Abstract
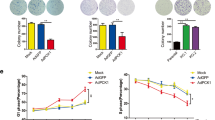
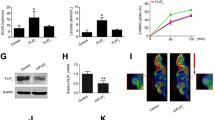
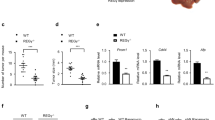
To investigate the role of neuropilin1 (Nrp1) in glucose metabolism and proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and to analyze its mechanism of action. The CRISPR gene knockout technique was used to knock out the Nrp1 gene in two HCC cell lines. The effect of Nrp1 on the proliferation of HCC cells was assessed in the CCK8 assay and plate cloning assay. The expression levels of glucose consumption, lactate production, and essential proteins of the glycolytic pathway were detected to explore the effect of Nrp1 on glucose metabolism in HCC cells. Using CoCl2 to revert the expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), the role of HIF-1α in the pro-HCC cell metabolism of Nrp1 were demonstrated. The protein synthesis inhibitor CHX and proteasome inhibitor MG-132 was used to analyze the molecular mechanism of action of Nrp1 on HIF-1α. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to calculate survival rates and plot survival curves. Based on the CCK8 assay and plate cloning assay, we found that Nrp1 knockout significantly inhibited the proliferation of HCC cells. Nrp1 inhibitor suppressed lactate production and glucose consumption in HCC cells. Knockout of Nrp1 decreased the expression of glycolytic pathway-related proteins and HIF-1α protein. Furthermore, by joint use of CoCl2 and NRP1 knockout, we confirmed that reverting HIF-1α expression could reverse the effect of Nrp1 knockout on HCC cell metabolism in vitro. Mechanistically, Nrp1 showed a close correlation with the stability of HIF-1α protein in protein stability assay. Finally, we revealed that high expression of Nrp1 in HCC tissues was associated with poor overall survival and disease-free survival of the patients. Nrp1 accelerates glycolysis and promotes proliferation of HCC by regulating HIF-1α protein stability and through the VEGF/Nrp1/HIF-1α positive feedback loop.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
**a C, Dong X, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, He S, Yang F, Yan X, Zhang S, Li N, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin Med J. 2022;135:584–90.
Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X, Yin P, Zhu J, Chen W, Li X, Wang L, Wang L, Liu Y, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;394(10204):1145–58.
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–32.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424.
Matsubara T, Kanto T, Kuroda S, Yoshio S, Higashitani K, Kakita N, Miyazaki M, Sakakibara M, Hiramatsu N, Kasahara A, et al. TIE2-expressing monocytes as a diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with angiogenesis. Hepatology. 2013;57(4):1416–25.
**ang ZL, Zeng ZC, Fan J, Tang ZY, Zeng HY, Gao DM. Gene expression profiling of fixed tissues identified hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, VEGF, and matrix metalloproteinase-2 as biomarkers of lymph node metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(16):5463–72.
Bergé M, Allanic D, Bonnin P, de Montrion C, Richard J, Suc M, Boivin JF, Contrerès JO, Lockhart BP, Pocard M, et al. Neuropilin-1 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and contributes to tumour growth and vascular remodelling. J Hepatol. 2011;55(4):866–75.
Xu L, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Ancukiewicz M, Chung DC, Lauwers GY, Samuel R, Shellito P, Czito BG, Lin PC, et al. Direct evidence that bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody, up-regulates SDF1alpha, CXCR4, CXCL6, and neuropilin 1 in tumors from patients with rectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69(20):7905–10.
Shi S, Xu J, Zhang B, Ji S, Xu W, Liu J, ** K, Liang D, Liang C, Liu L, et al. VEGF promotes glycolysis in pancreatic cancer via HIF1α up-regulation. Curr Mol Med. 2016;16(4):394–403.
Djordjevic S, Driscoll PC. Targeting VEGF signalling via the neuropilin co-receptor. Drug Discov Today. 2013;18(9–10):447–55.
Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL. X-tile: a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(21):7252–9.
Lampropoulou A, Ruhrberg C. Neuropilin regulation of angiogenesis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014;42(6):1623–8.
Peng K, Bai Y, Zhu Q, Hu B, Xu Y. Targeting VEGF–neuropilin interactions: a promising antitumor strategy. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24(2):656–64.
Beck B, Driessens G, Goossens S, Youssef KK, Kuchnio A, Caauwe A, Sotiropoulou PA, Loges S, Lapouge G, Candi A, et al. A vascular niche and a VEGF-Nrp1 loop regulate the initiation and stemness of skin tumours. Nature. 2011;478(7369):399–403.
Hamerlik P, Lathia JD, Rasmussen R, Wu Q, Bartkova J, Lee M, Moudry P, Bartek J, Fischer W, Lukas J, et al. Autocrine VEGF-VEGFR2-neuropilin-1 signaling promotes glioma stem-like cell viability and tumor growth. J Exp Med. 2012;209(3):507–20.
Grun D, Adhikary G, Eckert RL. VEGF-A acts via neuropilin-1 to enhance epidermal cancer stem cell survival and formation of aggressive and highly vascularized tumors. Oncogene. 2016;35(33):4379–87.
Jang JE, Hajdu CH, Liot C, Miller G, Dustin ML, Bar-Sagi D. Crosstalk between regulatory T cells and tumor-associated dendritic cells negates anti-tumor immunity in pancreatic cancer. Cell Rep. 2017;20(3):558–71.
Hansen W. Neuropilin 1 guides regulatory T cells into VEGF-producing melanoma. Oncoimmunology. 2013;2(2):e23039.
Lin J, Zhang Y, Wu J, Li L, Chen N, Ni P, Song L, Liu X. Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) is a novel tumor marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;485:158–65.
Xu J, **a J. NRP-1 silencing suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Exp Ther Med. 2013;5(1):150–4.
Zhang D, Wang Y, Shi Z, Liu J, Sun P, Hou X, Zhang J, Zhao S, Zhou BP, Mi J. Metabolic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts by IDH3α downregulation. Cell Rep. 2015;10(8):1335–48.
Chow AK, Yau TC, Ng L, Chu AC, Law WL, Poon RT, Pang RW. A preclinical study on the combination therapy of everolimus and transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma. AM J Cancer Res. 2015;5(8):2376–86.
Xue TM, Tao LD, Zhang M, Zhang J, Liu X, Chen GF, Zhu YJ, Zhang PJ. Clinicopathological Significance of MicroRNA-20b expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and regulation of HIF-1α and VEGF effect on cell biological behaviour. Dis Markers. 2015;2015:325176.
Marín-Hernández A, Gallardo-Pérez JC, Ralph SJ, Rodríguez-Enríquez S, Moreno-Sánchez R. HIF-1alpha modulates energy metabolism in cancer cells by inducing over-expression of specific glycolytic isoforms. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009;9(9):1084–101.
Masoud GN, Li W. HIF-1α pathway: role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015;5(5):378–89.
Borsi E, Terragna C, Brioli A, Tacchetti P, Martello M, Cavo M. Therapeutic targeting of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in multiple myeloma. Transl Res. 2015;165(6):641–50.
Goel HL, Mercurio AM. VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(12):871–82.
Casazza A, Di Conza G, Wenes M, Finisguerra V, Deschoemaeker S, Mazzone M. Tumor stroma: a complexity dictated by the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Oncogene. 2014;33(14):1743–54.
Fang P, Hu JH, Cheng ZG, Liu ZF, Wang JL, Jiao SC. Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of phase II trials. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e49717.
Yau T, Wong H, Chan P, Yao TJ, Pang R, Cheung TT, Fan ST, Poon RT. Phase II study of bevacizumab and erlotinib in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients with sorafenib-refractory disease. Invest New Drugs. 2012;30(6):2384–90.
Lambrechts D, Lenz HJ, de Haas S, Carmeliet P, Scherer SJ. Markers of response for the antiangiogenic agent bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(9):1219–30.
Geretti E, van Meeteren LA, Shimizu A, Dudley AC, Claesson-Welsh L, Klagsbrun M. A mutated soluble neuropilin-2 B domain antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor bioactivity and inhibits tumor progression. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8(8):1063–73.
Jubb AM, Miller KD, Rugo HS, Harris AL, Chen D, Reimann JD, Cobleigh MA, Schmidt M, Langmuir VK, Hillan KJ, et al. Impact of exploratory biomarkers on the treatment effect of bevacizumab in metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(2):372–81.
Van Cutsem E, de Haas S, Kang YK, Ohtsu A, Tebbutt NC, Ming Xu J, Peng Yong W, Langer B, Delmar P, Scherer SJ, et al. Bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy as first-line therapy in advanced gastric cancer: a biomarker evaluation from the AVAGAST randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(17):2119–27.
Abdel Ghafar MT, Elkhouly RA, Elnaggar MH, Mabrouk MM, Darwish SA, Younis RL, Elkholy RA. Utility of serum neuropilin-1 and angiopoietin-2 as markers of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Investig Med. 2021;69(6):1222–9.
Li JH, Tao YF, Shen CH, Li RD, Wang Z, **ng H, Ma ES, Xue HY, Zhang QB, Ma ZY, et al. Integrated multi-omics analysis identifies ENY2 as a predictor of recurrence and a regulator of telomere maintenance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2022;12:939948.
Fernández-Palanca P, Payo-Serafín T, Méndez-Blanco C, San-Miguel B, Tuñón MJ, González-Gallego J, Mauriz JL. Neuropilins as potential biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of basic and clinical implications. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023;29(2):293–319.
Zhang Y, Liu P, Jiang Y, Dou X, Yan J, Ma C, Fan Q, Wang W, Su F, Tang H, et al. High expression of neuropilin-1 associates with unfavorable clinicopathological features in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 2016;22(2):367–75.
Funding
The study was funded by Chongqing medical scientific research project (Joint project of Chongqing Health Commission and Science and Technology Bureau: No. 2021MSXM139), Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (No. cstc2020jcyj-bshX0033), and General program of Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (No. cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0294).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and design: YBW, KWZ, ZYZ, and XD; Methodology: YBW, KWZ, YYH, SH, and XD; In vitro and in vivo experiment: YBW, KWZ, FFW, and SH; Writing-review and editing: YBW, KWZ, YYH, SH, ZYZ, and XD; Funding acquisition: YBW and XD; Supervision: XD. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of the second affiliated hospital of Chongqing Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YB., Zheng, KW., Hu, YY. et al. VEGF/Nrp1/HIF-1α promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma through a positive feedback loop. Med Oncol 40, 339 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02202-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02202-7