Abstract
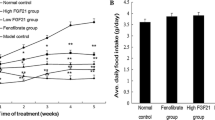
The aim of this study is to investigate the role of FGF21 in obesity-related inflammation in livers of monosodium glutamate (MSG)-induced obesity rats. The MSG rats were injected with recombinant murine fibroblast growth factor 21(FGF21) or equal volumes of vehicle. Metabolic parameters including body weight, Lee’s index, food intake, visceral fat and liver weight, intraperitoneal glucose tolerance, glucose, and lipid levels were dynamically measured at specific time points. Liver function and routine blood test were also analyzed. Further, systemic inflammatory cytokines such as glucose transporter 1 (GLUT-1), leptin, TNF-α, and IL-6 mRNAs were determined by real-time PCR. FGF21 independently decreased body weight and whole-body fat mass without reducing food intake in the MSG rats. FGF21 reduced blood glucose level, Lee’s index, visceral fat, and liver weight, and improved glucose tolerance, lipid metabolic spectrum, and hepatic steatosis in the MSG-obesity rats. Liver function parameters including AST, ALT, ALP, TP, T.Bili, and D.Bili levels significantly reduced in the FGF21-treated obesity rats compared to the controls. Further, FGF21 ameliorated the total and differential white blood cell (WBC) count, serum C-reactive protein (CRP), IL-6, and TNF-α levels in adipose tissues of the obesity rats, suggesting inflammation amelioration in the in the obesity rats by FGF21. FGF21 improves multiple metabolic disorders and ameliorates obesity-related inflammation in the MSG-induced obesity rats.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Itoh, D.M. Ornitz, Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends. Genet. 20, 563–569 (2004)
T. Nishimura, Y. Nakatake, M. Konishi, N. Itoh, Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1492, 203–206 (2000)
A. Kharitonenkov, T.L. Shiyanova, A. Koester, A.M. Ford, R. Micanovic, E.J. Galbreath et al., FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J Clin Invest. 115, 1627–1635 (2005)
J. Xu, D.J. Lloyd, C. Hale, S. Stanislaus, M. Chen, G. Sivits et al., FGF21 reverses hepatic steatosis, increases energy expenditure and improves insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes 58, 250–259 (2008)
T. Coskun, H.A. Bina, M.A. Schneider, J.D. Dunbar, C.C. Hu, Y. Chen et al., FGF21 corrects obesity in mice. Endocrinology 149, 6018–6127 (2008)
A. Kharitonenkov, V.J. Wroblewski, A. Koester, Y.F. Chen, C.K. Clutinger, X.T. Tigno et al., The metabolic state of diabetic monkeys is regulated by fibroblast growth factor-21. Endocrinology 148, 774–781 (2007)
A.H. Goris, K.R. Westerterp, Physical activity, fat intake and body fat. Physiol. Behav. 94, 164–168 (2008)
R.H. Unger, P.E. Scherer, Gluttony, sloth and the metabolic syndrome: a roadmap to lipotoxicity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 21, 345–352 (2010)
M. Nagata, W. Suzuki, S. Iizuka, M. Tabuchi, H. Maruyama et al., Type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese mouse model induced by monosodium glutamate. Exp. Anim. 55, 109–115 (2006)
Y. Nakanishi, K. Tsuneyama, M. Fujimoto, T.L. Salunga, K. Nomoto, J.L. An et al., Monosodium glutamate (MSG): a villain and promoter of liver inflammation and dysplasia. J. Autoimmun. 30, 42–50 (2008)
N. Aoi, M. Soma, T. Nakayama, D. Rahmutula, K. Kosuge, Y. Izumi et al., Variable number of tandem repeat of the 5’-flanking region of type-C human natriuretic peptide receptor gene influences blood pressure levels in obesity-associated hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 27, 711–716 (2004)
K. Kosuge, M. Soma, T. Nakayama, N. Aoi, M. Sato, A. Haketa et al., Human uncoupling protein 2 and 3 genes are associated with obesity in Japanese. Endocrine 34, 87–95 (2008)
K. Strohacker, B.K. McFarlin, Influence of obesity, physical inactivity, and weight cycling on chronic inflammation. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2, 98–104 (2010)
I. Majumdar, L.D. Mastrandrea, Serum sphingolipids and inflammatory mediators in adolescents at risk for metabolic syndrome. Endocrine 41, 442–449 (2012)
P. Marzullo, A. Minocci, P. Giarda, C. Marconi, A. Tagliaferri, G.E. Walker, M. Scacchi, G. Aimaretti, A. Liuzzi, Lymphocytes and immunoglobulin patterns across the threshold of severe obesity. Endocrine 45, 392–400 (2014)
M. Rondanelli, A. Opizzi, S. Perna, M. Faliva, S.B. Solerte, M. Fioravanti, C. Klersy, E. Cava, M. Paolini, L. Scavone, P. Ceccarelli, E. Castellaneta, C. Savina, L.M. Donini, Improvement in insulin resistance and favourable changes in plasma inflammatory adipokines after weight loss associated with two months’ consumption of a combination of bioactive food ingredients in overweight subjects. Endocrine 44, 391–401 (2013)
T. Inagaki, P. Dutchak, G. Zhao, X. Ding, L. Gautron, V. Parameswara et al., Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPARalpha-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Metab. 5, 415–425 (2007)
A. Kharitonenkov, A.B. Shanafelt, Fibroblast growth factor-21 as a therapeutic agent for metabolic diseases. BioDrugs. 22, 37–44 (2008)
T. Nakagawa, K. Ukai, T. Ohyama, Y. Gomita, H. Okamura, Effects of chronic administration of sibutramine on body weight, food intake and motor activity in neonatally monosodium glutamate-treated obese female rats: relationship of antiobesity effect with monoamines. Exp. Anim. 49, 239–249 (2000)
M. Nagata, W. Suzuki, S. Iizuka, M. Tabuchi, H. Maruyama, S. Takeda et al., Type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese mouse model induced by monosodium glutamate. Exp. Anim. 55, 109–115 (2006)
S.M. Kang, J.W. Yoon, H.Y. Ahn, S.Y. Kim, K.H. Lee, H. Shin et al., Android fat depot is more closely associated with metabolic syndrome than abdominal visceral fat in elderly people. PLoS ONE 6, e27694 (2011)
J. Liu, F. Zhang, C. Li, M. Lin, M.R. Briggs, Synergistic activation of human LDL receptor expression by SCAP ligand and cytokine oncostatin M. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23, 90–96 (2003)
S.M. Grundy, Statin trials and goals of cholesterol-lowering therapy. Circulation 97, 1436–1439 (1998)
E.D. Berglund, C.Y. Li, H.A. Bina, S.E. Lynes, M.D. Michael, A.B. Shanafelt et al., Fibroblast growth factor 21 controls glycemia via regulation of hepatic glucose flux and insulin sensitivity. Endocrinology 150, 4084–4093 (2009)
F.M. Fisher, P.C. Chui, P.J. Antonellis, H.A. Bina, A. Kharitonenkov, J.S. Flier et al., Obesity is an FGF21 resistant state. Diabetes 59, 2781–2789 (2010)
T. Lundåsen, M.C. Hunt, L.M. Nilsson, S. Sanyal, B. Angelin, S.E. Alexson et al., PPARalpha is a key regulator of hepatic FGF21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 360, 437–440 (2007)
Y.L. Zhang, A. Hernandez-Ono, P. Siri, S. Weisberg, D. Conlon, M.J. Graham et al., Aberrant hepatic expression of PPARgamma2 stimulates hepatic lipogenesis in a mouse model of obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hepatic steatosis. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 37603–37615 (2006)
J.S. Moyers, T.L. Shiyanova, F. Mehrbod, J.D. Dunbar, T.W. Noblitt, K.A. Otto et al., Molecular determinants of FGF-21 activity - synergy and cross-talk with PPARγ signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 210, 1–6 (2007)
H. Wang, L. Qiang, S.R. Farmer, Identification of a domain within peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma regulating expression of a group of genes containing fibroblast growth factor 21 that are selectively repressed by SIRT1 in adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 188–200 (2008)
Z. Wang, T. Nakayama, Inflammation, a link between obesity and cardiovascular disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2010, 535918 (2010)
Tamer Coskn, Holly au Bina, Michael a Schneider, James D Dunbar, Charlie C Hu, Yanyun Chen, David E Moller, and Alexei Kharitonenkov. “Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Corrects Obesity in Mice”. Endocrinology 149, 6018–6027 (2008)
M.J. Potthoff, T. Inagaki, S. Satapati, X. Ding, T. He, R. Goetz et al., FGF21 induces PGC-1alpha and regulates carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism during the adaptive starvation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 106, 10853–10858 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.81172741 and 30972537).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, WF., Li, SM., Ren, GP. et al. Recombinant murine fibroblast growth factor 21 ameliorates obesity-related inflammation in monosodium glutamate-induced obesity rats. Endocrine 49, 119–129 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0433-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0433-5