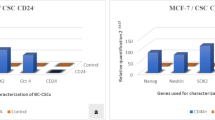
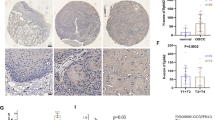
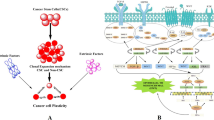
Abstract
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a group of tumor cells with high tumorigenic ability and self-renewal potential similar to those of normal stem cells. CSCs are the key “seeds” for tumor development, metastasis, and recurrence. A better insight into the key mechanisms underlying CSC survival improves the efficiency of cancer therapy via specific targeting of CSCs. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)/IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) signaling plays an important role in the maintenance of cancer stemness. However, the effect of IGF/IGF-1R signaling on stemness and CSCs and the underlying mechanisms are still controversial. Based on the similarity between CSCs and normal stem cells, this review discusses emerging data on the functions of IGF/IGF-1R signaling in normal stem cells and CSCs and dissects the underlying mechanisms by which IGF/IGF-1R signaling is involved in CSCs. On the other hand, this review highlighted the role of IGF/IGF-1R signaling blockade in multiple CSCs as a potential strategy to improve CSC-based therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Saygin C, Matei D, Majeti R, Reizes O, Lathia JD. Targeting cancer stemness in the clinic: from hype to hope. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;24(1):25–40.
Lytle NK, Barber AG, Reya T. Stem cell fate in cancer growth, progression and therapy resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(11):669–80.
Nassar D, Blanpain C. Cancer stem cells: basic concepts and therapeutic implications. Annu Rev Pathol. 2016;11:47–76.
Yang L, Shi P, Zhao G, Xu J, Peng W, Zhang J, Zhang G, Wang X, Dong Z, Chen F, et al. Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):8.
Batlle E, Clevers H. Cancer stem cells revisited. Nat Med. 2017;23(10):1124–34.
Hua H, Kong Q, Yin J, Zhang J, Jiang Y. Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in tumorigenesis and drug resistance: a challenge for cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):64.
Cao D, Lei Y, Ye Z, Zhao L, Wang H, Zhang J, He F, Huang L, Shi D, Liu Q, et al. Blockade of IGF/IGF-1R signaling axis with soluble IGF-1R mutants suppresses the cell proliferation and tumor growth of human osteosarcoma. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10(10):3248–66.
Lero MW, Shaw LM. Diversity of insulin and IGF signaling in breast cancer: implications for therapy. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;527:111213.
Lin SL, Lin CY, Lee W, Teng CF, Shyu WC, Jeng LB. Mini review: molecular interpretation of the IGF/IGF-1R axis in cancer treatment and stem cells-based therapy in regenerative medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):11781.
Weroha SJ, Haluska P. The insulin-like growth factor system in cancer. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2012;41(2):335–50.
Mancarella C, Morrione A, Scotlandi K. Novel regulators of the IGF system in cancer. Biomolecules. 2021;11(2):273.
Ziegler AN, Levison SW, Wood TL. Insulin and IGF receptor signalling in neural-stem-cell homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015;11(3):161–70.
Takahashi SI. IGF research 2016–2018. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2019;48–49:65–9.
Kolb H, Kempf K, Rohling M, Martin S. Insulin: too much of a good thing is bad. BMC Med. 2020;18(1):224.
Vigneri R, Sciacca L, Vigneri P. Rethinking the relationship between insulin and cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020;31(8):551–60.
Clemmons DR. Modifying IGF1 activity: an approach to treat endocrine disorders, atherosclerosis and cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6(10):821–33.
Junnila RK, List EO, Berryman DE, Murrey JW, Kopchick JJ. The GH/IGF-1 axis in ageing and longevity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013;9(6):366–76.
Nordin M, Bergman D, Halje M, Engstrom W, Ward A. Epigenetic regulation of the Igf2/H19 gene cluster. Cell Prolif. 2014;47(3):189–99.
Selenou C, Brioude F, Giabicani E, Sobrier ML, Netchine I. IGF2: development, genetic and epigenetic abnormalities. Cells. 2022;11(12):1886.
DeChiara TM, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Parental imprinting of the mouse insulin-like growth factor II gene. Cell. 1991;64(4):849–59.
Ma L, Zhao W, Huang S, Xu F, Wang Y, Deng D, Zhang T, Shu S, Chen X. IGF/IGF-1R signal pathway in pain: a promising therapeutic target. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(11):3472–82.
Bach LA. IGF-binding proteins. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018;61(1):T11–28.
Forbes BE, Blyth AJ, Wit JM. Disorders of IGFs and IGF-1R signaling pathways. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020;518: 111035.
Miller BS, Rogol AD, Rosenfeld RG. The history of the insulin-like growth factor system. Horm Res Paediatr. 2022;95(6):619–30.
LeRoith D, Holly JMP, Forbes BE. Insulin-like growth factors: ligands, binding proteins, and receptors. Mol Metab. 2021;52:101245.
Wamaitha SE, Grybel KJ, Alanis-Lobato G, Gerri C, Ogushi S, McCarthy A, Mahadevaiah SK, Healy L, Lea RA, Molina-Arcas M, et al. IGF1-mediated human embryonic stem cell self-renewal recapitulates the embryonic niche. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):764.
Magner NL, Jung Y, Wu J, Nolta JA, Zern MA, Zhou P. Insulin and IGFs enhance hepatocyte differentiation from human embryonic stem cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Stem Cells. 2013;31(10):2095–103.
Young K, Eudy E, Bell R, Loberg MA, Stearns T, Sharma D, Velten L, Haas S, Filippi MD, Trowbridge JJ. Decline in IGF1 in the bone marrow microenvironment initiates hematopoietic stem cell aging. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28(8):1473-1482 e1477.
Cheng CW, Adams GB, Perin L, Wei M, Zhou X, Lam BS, Da Sacco S, Mirisola M, Quinn DI, Dorff TB, et al. Prolonged fasting reduces IGF-1/PKA to promote hematopoietic-stem-cell-based regeneration and reverse immunosuppression. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14(6):810–23.
Kuo YC, Au HK, Hsu JL, Wang HF, Lee CJ, Peng SW, Lai SC, Wu YC, Ho HN, Huang YH. IGF-1R Promotes symmetric self-renewal and migration of alkaline phosphatase(+) germ stem cells through HIF-2alpha-OCT4/CXCR4 loop under hypoxia. Stem Cell Rep. 2018;10(2):524–37.
Zheng Y, Song Y, Han Q, Liu W, Xu J, Yu Z, Zhang R, Li N. Intestinal epithelial cell-specific IGF1 promotes the expansion of intestinal stem cells during epithelial regeneration and functions on the intestinal immune homeostasis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018;315(4):E638–49.
Deng M, Guerrero-Juarez CF, Sheng X, Xu J, Wu X, Yao K, Li M, Yang X, Li G, **ao J, et al. Lepr(+) mesenchymal cells sense diet to modulate intestinal stem/progenitor cells via Leptin-Igf1 axis. Cell Res. 2022;32(7):670–86.
Zheng Y, Luo L, Lambertz IU, Conti CJ, Fuchs-Young R. Early dietary exposures epigenetically program mammary cancer susceptibility through Igf1-mediated expansion of the mammary stem cell compartment. Cells. 2022;11(16):2258.
Arsenijevic Y, Weiss S, Schneider B, Aebischer P. Insulin-like growth factor-I is necessary for neural stem cell proliferation and demonstrates distinct actions of epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2. J Neurosci. 2001;21(18):7194–202.
Kharat A, Chandravanshi B, Gadre S, Patil V, Bhonde R, Dubhashi A. IGF-1 and somatocrinin trigger islet differentiation in human amniotic membrane derived mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2019;216:287–94.
An C, Cheng Y, Yuan Q, Li J. IGF-1 and BMP-2 induces differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes-like cells. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38(4):1647–54.
Zhang X, Zhang L, Cheng X, Guo Y, Sun X, Chen G, Li H, Li P, Lu X, Tian M, et al. IGF-1 promotes Brn-4 expression and neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(12):e113801.
Zhao L, Feng Y, Chen X, Yuan J, Liu X, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Liu P, Li Y. Effects of IGF-1 on neural differentiation of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2016;151:93–101.
Huang B, Ning S, Zhang Q, Chen A, Jiang C, Cui Y, Hu J, Li H, Fan G, Qin L, et al. Bisphenol a represses dopaminergic neuron differentiation from human embryonic stem cells through downregulating the expression of insulin-like growth factor 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(5):3798–812.
Li J, Zhu K, Wang Y, Zheng J, Guo C, Lai H, Wang C. Combination of IGF-1 gene manipulation and 5-AZA treatment promotes differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(2):815–20.
Muguruma Y, Reyes M, Nakamura Y, Sato T, Matsuzawa H, Miyatake H, Akatsuka A, Itoh J, Yahata T, Ando K, et al. In vivo and in vitro differentiation of myocytes from human bone marrow-derived multipotent progenitor cells. Exp Hematol. 2003;31(12):1323–30.
Bartunek J, Croissant JD, Wijns W, Gofflot S, de Lavareille A, Vanderheyden M, Kaluzhny Y, Mazouz N, Willemsen P, Penicka M, et al. Pretreatment of adult bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with cardiomyogenic growth factors and repair of the chronically infarcted myocardium. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292(2):H1095-1104.
Huang YL, Qiu RF, Mai WY, Kuang J, Cai XY, Dong YG, Hu YZ, Song YB, Cai AP, Jiang ZG. Effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 on the properties of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2012;13(1):20–8.
Chen RL, Kassem NA, Sadeghi M, Preston JE. Insulin-like growth factor-II uptake into choroid plexus and brain of young and old sheep. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2008;63(2):141–8.
DeChiara TM, Efstratiadis A, Robertson EJ. A growth-deficiency phenotype in heterozygous mice carrying an insulin-like growth factor II gene disrupted by targeting. Nature. 1990;345(6270):78–80.
Bendall SC, Stewart MH, Menendez P, George D, Vijayaragavan K, Werbowetski-Ogilvie T, Ramos-Mejia V, Rouleau A, Yang J, Bosse M, et al. IGF and FGF cooperatively establish the regulatory stem cell niche of pluripotent human cells in vitro. Nature. 2007;448(7157):1015–21.
Montes R, Ligero G, Sanchez L, Catalina P, de la Cueva T, Nieto A, Melen GJ, Rubio R, Garcia-Castro J, Bueno C, et al. Feeder-free maintenance of hESCs in mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned media: distinct requirements for TGF-beta and IGF-II. Cell Res. 2009;19(6):698–709.
Ziegler AN, Schneider JS, Qin M, Tyler WA, Pintar JE, Fraidenraich D, Wood TL, Levison SW. IGF-II promotes stemness of neural restricted precursors. Stem Cells. 2012;30(6):1265–76.
Ziegler AN, Chidambaram S, Forbes BE, Wood TL, Levison SW. Insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) and IGF-II analogs with enhanced insulin receptor-a binding affinity promote neural stem cell expansion. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(8):4626–33.
Ziegler AN, Feng Q, Chidambaram S, Testai JM, Kumari E, Rothbard DE, Constancia M, Sandovici I, Cominski T, Pang K, et al. Insulin-like growth factor II: an essential adult stem cell niche constituent in brain and intestine. Stem Cell Rep. 2019;12(4):816–30.
Li J, Li R, Jiang W, Sun J, Li J, Guo Y, Zhu K, Zhang C, Kong G, Li Z. Splenic serum from portal hypertensive patients enhances liver stem cell proliferation and self-renewal via the IGF-II/ERK signaling pathway. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52(2):205–13.
Sui Y, Zhang W, Tang T, Gao L, Cao T, Zhu H, You Q, Yu B, Yang T. Insulin-like growth factor-II overexpression accelerates parthenogenetic stem cell differentiation into cardiomyocytes and improves cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):86.
Lozano-Urena A, Lazaro-Carot L, Jimenez-Villalba E, Montalban-Loro R, Mateos-White I, Duart-Abadia P, Martinez-Gurrea I, Nakayama KI, Farinas I, Kirstein M, et al. IGF2 interacts with the imprinted gene Cdkn1c to promote terminal differentiation of neural stem cells. Development. 2023;150(1):200563.
Venkatraman A, He XC, Thorvaldsen JL, Sugimura R, Perry JM, Tao F, Zhao M, Christenson MK, Sanchez R, Yu JY, et al. Maternal imprinting at the H19-Igf2 locus maintains adult haematopoietic stem cell quiescence. Nature. 2013;500(7462):345–9.
Barroca V, Lewandowski D, Jaracz-Ros A, Hardouin SN. Paternal insulin-like growth factor 2 (Igf2) regulates stem cell activity during adulthood. EBioMedicine. 2017;15:150–62.
Wang L, Schulz TC, Sherrer ES, Dauphin DS, Shin S, Nelson AM, Ware CB, Zhan M, Song CZ, Chen X, et al. Self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells requires insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and ERBB2 receptor signaling. Blood. 2007;110(12):4111–9.
Ungewitter E, Scrable H. Delta40p53 controls the switch from pluripotency to differentiation by regulating IGF signaling in ESCs. Genes Dev. 2010;24(21):2408–19.
Cheng CL, Yang SC, Lai CY, Wang CK, Chang CF, Lin CY, Chen WJ, Lin PY, Wu HC, Ma N, et al. CXCL14 maintains hESC self-renewal through binding to IGF-1R and activation of the IGF-1R pathway. Cells. 2020;9(7):1706.
Baxter RC. IGF binding proteins in cancer: mechanistic and clinical insights. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14(5):329–41.
Huynh H, Zheng J, Umikawa M, Zhang C, Silvany R, Iizuka S, Holzenberger M, Zhang W, Zhang CC. IGF binding protein 2 supports the survival and cycling of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2011;118(12):3236–43.
Zhang CC, Kaba M, Iizuka S, Huynh H, Lodish HF. Angiopoietin-like 5 and IGFBP2 stimulate ex vivo expansion of human cord blood hematopoietic stem cells as assayed by NOD/SCID transplantation. Blood. 2008;111(7):3415–23.
Wang Y, Liu Y, Fan Z, Liu D, Wang F, Zhou Y. IGFBP2 enhances adipogenic differentiation potentials of mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord via JNK and Akt signaling pathways. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(8):e0184182.
Kalluri HS, Dempsey RJ. IGFBP-3 inhibits the proliferation of neural progenitor cells. Neurochem Res. 2011;36(3):406–11.
Chang KH, Chan-Ling T, McFarland EL, Afzal A, Pan H, Baxter LC, Shaw LC, Caballero S, Sengupta N, Li Calzi S, et al. IGF binding protein-3 regulates hematopoietic stem cell and endothelial precursor cell function during vascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(25):10595–600.
Kim JH, Yoon SM, Song SU, Park SG, Kim WS, Park IG, Lee J, Sung JH. Hypoxia suppresses spontaneous mineralization and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via IGFBP3 up-regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(9):1389.
D’Addio F, La Rosa S, Maestroni A, Jung P, Orsenigo E, Ben Nasr M, Tezza S, Bassi R, Finzi G, Marando A, et al. Circulating IGF-I and IGFBP3 levels control human colonic stem cell function and are disrupted in diabetic enteropathy. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17(4):486–98.
Vassilieva I, Kosheverova V, Vitte M, Kamentseva R, Shatrova A, Tsupkina N, Skvortsova E, Borodkina A, Tolkunova E, Nikolsky N, et al. Paracrine senescence of human endometrial mesenchymal stem cells: a role for the insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(2):1987–2004.
Minato A, Ise H, Goto M, Akaike T. Cardiac differentiation of embryonic stem cells by substrate immobilization of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 4 with elastin-like polypeptides. Biomaterials. 2012;33(2):515–23.
Xue Y, Yan Y, Gong H, Fang B, Zhou Y, Ding Z, Yin P, Zhang G, Ye Y, Yang C, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 4 enhances cardiomyocytes induction in murine-induced pluripotent stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(9):1495–504.
Severino V, Alessio N, Farina A, Sandomenico A, Cipollaro M, Peluso G, Galderisi U, Chambery A. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 4 and 7 released by senescent cells promote premature senescence in mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4(11):e911.
Han N, Zhang F, Li G, Zhang X, Lin X, Yang H, Wang L, Cao Y, Du J, Fan Z. Local application of IGFBP5 protein enhanced periodontal tissue regeneration via increasing the migration, cell proliferation and osteo/dentinogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in an inflammatory niche. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):210.
Wang Y, Jia Z, Diao S, Lin X, Lian X, Wang L, Dong R, Liu D, Fan Z. IGFBP5 enhances osteogenic differentiation potential of periodontal ligament stem cells and Wharton’s jelly umbilical cord stem cells, via the JNK and MEK/Erk signalling pathways. Cell Prolif. 2016;49(5):618–27.
Li L, Wang H, Yu D, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Yang H, Cao Y, Cao Y. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 accelerate the senescence of periodontal ligament stem cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2023;24(1):231–9.
Aboalola D, Han VKM. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 promotes the differentiation of placental mesenchymal stem cells into skeletal muscle independent of insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 and insulin receptor. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:9245938.
Jeon HJ, Park J, Shin JH, Chang MS. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 released from human mesenchymal stem cells confers neuronal protection through IGF-1R-mediated signaling. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):1860–8.
Infante A, Rodriguez CI. Secretome analysis of in vitro aged human mesenchymal stem cells reveals IGFBP7 as a putative factor for promoting osteogenesis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):4632.
Zhang W, Chen E, Chen M, Ye C, Qi Y, Ding Q, Li H, Xue D, Gao X, Pan Z. IGFBP7 regulates the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2018;32(4):2280–91.
Li N, Han J, Tang J, Ying Y. IGFBP-7 inhibits the differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells via regulation of Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(6):4742–50.
Li X, Feng L, Zhang C, Wang J, Wang S, Hu L. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 7 prevents dental pulp-derived mesenchymal stem cell senescence via metabolic downregulation of p21. Sci China Life Sci. 2022;65(11):2218–32.
Osuka S, Zhu D, Zhang Z, Li C, Stackhouse CT, Sampetrean O, Olson JJ, Gillespie GY, Saya H, Willey CD, et al. N-cadherin upregulation mediates adaptive radioresistance in glioblastoma. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(6):136098.
Ramakrishnan V, Xu B, Akers J, Nguyen T, Ma J, Dhawan S, Ning J, Mao Y, Hua W, Kokkoli E, et al. Radiation-induced extracellular vesicle (EV) release of miR-603 promotes IGF1-mediated stem cell state in glioblastomas. EBioMedicine. 2020;55:102736.
Bu Y, Jia QA, Ren ZG, Zhang JB, Jiang XM, Liang L, Xue TC, Zhang QB, Wang YH, Zhang L, et al. Maintenance of stemness in oxaliplatin-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with increased autocrine of IGF1. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(3):e89686.
Cao Z, Scandura JM, Inghirami GG, Shido K, Ding BS, Rafii S. Molecular checkpoint decisions made by subverted vascular niche transform indolent tumor cells into chemoresistant cancer stem cells. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(1):110–26.
Murakami A, Takahashi F, Nurwidya F, Kobayashi I, Minakata K, Hashimoto M, Nara T, Kato M, Tajima K, Shimada N, et al. Hypoxia increases gefitinib-resistant lung cancer stem cells through the activation of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(1):e86459.
Liu P, Zhang R, Yu W, Ye Y, Cheng Y, Han L, Dong L, Chen Y, Wei X, Yu J. FGF1 and IGF1-conditioned 3D culture system promoted the amplification and cancer stemness of lung cancer cells. Biomaterials. 2017;149:63–76.
Giambra V, Gusscott S, Gracias D, Song R, Lam SH, Panelli P, Tyshchenko K, Jenkins CE, Hoofd C, Lorzadeh A et al. (2018) Epigenetic Restoration of Fetal-like IGF1 Signaling Inhibits Leukemia Stem Cell Activity. Cell Stem Cell 23(5): 714–726717.
Kaneda A, Wang CJ, Cheong R, Timp W, Onyango P, Wen B, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Ohlsson R, Andraos R, Pearson MA, et al. Enhanced sensitivity to IGF-II signaling links loss of imprinting of IGF2 to increased cell proliferation and tumor risk. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(52):20926–31.
Gao T, Liu X, He B, Pan Y, Wang S. IGF2 loss of imprinting enhances colorectal cancer stem cells pluripotency by promoting tumor autophagy. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(21):21236–52.
Xu WW, Li B, Zhao JF, Yang JG, Li JQ, Tsao SW, He QY, Cheung ALM. IGF2 induces CD133 expression in esophageal cancer cells to promote cancer stemness. Cancer Lett. 2018;425:88–100.
Tominaga K, Shimamura T, Kimura N, Murayama T, Matsubara D, Kanauchi H, Niida A, Shimizu S, Nishioka K, Tsuji EI, et al. Addiction to the IGF2-ID1-IGF2 circuit for maintenance of the breast cancer stem-like cells. Oncogene. 2017;36(9):1276–86.
Vaquero J, Lobe C, Tahraoui S, Claperon A, Mergey M, Merabtene F, Wendum D, Coulouarn C, Housset C, Desbois-Mouthon C, et al. The IGF2/IR/IGF1R pathway in tumor cells and myofibroblasts mediates resistance to EGFR inhibition in cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(17):4282–96.
Murayama T, Nakaoku T, Enari M, Nishimura T, Tominaga K, Nakata A, Tojo A, Sugano S, Kohno T, Gotoh N. Oncogenic fusion gene CD74-NRG1 confers cancer stem cell-like properties in lung cancer through a IGF2 autocrine/paracrine circuit. Cancer Res. 2016;76(4):974–83.
Xu DD, Wang Y, Zhou PJ, Qin SR, Zhang R, Zhang Y, Xue X, Wang J, Wang X, Chen HC, et al. The IGF2/IGF1R/Nanog signaling pathway regulates the proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:687.
Shan J, Shen J, Liu L, **a F, Xu C, Duan G, Xu Y, Ma Q, Yang Z, Zhang Q, et al. Nanog regulates self-renewal of cancer stem cells through the insulin-like growth factor pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;56(3):1004–14.
Chen WJ, Ho CC, Chang YL, Chen HY, Lin CA, Ling TY, Yu SL, Yuan SS, Chen YJ, Lin CY, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts regulate the plasticity of lung cancer stemness via paracrine signalling. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3472.
Lv J, Liu C, Chen FK, Feng ZP, Jia L, Liu PJ, Yang ZX, Hou F, Deng ZY. M2-like tumour-associated macrophage-secreted IGF promotes thyroid cancer stemness and metastasis by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(2):604.
Li L, Li JC, Yang H, Zhang X, Liu LL, Li Y, Zeng TT, Zhu YH, Li XD, Li Y, et al. Expansion of cancer stem cell pool initiates lung cancer recurrence before angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(38):E8948–57.
Hsieh A, Ellsworth R, Hsieh D. Hedgehog/GLI1 regulates IGF dependent malignant behaviors in glioma stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(4):1118–27.
Ferreira Mendes JM, de Faro VL, Torres Andion Vidal M, Paredes BD, Coelho P, Allahdadi KJ, Coletta RD, Souza BSF, Rocha CAG: Effects of IGF-1 on proliferation, angiogenesis, tumor stem cell populations and activation of AKT and hedgehog pathways in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):6487.
Xu C, **e D, Yu SC, Yang XJ, He LR, Yang J, ** YF, Wang B, Yang L, Xu SL, et al. beta-Catenin/POU5F1/SOX2 transcription factor complex mediates IGF-I receptor signaling and predicts poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2013;73(10):3181–9.
Chan YT, Lin RJ, Wang YH, Hung TH, Huang Y, Yu J, Yu JC, Yu AL. The interplay between IGF-1R signaling and Hippo-YAP in breast cancer stem cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):81.
Lee JH, Choi SI, Kim RK, Cho EW, Kim IG. Tescalcin/c-Src/IGF1Rbeta-mediated STAT3 activation enhances cancer stemness and radioresistant properties through ALDH1. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):10711.
Bodzin AS, Wei Z, Hurtt R, Gu T, Doria C. Gefitinib resistance in HCC mahlavu cells: upregulation of CD133 expression, activation of IGF-1R signaling pathway, and enhancement of IGF-1R nuclear translocation. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(7):2947–52.
Verhagen H, van Gils N, Martianez T, van Rhenen A, Rutten A, Denkers F, de Leeuw DC, Smit MA, Tsui ML, de Vos Klootwijk LLE, et al. IGFBP7 induces differentiation and loss of survival of human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells without affecting normal hematopoiesis. Cell Rep. 2018;25(11):3021-3035 e3025.
van Gils N, Verhagen H, Rutten A, Menezes RX, Tsui ML, Vermue E, Dekens E, Brocco F, Denkers F, Kessler FL, et al. IGFBP7 activates retinoid acid-induced responses in acute myeloid leukemia stem and progenitor cells. Blood Adv. 2020;4(24):6368–83.
Chen X, Zheng J, Zou Y, Song C, Hu X, Zhang CC. IGF binding protein 2 is a cell-autonomous factor supporting survival and migration of acute leukemia cells. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6(1):72.
Hsieh D, Hsieh A, Stea B, Ellsworth R. IGFBP2 promotes glioma tumor stem cell expansion and survival. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;397(2):367–72.
Masuo K, Chen R, Yogo A, Sugiyama A, Fukuda A, Masui T, Uemoto S, Seno H, Takaishi S. SNAIL2 contributes to tumorigenicity and chemotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer by regulating IGFBP2. Cancer Sci. 2021;112(12):4987–99.
Lin W, Niu R, Park SM, Zou Y, Kim SS, **a X, **ng S, Yang Q, Sun X, Yuan Z, et al. IGFBP5 is an ROR1 ligand promoting glioblastoma invasion via ROR1/HER2-CREB signaling axis. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):1578.
Takada Y, Takada YK, Fujita M. Crosstalk between insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor and integrins through direct integrin binding to IGF1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017;34:67–72.
Meier C, Hardtstock P, Joost S, Alla V, Putzer BM. p73 and IGF1R regulate emergence of aggressive cancer stem-like features via miR-885-5p control. Cancer Res. 2016;76(2):197–205.
Leong HS, Chong FT, Sew PH, Lau DP, Wong BH, Teh BT, Tan DS, Iyer NG. Targeting cancer stem cell plasticity through modulation of epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(9):1055–65.
Dixit D, Prager BC, Gimple RC, Poh HX, Wang Y, Wu Q, Qiu Z, Kidwell RL, Kim LJY, **e Q, et al. The RNA m6A reader YTHDF2 maintains oncogene expression and is a targetable dependency in glioblastoma stem cells. Cancer Discov. 2021;11(2):480–99.
Guo Y, Mehrabi Nasab E, Hassanpour F, Athari SS. Linsitinib and aspirin as the IGF1-R antagonists, inhibit regorafenib-resistant chemotherapy in colon cancer. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022;29(2):872–7.
Hart LS, Dolloff NG, Dicker DT, Koumenis C, Christensen JG, Grimberg A, El-Deiry WS. Human colon cancer stem cells are enriched by insulin-like growth factor-1 and are sensitive to figitumumab. Cell Cycle. 2011;10(14):2331–8.
Chang WW, Lin RJ, Yu J, Chang WY, Fu CH, Lai A, Yu JC, Yu AL. The expression and significance of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and its pathway on breast cancer stem/progenitors. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(3):R39.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 82103662).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, L.F.C.; writing—original draft, L.F.C.; writing—review and editing, L.F.C; Y.S.S. and Z.L.; supervision, Y.S.S.; N.Q.H and Z.L., financial Acquisition, L.F.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Consent to publish
All authors agree to submit the manuscripts to the journal.
Ethical approval (Research involving human participants and/or animals)
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Ye, S., Zhao, L. et al. The role of IGF/IGF-1R signaling in the regulation of cancer stem cells. Clin Transl Oncol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-024-03561-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-024-03561-x