Abstract
Introduction
Auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD) is a distinct type of SNHL that is characterized by the presence of otoacoustic emissions and/or cochlear microphonics. Cochlear implantation was initially not recommended for ANSD children, later studies showed variable outcomes among ANSD. CI is currently the intervention option of choice for many children with ANSD who are unable to obtain benefit from conventional amplification.
Aim and Objectives
To review experiences with some of the preoperative and postoperative findings in a child who was diagnosed with auditory neuropathy and provided with cochlear implant. To describe changes in auditory function, which enabled to have significant improvement in hearing and communication skills through auditory verbal therapy (AVT) and regular follow ups.
Study Design
Pre and postoperative, findings in cochlear implant recipient who was diagnosed with ANSD. Child received complete medical examinations, including related consultations in audiology, otorhinolaryngology, paediatrics, neurology, psychology, speech language pathology, and radiology.
Methodology/Case Report
A 3-year-old-female have brought to the hospital with a C/o not responding to sounds, name call and unable to speak. Medical and Audiological evaluations were initiated. The hearing assessments of the child included appropriate behavioural audiometric techniques, objective measures of middle ear function, acoustic reflex studies, transient evoked (TEOAE), distortion product (DPOAE) otoacoustic emissions and auditory brainstem responses (ABR). Implanted with (HiRes Ultra CI HiFocus SlimJ Electrode), and objective measures were recorded intraoperatively electrode impedances and neural response telemetry (NRT) to assess the outcomes technically. These intraoperative objective measures were used to help program the speech processor for the child. Postoperatively, child has had regular follow-up with otorhinolaryngologist to assure complete healing of the surgical incision, to assess their general medical conditions, and audiologist for switch-on (speech processor) followed by map**. The hearing and communication skills have been assessed, also continued Auditory Verbal Therapy (AVT) on a regular basis. Postoperatively, objective measures were recorded in regular intervals and monitored with therapy outcomes.
Results
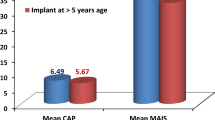
The child has shown significant improvement in sound detection, speech perception abilities, communication skills and shown evidence of progression of good NRT results, which were recorded and had no postoperative complications.
Conclusion
Experience with cochlear implantation for child diagnosed with ANSD that effectively received and benefited from CI. A detailed and careful evaluations, audiological follow-ups and tailored rehabilitation plans, can be considered as a beneficial management approach for CI, especially who diagnosed with ANSD. The regular use of cochlear implant in this diagnosis can lead to a clear increase in speech comprehension, development and overall progress in quality of life. Success or lack of success with a CI appears to be somewhat dependent on the specific site of lesion (pre- or post-synaptic). Currently there are no clinical measures available to diagnose the specific site of lesion. Indeed, CI appears to be an effective rehabilitation modality for ANSD patients. This may be explained by the fact that the implanted electrode delivers synchronized electrical impulses directly to the auditory nerve, bypassing the presynaptic IHCs and its synapse involved in the unsynchronized firing of the auditory nerve described in ANSD. However, genetic studies that have proven to be essential in the knowledge of underlying mechanisms of ANSD represent a promising therapeutic approach in the management of ANSD.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANSD:
-
Auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder
- SNHL:
-
Sensorineural hearing loss
- CI:
-
Cochlear implant
- TEOAE:
-
Transient evoked otoacoustic emissions
- DPOAE:
-
Distortion product otoacoustic emissions
- ABR:
-
Auditory brainstem response
- AABR:
-
Automated auditory brainstem response
- NRT:
-
Neural response telemetry
- AVT:
-
Auditory verbal therapy
- CM:
-
Cochlear microphonics
- HRCT:
-
High resolution computed tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- Modified CAP:
-
Modified categories of auditory perception
- SIR:
-
Speech intelligibility rating
- ISD:
-
Integrated scales of development
- IT-MAIS:
-
Infant–toddler meaningful auditory integration scale
References
Breneman AI, Gifford RH, DeJong MD (2012) Cochlear implantation in children with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder: long-term outcomes. J Am Acad Audiol 23(01):005–017
De Siati RD, Rosenzweig F, Gersdorff G, Gregoire A, Rombaux P, Deggouj N (2020) Auditory neuropathy spectrum disorders: from diagnosis to treatment: literature review and case reports. J Clin Med 9(4):1074
Di Bari M, Law-Ye B, Bernardeschi D, Lahlou G, Sterkers O, Colombo G, et al. (2023). Long-term clinical and radiological results for fat graft obliteration in subtotal petrosectomy and cochlear implant surgery: a retrospective clinical study. Eur Archiv Oto-Rhino-Laryngol, pp 1–10
Harrison RV, Gordon KA, Papsin BC, Negandhi J, James AL (2015) Auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD) and cochlear implantation. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 79(12):1980–1987
Jafari, Z. (2023). Predictors of cochlear implantation outcomes in children with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorders (Doctoral dissertation, Université d'Ottawa/University of Ottawa).
Keintzel T, Raffelsberger T, Niederwanger L, Gundacker G, Rasse T (2023) Systematic literature review and early benefit of cochlear implantation in two pediatric auditory neuropathy cases. J Personal Med 13(5):848
Kontorinis G, Lloyd SK, Henderson L, Jayewardene-Aston D, Milward K, Bruce IA, Freeman SR (2014) Cochlear implantation in children with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorders. Cochlear Implants Int 15(sup1):S51–S54
Kurt E, Akgül F (2023) Results of cochlear implant surgery in patients with auditory neuropathy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 165:111431
Ramanathan D, Mahomva C, Goldberg D, Liu YCC, Anne S, Lyle W (2023) Speech and language outcomes in auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD) children managed with amplification. Am J Otolaryngol 44(2):103753
Roush P, Frymark T, Venediktov R, Wang B (2011) Audiologic management of auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder in children: a systematic review of the literature.
Teagle HF, Roush PA, Woodard JS, Hatch DR, Zdanski CJ, Buss E, Buchman CA (2010) Cochlear implantation in children with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder. Ear Hear 31(3):325–335
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my sincere appreciation to all those who contributed to the completion of this study. I extend my heartfelt gratitude to Dr.SKE Apparao sir for unwavering guidance, invaluable insights. I would like to thank Department of Otorhinolaryngology, GVPIHC&MT for the support. Grateful for my Co-Authors Dr. Suryaprakasa Rao Sir, Dr. DRKLN Raju Sir and Vikas Sir whose contribution enriched this work and added depth to the findings. Last but not the least, I am forever grateful for the participant, your contribution and support have been invaluable in bringing this study to fruition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funds
No funds were obtained.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript and there is no financial interest to report. We certify that the submission is original work and is not under review at any other publication.
Ethics Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participant. The report compiles with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patient’s parent prior to the study (The identity of the patient is confidential and the operative pictures do not bear any identification marks).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Penumaka, M.S., Sreerama, S., Raju, D. et al. Outcomes of Cochlear Implant Recipient With ANSD: Intra and Post Operative Findings, Progress in Audition and Speech Skills. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 76, 2746–2754 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-04448-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-04448-z