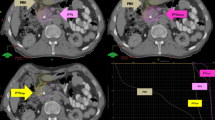
Abstract
Introduction
Surgery is the standard treatment for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNETs), obtaining favorable results but associating high morbidity and mortality rates. This study assesses stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) as a radical approach for small (< 2 cm) nonfunctioning pNETs.
Materials and methods
From January 2017 to June 2023, 20 patients with small pNETs underwent SBRT in an IRB-approved study. Endpoints included local control, tolerance, progression-free survival, and overall survival (OS). Diagnostic assessments comprised endoscopy, CT scans, OctreScan or PET-Dotatoc, abdominal MRI, and histological confirmatory samples.
Results
In a 30-month follow-up of 20 patients (median age 55.5 years), SBRT was well-tolerated with no grade > 2 toxicity. 40% showed morphological response, 55% remained stable. Metabolically, 50% achieved significant improvement. With a median OS of 41.5 months, all patients were alive without local or distant progression or need for surgical resection.
Conclusion
SBRT is a feasible and well-tolerated approach for small neuroendocrine pancreatic tumors, demonstrating effective local control. Further investigations are vital for validation and extension of these findings.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data will be available at a reasonable request.
References
Franko J, Feng W, Yip L, Genovese E, Moser AJ. Non-functional neuroendocrine carcinoma of the pancreas: incidence, tumor biology, and outcomes in 2,158 patients. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14(3):541–8.
Halfdanarson TR, Rabe KG, Rubin J, Petersen GM. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs): incidence, prognosis and recent trend toward improved survival. Ann Oncol. 2008;19(10):1727–33.
Hill JS, McPhee JT, McDade TP, Zhou Z, Sullivan ME, Whalen GF, et al. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: the impact of surgical resection on survival. Cancer. 2009;115(4):741–51.
Gratian L, Pura J, Dinan M, Roman S, Reed S, Sosa JA. Impact of extent of surgery on survival in patients with small nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in the United States. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(11):3515–21.
Zhou C, Zhang J, Zheng Y, Zhu Z. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a comprehensive review. Int J cancer. 2012;131(5):1013–22.
Falconi M, Bartsch DK, Eriksson B, Klöppel G, Lopes JM, O’Connor JM, et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the management of patients with digestive neuroendocrine neoplasms of the digestive system: well-differentiated pancreatic non-functioning tumors. Neuroendocrinology. 2012;95(2):120–34.
Bettini R, Partelli S, Boninsegna L, Capelli P, Crippa S, Pederzoli P, et al. Tumor size correlates with malignancy in nonfunctioning pancreatic endocrine tumor. Surgery. 2011;150(1):75–82.
Birnbaum DJ, Gaujoux S, Cherif R, Dokmak S, Fuks D, Couvelard A, et al. Sporadic nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: prognostic significance of incidental diagnosis. Surgery. 2014;155(1):13–21.
Haynes AB, Deshpande V, Ingkakul T, Vagefi PA, Szymonifka J, Thayer SP, et al. Implications of incidentally discovered, nonfunctioning pancreatic endocrine tumors: short-term and long-term patient outcomes. Arch Surg. 2011;146(5):534–8.
Kuo EJ, Salem RR. Population-level analysis of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors 2 cm or less in size. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(9):2815–21.
Cheema A, Weber J, Strosberg JR. Incidental detection of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: an analysis of incidence and outcomes. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19(9):2932–6.
Sadot E, Reidy-Lagunes DL, Tang LH, Do RKG, Gonen M, D’Angelica MI, et al. Observation versus resection for small asymptomatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a matched case-control study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23(4):1361–70.
Yang G, Ji M, Chen J, Chen R, Chen Y, Fu D, et al. Surgery management for sporadic small (≤2 cm), non-functioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a consensus statement by the Chinese Study Group for Neuroendocrine Tumors (CSNET). Int J Oncol. 2017;50(2):567–74.
Perri G, Prakash LR, Katz MHG. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2019;35(5):468–77.
Howe JR, Merchant NB, Conrad C, Keutgen XM, Hallet J, Drebin JA, et al. The North American Neuroendocrine Tumor Society consensus paper on the surgical management of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Pancreas. 2020;49(1):1–33.
Smith JK, Ng SC, Hill JS, Simons JP, Arous EJ, Shah SA, et al. Complications after pancreatectomy for neuroendocrine tumors: a national study. J Surg Res. 2010;163(1):63–8.
Gaujoux S, Partelli S, Maire F, D’Onofrio M, Larroque B, Tamburrino D, et al. Observational study of natural history of small sporadic nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(12):4784–9.
Lee LC, Grant CS, Salomao DR, Fletcher JG, Takahashi N, Fidler JL, et al. Small, nonfunctioning, asymptomatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs): role for nonoperative management. Surgery. 2012;152(6):965–74.
Strosberg J, Hoffe S, Gardner N, Choi J, Kvols L. Effective treatment of locally advanced endocrine tumors of the pancreas with chemoradiotherapy. Neuroendocrinology. 2007;85(4):216–20.
Tennvall J, Ljungberg O, Ahrén B, Gustavsson A, Nillson LO. Radiotherapy for unresectable endocrine pancreatic carcinomas. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1992;18(1):73–6.
Torrisi JR, Treat J, Zeman R, Dritschilo A. Radiotherapy in the management of pancreatic islet cell tumors. Cancer. 1987;60(6):1226–31.
Moore FT, Nadler H, Radefeld DA, Zollinger RM. Prolonged remission of diarrhea due to nonbeta islet cell tumor of the pancreas by radiotherapy. Am J Surg. 1968;115(6):854–5.
Iwata T, Ueno H, Itami J, Ito Y, Inaba K, Morizane C, et al. Efficacy of radiotherapy for primary tumor in patients with unresectable pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2017;47(9):826–31.
Mahadevan A, Miksad R, Goldstein M, Sullivan R, Bullock A, Buchbinder E, et al. Induction gemcitabine and stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced nonmetastatic pancreas cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(4):e615–22.
Koong AC, Le QT, Ho A, Fong B, Fisher G, Cho C, et al. Phase I study of stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;58(4):1017–21.
Chuong MD, Springett GM, Freilich JM, Park CK, Weber JM, Mellon EA, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer is effective and well tolerated. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;86(3):516–22.
Mellon EA, Hoffe SE, Springett GM, Frakes JM, Strom TJ, Hodul PJ, et al. Long-term outcomes of induction chemotherapy and neoadjuvant stereotactic body radiotherapy for borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2015;54(7):979–85.
Zhong J, Patel K, Switchenko J, Cassidy RJ, Hall WA, Gillespie T, et al. Outcomes for patients with locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy versus conventionally fractionated radiation. Cancer. 2017;123(18):3486–93.
Chen-Zhao X, Hernando O, López M, Sánchez E, Montero A, García-Aranda M, et al. A prospective observational study of the clinical and pathological impact of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) as a neoadjuvant strategy of chemoradiation in pancreatic cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020;22:1499–505.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval, Research involving human participants and/or animals and Informed consent
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Research Committee and with the Helsinkli Declaration and informed consent was obtained from all individuals participants included in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
López Gonzalez, M., Hernando-Requejo, O., Ciervide Jurío, R. et al. Prospective study on stereotactic body radiotherapy for small pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: tolerance and effectiveness analysis. Clin Transl Oncol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-024-03538-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-024-03538-w