effect of geometrical factors on natural gas ejector performance, Applied Thermal Engineering, 59(1–2) (2013) 21–29.
Y. Zhang, J. Zhao, Z. Liu, P. Zuo and A. R. Kwabena, Numerical simulation and parameter study of ejector in casing gas recovery system, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 35(6) (2021) 2689–2696.
R.X. Li, J. Yan and C. Reddick, Optimization of three key ejector geometries under fixed and varied operating conditions: a numerical study, Applied Thermal Engineering, 211 (2022).
N. Ruangtrakoon, S. Aphornratana and T. Sriveerakul, Experimental studies of a steam jet refrigeration cycle: Effect of the primary nozzle geometries to system performance, Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 35(4) (2011) 676–683.
N. Ruangtrakoon, T. Thongtip, S. Aphornratana and T. Sriveerakul, CFD simulation on the effect of primary nozzle geometries for a steam ejector in refrigeration cycle, International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 63 (2013) 133–145.
W. N. Fu, Z. L. Liu, Y. X. Li, H. Q. Wu and Y. Z. Tang, Numerical study for the influences of primary steam nozzle distance and mixing chamber throat diameter on steam ejector performance, International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 132 (2018) 509–516.
M. Falsafioon, Z. Aidoun and K. Ameur, Numerical investigation on the effects of internal flow structure on ejector performance, Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics, 12(6) (2019) 2003–2015.
B. Elhub, S. Mat, K. Sopian, A. M. Elbreki, M. H. Raslan and A. A. Ammar, Performance evaluation and parametric studies on variable nozzle ejector using R134A, Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 12 (2018) 258–270.
H. Wang, W. J. Cai, Y. Y. Wang, J. Yan and L. Wang, Experimental study of the behavior of a hybrid ejector-based air-conditioning system with R134a, Energy Conversion and Management, 112 (2016) 31–40.
N. Sharifi and M. Sharifi, Reducing energy consumption of a steam ejector through experimental optimization of the nozzle geometry, Energy, 66 (2014) 860–867.
I. W. Eames, A. E. Ablwaifa and V. Petrenko, Results of an experimental study of an advanced jet-pump refrigerator operating with R245fa, Applied Thermal Engineering, 27(17–18) (2007) 2833–2840.
A. Hakkaki-Fard, Z. Aidoun and M. Ouzzane, A computational methodology for ejector design and performance maximisation, Energy Conversion and Management, 105 (2015) 1291–1302.
T. Sriveerakul, S. Aphornratana and K. Chunnanond, Performance prediction of steam ejector using computational fluid dynamics: part 2, flow structure of a steam ejector influenced by operating pressures and geometries, International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 46(8) (2007) 823–833.
S. Croquer, S. Poncet and Z. Aidoun, Turbulence modeling of a single-phase R134a supersonic ejector, part 1: numerical benchmark, International Journal of Refrigeration-Revue Internationale Du Froid, 61 (2016) 140–152.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Research Program supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 12102331 and 51790512).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhu Huang is an Associate Professor of the Department of Fluid Machinery and Engineering, **’an Jiaotong University, **’an, China. He received his Ph.D. in Fluid Machinery and Engineering from **’an Jiaotong University. His research interests include turbulence modeling, uncertainty quantification and machine learning in CFD, spectral methods and high order shock capturing schemes, hydrodynamics stability, transition to turbulence.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, A., Chen, J., **, G. et al. Numerical investigation of the effect of primary nozzle geometries on flow structure and ejector performance for optimal design. J Mech Sci Technol 37, 2139–2148 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-023-2101-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-023-2101-2