Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the risk of acquiring COVID-19 infection in patients who have undergone adeno-tonsillectomy (AT) as compared to their siblings.
Methods
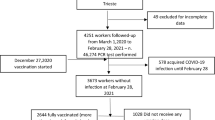
In this bidirectional cohort control study, 36 cohorts, younger than 18 y, who underwent AT, and 27 controls (siblings of the enrolled cohorts, younger than 18 y) were recruited. Incidence of COVID-19 was analyzed by symptoms suggestive of COVID-19 infection, COVID-19 testing, and SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody measurement.
Results
In the cohort group, the overall COVID-19 positivity rate was 80.5% (n = 29/36) and symptomatic COVID-19 positivity rate was 68.9% (n = 20/29). Among the controls, the overall COVID-19 positivity rate was 44% (n = 12/27) and symptomatic COVID-19 positivity rate was 16% (n = 2/12). The cohorts had 1.8 times higher risk of contracting COVID-19 infection and the relative risk of symptomatic COVID-19 infections as compared to controls was 4.14.
Conclusions
This pilot study indicates that adeno-tonsillectomy poses children at a significantly higher risk of COVID-19 infections and likely other viral upper respiratory tract infections.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi HG, Park B, Sim S, Ahn S-H. Tonsillectomy does not reduce upper respiratory infections: a national cohort study. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0169264.
Afzal A. Molecular diagnostic technologies for COVID-19: limitations and challenges. J Adv Res. 2020;26:149–59.
Yavuz S, Kesici S, Bayrakci B. Physiological advantages of children against COVID-19. Acta Paediatr. 2020;109:1691.
Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India. Guidelines for Management of COVID-19 in Children (below 18 years), June 2022. Available at: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/. Accessed on Jan 2023.
Lauer SA, Grantz KH, Bi Q, et al. The incubation period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly reported confirmed cases: estimation and application. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172:577–82.
Letko M, Marzi A, Munster V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-COV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat Microbiol. 2020;5:562–9.
Scadding GK. Immunology of the tonsil: a review. J R Soc Med. 1990;83:104–7.
Mateus J, Grifoni A, Tarke A, et al. Selective and cross-reactive SARS-COV-2 T cell epitopes in unexposed humans. Science. 2020;370:89–94.
Grifoni A, Weiskopf D, Ramirez SI, et al. Targets of T cell responses to SARS-COV-2 coronavirus in humans with COVID-19 disease and unexposed individuals. Cell. 2020;181:1489-501.e15.
Sahi PK, Jhamb U, Dabas A. Pediatric coronavirus disease 2019: clinical features and management. Indian Pediatr. 2021;58:453–60.
Xu Q, Milanez-Almeida P, Martins AJ, et al. Robust, persistent adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 in the oropharyngeal lymphoid tissue of children. Preprint. Res Sq. 2022;rs.3.rs-1276578. Published 2022 Mar 23.
Niessl J, Sekine T, Lange J, et al. Identification of resident memory CD8+ T cells with functional specificity for SARS-COV-2 in unexposed oropharyngeal lymphoid tissue. Sci Immunol. 2021;6:eabk0894.
Byars SG, Stearns SC, Boomsma JJ. Association of long-term risk of respiratory, allergic, and infectious diseases with removal of adenoids and tonsils in childhood. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;144:594–603.
Semih, Doblan A. History of tonsillectomy is associated with a relatively higher risk of symptomatic disease in patients with COVID-19. Am J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;4:Article 1138.
Brodin P. Why is COVID-19 so mild in children? Acta Paediatr. 2020;109:1082–3.
Senthilkumaran S, Meenakshisundaram R, Shah S, Thirumalaikolundusubramanian P. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in children: Indian perspectives. Indian Pediatr. 2020;57:585–6.
Alfego D, Sullivan A, Poirier B, Williams J, Adcock D, Letovsky S. A population-based analysis of the longevity of SARS-COV-2 antibody seropositivity in the United States. EClinicalMedicine. 2021;36:100902.
Funding
In this research project, the antibody testing kits were procured using the financial grant from Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) with reference number MD20DEC-0734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RM: Data collection, fund acquisition and manuscript drafting; PS: Conceptualization, data collection and manuscript drafting; RajeevK, PKC, CAS, RakeshK: Data collection and manuscript drafting; SKK, AT: Conceptualization and manuscript drafting; MAK: Statistical analysis and manuscript drafting. PS will act as guarantor for this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Murugesan, R., Sagar, P., Kumar, R. et al. Long Term Impact of Adeno-tonsillectomy on Immunity Against Respiratory Viral Infections; Evidence Deduced During COVID-19 Pandemic. Indian J Pediatr (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-024-05125-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-024-05125-x