Abstract
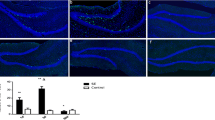
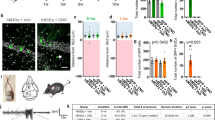
Notch signaling in the nervous system is often regarded as a developmental pathway. However, recent studies have suggested that Notch is associated with neuronal discharges. Here, focusing on temporal lobe epilepsy, we found that Notch signaling was activated in the kainic acid (KA)-induced epilepsy model and in human epileptogenic tissues. Using an acute model of seizures, we showed that DAPT, an inhibitor of Notch, inhibited ictal activity. In contrast, pretreatment with exogenous Jagged1 to elevate Notch signaling before KA application had proconvulsant effects. In vivo, we demonstrated that the impacts of activated Notch signaling on seizures can in part be attributed to the regulatory role of Notch signaling on excitatory synaptic activity in CA1 pyramidal neurons. In vitro, we found that DAPT treatment impaired synaptic vesicle endocytosis in cultured hippocampal neurons. Taken together, our findings suggest a correlation between aberrant Notch signaling and epileptic seizures. Notch signaling is up-regulated in response to seizure activity, and its activation further promotes neuronal excitation of CA1 pyramidal neurons in acute seizures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ables JL, Breunig JJ, Eisch AJ, Rakic P (2011) Not(ch) just development: Notch signalling in the adult brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(5):269–283. doi:10.1038/nrn3024
Pierfelice T, Alberi L, Gaiano N (2011) Notch in the vertebrate nervous system: an old dog with new tricks. Neuron 69(5):840–855. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.02.031
Alberi L, Liu S, Wang Y, Badie R, Smith-Hicks C, Wu J, Pierfelice TJ, Abazyan B, Mattson MP, Kuhl D, Pletnikov M, Worley PF, Gaiano N (2011) Activity-induced Notch signaling in neurons requires Arc/Arg3.1 and is essential for synaptic plasticity in hippocampal networks. Neuron 69(3):437–444. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.01.004
Lieber T, Kidd S, Struhl G (2011) DSL-Notch signaling in the Drosophila brain in response to olfactory stimulation. Neuron 69(3):468–481. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.12.015
Hortopan GA, Baraban SC (2011) Aberrant expression of genes necessary for neuronal development and Notch signaling in an epileptic mind bomb zebrafish. Dev Dyn: Off Publ Am Assoc Anat 240(8):1964–1976. doi:10.1002/dvdy.22680
Jiang YH, Armstrong D, Albrecht U, Atkins CM, Noebels JL, Eichele G, Sweatt JD, Beaudet AL (1998) Mutation of the Angelman ubiquitin ligase in mice causes increased cytoplasmic p53 and deficits of contextual learning and long-term potentiation. Neuron 21(4):799–811
Hortopan GA, Dinday MT, Baraban SC (2010) Spontaneous seizures and altered gene expression in GABA signaling pathways in a mind bomb mutant zebrafish. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 30(41):13718–13728. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1887-10.2010
Riban V, Bouilleret V, Pham-Le BT, Fritschy JM, Marescaux C, Depaulis A (2002) Evolution of hippocampal epileptic activity during the development of hippocampal sclerosis in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience 112(1):101–111
Bouilleret V, Ridoux V, Depaulis A, Marescaux C, Nehlig A, Le Gal La Salle G (1999) Recurrent seizures and hippocampal sclerosis following intrahippocampal kainate injection in adult mice: electroencephalography, histopathology and synaptic reorganization similar to mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience 89(3):717–729
Breunig JJ, Silbereis J, Vaccarino FM, Sestan N, Rakic P (2007) Notch regulates cell fate and dendrite morphology of newborn neurons in the post-natal dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(51):20558–20563. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710156104
Balosso S, Ravizza T, Perego C, Peschon J, Campbell IL, De Simoni MG, Vezzani A (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits seizures in mice via p75 receptors. Ann Neurol 57(6):804–812. doi:10.1002/ana.20480
Balosso S, Maroso M, Sanchez-Alavez M, Ravizza T, Frasca A, Bartfai T, Vezzani A (2008) A novel non-transcriptional pathway mediates the proconvulsive effects of interleukin-1beta. Brain J Neurol 131(Pt 12):3256–3265. doi:10.1093/brain/awn271
Warnock DE, Schmid SL (1996) Dynamin GTPase, a force-generating molecular switch. BioEssays 18(11):885–893. doi:10.1002/bies.950181107
Sudhof TC (2004) The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu Rev Neurosci 27:509–547. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131412
Meyers JR, MacDonald RB, Duggan A, Lenzi D, Standaert DG, Corwin JT, Corey DP (2003) Lighting up the senses: FM1-43 loading of sensory cells through nonselective ion channels. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 23(10):4054–4065
Bolte S, Talbot C, Boutte Y, Catrice O, Read ND, Satiat-Jeunemaitre B (2004) FM-dyes as experimental probes for dissecting vesicle trafficking in living plant cells. J Microsc 214(Pt 2):159–173. doi:10.1111/j.0022-2720.2004.01348.x
Salama-Cohen P, Arevalo MA, Grantyn R, Rodriguez-Tebar A (2006) Notch and NGF/p75NTR control dendrite morphology and the balance of excitatory/inhibitory synaptic input to hippocampal neurones through Neurogenin 3. J Neurochem 97(5):1269–1278. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03783.x
Wang Y, Chan SL, Miele L, Yao PJ, Mackes J, Ingram DK, Mattson MP, Furukawa K (2004) Involvement of Notch signaling in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(25):9458–9462. doi:10.1073/pnas.0308126101
Hinshaw JE (2000) Dynamin and its role in membrane fission. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:483–519. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.483
Xu B, Li S, Brown A, Gerlai R, Fahnestock M, Racine RJ (2003) EphA/ephrin-A interactions regulate epileptogenesis and activity-dependent axonal sprouting in adult rats. Mol Cell Neurosci 24(4):984–999
Matsui C, Inoue E, Kakita A, Arita K, Deguchi-Tawarada M, Togawa A, Yamada A, Takai Y, Takahashi H (2012) Involvement of the gamma-secretase-mediated EphA4 signaling pathway in synaptic pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Brain Pathol 22(6):776–787. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2012.00587.x
Wei J, Hemmings GP (2000) The NOTCH4 locus is associated with susceptibility to schizophrenia. Nat Genet 25(4):376–377. doi:10.1038/78044
Chang YT, Chen PC, Tsai IJ, Sung FC, Chin ZN, Kuo HT, Tsai CH, Chou IC (2011) Bidirectional relation between schizophrenia and epilepsy: a population-based retrospective cohort study. Epilepsia 52(11):2036–2042. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03268.x
Yizhar O, Fenno LE, Prigge M, Schneider F, Davidson TJ, O'Shea DJ, Sohal VS, Goshen I, Finkelstein J, Paz JT, Stehfest K, Fudim R, Ramakrishnan C, Huguenard JR, Hegemann P, Deisseroth K (2011) Neocortical excitation/inhibition balance in information processing and social dysfunction. Nature 477(7363):171–178. doi:10.1038/nature10360
Dudek FE (2009) Epileptogenesis: a new twist on the balance of excitation and inhibition. Epilepsy Curr Am Epilepsy Soc 9(6):174–176. doi:10.1111/j.1535-7511.2009.01334.x
Toro CT, Deakin JF (2007) Adult neurogenesis and schizophrenia: a window on abnormal early brain development? Schizophr Res 90(1–3):1–14. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2006.09.030
Kuruba R, Hattiangady B, Shetty AK (2009) Hippocampal neurogenesis and neural stem cells in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav E&B 14(Suppl 1):65–73. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2008.08.020
Ledergerber D, Fritschy JM, Kralic JE (2006) Impairment of dentate gyrus neuronal progenitor cell differentiation in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Exp Neurol 199(1):130–142. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.02.010
Kralic JE, Ledergerber DA, Fritschy JM (2005) Disruption of the neurogenic potential of the dentate gyrus in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy with focal seizures. Eur J Neurosci 22(8):1916–1927. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04386.x
Elliott RC, Khademi S, Pleasure SJ, Parent JM, Lowenstein DH (2001) Differential regulation of basic helix-loop-helix mRNAs in the dentate gyrus following status epilepticus. Neuroscience 106(1):79–88
Sibbe M, Haussler U, Dieni S, Althof D, Haas CA, Frotscher M (2012) Experimental epilepsy affects Notch1 signalling and the stem cell pool in the dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci 36(12):3643–3652. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08279.x
Parent JM, Elliott RC, Pleasure SJ, Barbaro NM, Lowenstein DH (2006) Aberrant seizure-induced neurogenesis in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol 59(1):81–91. doi:10.1002/ana.20699
Rensing NR, Guo D, Wong M (2012) Video-EEG monitoring methods for characterizing rodent models of tuberous sclerosis and epilepsy. Methods Mol Biol 821:373–391. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-430-8_24
Maroso M, Balosso S, Ravizza T, Liu J, Aronica E, Iyer AM, Rossetti C, Molteni M, Casalgrandi M, Manfredi AA, Bianchi ME, Vezzani A (2010) Toll-like receptor 4 and high-mobility group box-1 are involved in ictogenesis and can be targeted to reduce seizures. Nat Med 16(4):413–419. doi:10.1038/nm.2127
Ge R, Qian H, Wang JH (2011) Physiological synaptic signals initiate sequential spikes at soma of cortical pyramidal neurons. Mol Brain 4:19. doi:10.1186/1756-6606-4-19
Wang JH, Zhang MJ (2004) Differential modulation of glutamatergic and cholinergic synapses by calcineurin in hippocampal CA1 fast-spiking interneurons. Brain Res 1004(1–2):125–135. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.01.025
Zakharenko SS, Zablow L, Siegelbaum SA (2001) Visualization of changes in presynaptic function during long-term synaptic plasticity. Nat Neurosci 4(7):711–717. doi:10.1038/89498
Anggono V, Cousin MA, Robinson PJ (2008) Styryl dye-based synaptic vesicle recycling assay in cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Methods Mol Biol 457:333–345
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all the patients for their support and participation. We thank Prof. Jun Wei for revising of the manuscript. This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China [2010CB529603, 2012CB517902], National Natural Science Foundation of China [30971001, 31222031, 31021091], Bei**g Natural Science Foundation [7102109], and Fok Ying Tong Education Foundation [121024].
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors Longze Sha and **aofeng Wu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 464 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sha, L., Wu, X., Yao, Y. et al. Notch Signaling Activation Promotes Seizure Activity in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Mol Neurobiol 49, 633–644 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8545-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8545-0