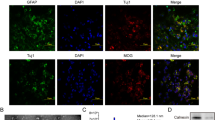
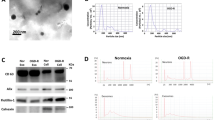
Abstract
Recent evidence suggests that hypoxia preconditioning can alter the microRNA (miRNA) profile of extracellular vesicles (EVs) and has better neuroprotective effects when enriched miRs are delivered to recipients. However, the roles of exosomal miRNAs in regulating ischaemia-reperfusion (IR)-induced pain hypersensitivity are largely unknown. Thus, we isolated EVs from normoxia-conditioned neurons (Nor-VSC EVs) and Hypo-VSC EVs by ultracentrifugation. After the initial screening by a microarray analysis and quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR), miR-126-3p, which was detected as the most altered miR in the Hypo-VSC EVs, was further confirmed by applying GW4869 to inhibit exosomal secretion. Moreover, transfection with a miR-126 mimic obviously increased miR-126-3p expression in Nor-VSC EVs, whereas a miR-126 inhibitor prevented the increase in miR-126-3p in Hypo-VSC EVs. A rat model of pain was established by performing 8-min occlusion of the aorta. Following IR, compared with the Nor-VSC EVs- or antagomir-126-injected rats, the Hypo-VSC EVs-injected rats displayed improved pain hypersensitivity demonstrated as higher PWT and PWL values. Mechanistically, PIK3R2 is a target of miR-126-3p and might be a modulator of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway as the PIK3R2 and PI3K immunoreactivities in each group were changed in opposite directions. Compared with the controls, higher protein levels of PI3K and phosphorylated Akt but lower levels of phosphorylated nuclear factor-κ B (NF-κB), tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-1β were detected in the spinal cords of the Hypo-VSC EVs-injected rats, and these effects were impaired by an injection of Hypo-VSC EVs combined with antagomir-126. Collectively, the miR-126-3p-enriched Hypo-VSC EVs attenuated IR-induced pain hypersensitivity by restoring miR-126-3p expression in the injured spinal cord and subsequently modulating PIK3R2-mediated PI3K/Akt and NF-κB signalling pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- antagomir-126:
-
miR-126 antagomir
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- FBS:
-
Foetal bovine serum
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- GM:
-
Golgi auto-antigen
- HBSS:
-
Hank’s balanced salt solution
- Hypo-VSC EVs:
-
Hypoxia-preconditioned neurons-derived extracellular vesicles
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IR:
-
Ischaemia-reperfusion
- miR:
-
microRNA
- MSC-Exos:
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes
- MT:
-
Mutant
- NTA:
-
Nanoparticle tracking analysis
- NC:
-
Negative control
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B
- Nor-VSC EVs:
-
Normoxia-conditioned neuron-derived extracellular vesicles
- OGD/R:
-
Oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion
- p-Akt:
-
Phosphorylation of Akt
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PIK3R2:
-
Phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- p-NF-κB:
-
Phosphorylated NF-κB
- t-Akt:
-
Total Akt
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- t-NF-κB:
-
Total NF-κB
References
Awad H, Ramadan ME, El Sayed HF, Tolpin DA, Tili E, Collard CD (2017) Spinal cord injury after thoracic endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. Can J Anaesth 64(12):1218–1235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12630-017-0974-1
Hu J, Yu Q, **e L, Zhu H (2016) Targeting the blood-spinal cord barrier: a therapeutic approach to spinal cord protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Life Sci 158:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.06.018
Yu Q, Huang J, Hu J, Zhu H (2016) Advance in spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury: blood-spinal cord barrier and remote ischemic preconditioning. Life Sci 154:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.03.046
Li XQ, Zhang ZL, Tan WF, Sun XJ, Ma H (2016) Down-regulation of CXCL12/CXCR4 expression alleviates ischemia- reperfusion- induced inflammatory pain via inhibiting glial TLR4 activation in the spinal cord. PLoS One 11(10):e0163807. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163807
Li XQ, Yu Q, Tan WF, Zhang ZL, Ma H (2018) MicroRNA-125b mimic inhibits ischemia reperfusion-induced neuroinflammation and aberrant p53apoptotic signalling activation through targeting TP53INP1. Brain Behav Immun 74:154–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2018.09.002
Werhagen L, Budh CN, Hultling C, Molander C (2004) Neuropathic pain after traumatic spinal cord injury--relations to gender, spinal level, completeness, and age at the time of injury. Spinal Cord 42(12):665–673. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101641
Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R et al (2018) Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles 7(1):1535750. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750
Jadli AS, Ballasy N, Edalat P, Patel VB (2020) Inside (sight) of tiny communicator: exosome biogenesis, secretion, and uptake. Mol Cell Biochem 467(1–2):77–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03703-z
McDonald MK, Tian Y, Qureshi RA, Gormley M, Ertel A, Gao R, Aradillas Lopez E, Alexander GM et al (2014) Functional significance of macrophage-derived exosomes in inflammation and pain. Pain 155(8):1527–1539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2014.04.029
Shiue SJ, Rau RH, Shiue HS, Hung YW, Li ZX, Yang KD, Cheng JK (2019) Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes as a cell-free therapy for nerve injury-induced pain in rats. Pain 160(1):210–223. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001395
Ren J, Liu N, Sun N, Zhang K, Yu L (2019) Mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes: promising therapeutics for chronic pain. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 14(8):644–653. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574888X14666190912162504
Li XQ, Yu Q, Zhang ZL, Sun XJ, Ma H (2019) MiR-187-3p mimic alleviates ischemia-reperfusion-induced pain hypersensitivity through inhibiting spinal P2X7R and subsequent mature IL-1ß release in mice. Brain Behav Immun 79:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.05.021
Xu J, Tang Y, **e M, Bie B, Wu J, Yang H, Foss JF, Yang B et al (2016) Activation of cannabinoid receptor 2 attenuates mechanical allodynia and neuroinflammatory responses in a chronic post-ischemic pain model of complex regional pain syndrome type I in rats. Eur J Neurosci 44(12):3046–3055. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13414
Chen O, Donnelly CR, Ji RR (2019) Regulation of pain by neuro-immune interactions between macrophages and nociceptor sensory neurons. Curr Opin Neurobiol 62:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2019.11.006
Lin Y, Chen Z, Tang J, Cao P, Shi R (2018) Acrolein contributes to the neuropathic pain and neuron damage after ischemic-reperfusion spinal cord injury. Neuroscience 384:120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.05.029
Dalbayrak S, Yaman O, Yilmaz T (2015) Current and future surgery strategies for spinal cord injuries. World J Orthop 6(1):34–41. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v6.i1.34
Goetzl EJ, Ledreux A, Granholm AC, Elahi FM, Goetzl L, Hiramoto J, Kapogiannis D (2019) Neuron-derived exosome proteins may contribute to progression from repetitive mild traumatic brain injuries to chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Front Neurosci 13:452. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00452
Goetzl EJ, Elahi FM, Mustapic M, Kapogiannis D, Pryhoda M, Gilmore A, Gorgens KA, Davidson B et al (2019) Altered levels of plasma neuron-derived exosomes and their cargo proteins characterize acute and chronic mild traumatic brain injury. FASEB J 33(4):5082–2088. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201802319R
Hill AF, Pegtel DM, Lambertz U, Leonardi T, O'Driscoll L, Pluchino S, Ter-Ovanesyan D (2013) ISEV position paper: extracellular vesicle RNA analysis and bioinformatics. J Extracell Vesicles;2. doi: https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v2i0.22859.
Yin Z, Han Z, Hu T, Zhang S, Ge X, Huang S, Wang L, Yu J et al (2020) Neuron-derived exosomes with high miR-21-5p expression promoted polarization of M1 microglia in culture. Brain Behav Immun 83:270–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.11.004
Song H, Zhang X, Chen R, Miao J, Wang L, Cui L, Ji H, Liu Y (2019) Cortical neuron-derived exosomal microRNA-181c-3p inhibits neuroinflammation by downregulating CXCL1 in astrocytes of a rat model with ischemic brain injury. Neuroimmunomodulation 26(5):217–233. https://doi.org/10.1159/000502694
** T, ** F, Zhu Y, Wang J, Tang L, Wang Y, Liebeskind DS, He Z (2017) MicroRNA-126-3p attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption, cerebral edema and neuronal injury following intracerebral hemorrhage by regulating PIK3R2 and Akt. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 494(1–2):144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.10.064
Hu J, Zeng L, Huang J, Wang G, Lu H (2015) miR-126 promotes angiogenesis and attenuates inflammation after contusion spinal cord injury in rats. Brain Res 1608:191–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.02.036
Yuan Y, Shen C, Zhao SL, Hu YJ, Song Y, Zhong QJ (2019) MicroRNA-126 affects cell apoptosis, proliferation, cell cycle and modulatesVEGF/TGF-β levels in pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(7):3058–3069. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201904_17588
McDonald MK, Ajit SK (2015) MicroRNA biology and pain. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 131:215–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2014.11.015
Zhou X, He Y, Jiang Y, He B, Deng X, Zhang Z, Yuan X, Li J (2019) MiR-126-3p inhibits apoptosis and promotes proliferation by targetingPIK3R2 in porcine ovarian granulosa cells. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 33:879–887. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.19.0290
Patel DB, Gray KM, Santharam Y, Lamichhane TN, Stroka KM, Jay SM (2017) Impact of cell culture parameters on production and vascularization bioactivity of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Bioeng Transl Med 2(2):170–179. https://doi.org/10.1002/btm2.10065
Almeria C, Weiss R, Roy M, Tripisciano C, Kasper C, Weber V, Egger D (2019) Hypoxia conditioned mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles induce increased vascular tube formation in vitro. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:292. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00292
Kilic T, Valinhas ATS, Wall I, Renaud P, Carrara S (2018) Label-free detection of hypoxia-induced extracellular vesicle secretion from MCF-7 cells. Sci Rep 8(1):9402. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27203-9
Yu X, Deng L, Wang D, Li N, Chen X, Cheng X, Yuan J, Gao X et al (2012) Mechanism of TNF-α autocrine effects in hypoxic cardiomyocytes: initiated by hypoxia inducible factor 1α, presented by exosomes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 53(6):848–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.10.002
Zhu LP, Tian T, Wang JY, He JN, Chen T, Pan M, Xu L, Zhang HX et al (2018) Hypoxia-elicited mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitates cardiac repair through miR-125b-mediated prevention of cell death in myocardial infarction. Theranostics 8(22):6163–6177. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.28021
Gray WD, French KM, Ghosh-Choudhary S, Maxwell JT, Brown ME, Platt MO, Searles CD, Davis ME (2015) Identification of therapeutic covariant microRNA clusters in hypoxia-treated cardiacprogenitor cell exosomes using systems biology. Circ Res 116(2):255–263. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.304360
Gabbouj S, Ryhänen S, Marttinen M, Wittrahm R, Takalo M, Kemppainen S, Martiskainen H, Tanila H et al (2019) Altered insulin signaling in Alzheimer’s disease brain-special emphasis on PI3K-Akt pathway. Front Neurosci 13:629. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00629
Yuan B, Pan S, Dong YQ, Zhang WW, He XD (2020) Effect of exosomes derived from mir-126-modified mesenchymal stem cells on the repair process of spinal cord injury in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(2):483–490. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202001_20025
Zhao L, Jiang X, Shi J, Gao S, Zhu Y, Gu T, Shi E (2019) Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing microRNA-25 protect spinal cords against transient ischemia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 157(2):508–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.07.095
Geng W, Tang H, Luo S, Lv Y, Liang D, Kang X, Hong W (2019) Exosomes from miRNA-126-modified ADSCs promotes functional recovery after stroke in rats by improving neurogenesis and suppressing microglia activation. Am J Transl Res 11(2):780–792 eCollection 2019
Maguire O, O'Loughlin K, Minderman H (2015) Simultaneous assessment of NF-κB/p65 phosphorylation and nuclear localization using imaging flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 423:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2015.03.018
Jayasooriya RG, Lee KT, Kang CH, Dilshara MG, Lee HJ, Choi YH, Choi IW, Kim GY (2014) Isobutyrylshikonin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production in BV2 microglial cells by suppressing the PI3K/Akt-mediated nuclear transcription factor-kappaB pathway. Nutr Res 34:1111–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2014.10.002
Zhou Y, Li P, Goodwin AJ, Cook JA, Halushka PV, Chang E, Zingarelli B, Fan H (2019) Exosomes from endothelial progenitor cells improve outcomes of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Crit Care 23(1):44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-019-2339-3
Meng F, Wang F, Wang L, Wong SC, Cho WC, Chan LW (2016) MiR-30a-5p overexpression may overcome EGFR-inhibitor resistance through regulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Front Genet 7:197. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2016.00197
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81601053 and 81771342) and the Scientific Research Fund of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (no. LK201636).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.W. and Z.-L.Z. participated in the animal care and generated the animal models. H.W. and C.-F.C. performed the cell models and prepared the samples for the RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry assays; C.-F.C., Z.H.-X. and Z.-L.Z performed the experiments and statistical analysis; X.-Q.L. isolated and identified the neuron-derived EVs; and H.M. guided the study design and provided important suggestions regarding the manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
All experiments performed in this study were approved by the Ethics Committee of China Medical University and performed in compliance with the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals under approved protocols.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Chen, FS., Zhang, ZL. et al. MiR-126-3p-Enriched Extracellular Vesicles from Hypoxia-Preconditioned VSC 4.1 Neurons Attenuate Ischaemia-Reperfusion-Induced Pain Hypersensitivity by Regulating the PIK3R2-Mediated Pathway. Mol Neurobiol 58, 821–834 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02159-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02159-y