Abstract
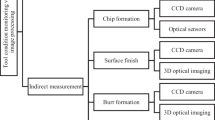
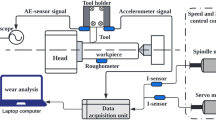
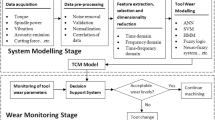
Measuring machining parameters is essential for influencing the quality and precision of the finished product in the manufacturing and machining industries. Machine vision systems, which provide an in-depth investigation of these parameters, are essential resources for this purpose. To evaluate machining parameters such as tool wear, surface roughness, and defects, this article investigates machine vision and its techniques. It also explores tool condition monitoring (TCM), a subject that is becoming more and more important. To achieve precision, high-resolution cameras with CCD or CMOS sensors in conjunction with deliberate illumination are essential. Area, compactness, and perimeter metrics are essential for assessing machining parameters because they offer insightful information about a variety of situations and enhance tool performance. By effectively utilizing these techniques, machinery can be converted into intelligent systems that improve safety, reliability, and product quality by preventing tool failure and optimizing cutting feed rates. A thorough review of the literature highlights the advantages of combining the direct and indirect TCM measurement methods, improving measurement accuracy. Additionally, the detection of tool wear problems like chip**, crater wear, and fractures is significantly aided by the integration of digital image processing techniques.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Santos, E., Xavier, W. B., Rodrigues, R. N., Botelho, S., Werhli, A.: Vision-based measurement applied to industrial instrumentation. Undefined. (2017) Accessed: Oct. 18, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Vision-Based-Measurementapplied-to-Industrial-Santos-Xavier/3441c577f3e13d348fa8c0420bb1788da40681a3
Chethan, Y.D., Ravindra, H.V., Krishnegowda, Y.T.: Optimisation of machining parameters in turning Nimonic-75 using machine vision and acoustic emission signals by Taguchi technique. Measurement 144, 144–154 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.05.035
Penumuru, D.P., Muthuswamy, S., Karumbu, P.: Identification and classification of materials using machine vision and machine learning in the context of industry 4.0. J. Intell. Manuf. Intell. Manuf. 31(5), 1229–1241 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01508-6
Kim, J.H., Moon, D.K., Lee, D.W., Kim, J.S., Kang, M.C., Kim, K.H.: Tool wear measuring technique on the machine using CCD and exclusive jig. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 130, 668–674 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00733-1
Ayub, M.A., Mohamed, A.B., Esa, A.H.: In-line inspection of roundness using machine vision. Procedia Technol. 15, 807–816 (2014)
Benbarrad, T., Salhaoui, M., Kenitar, S.B., Arioua, M.: Intelligent machine vision model for defective product inspection based on machine learning. J. Sens. Actuator Netw.Netw. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan10010007
Eshkevari, M., JahangoshaiRezaee, M., Zarinbal, M., Izadbakhsh, H.: Automatic dimensional defect detection for glass vials based on machine vision A heuristic segmentation method. J. Manuf. Process. 68, 973–989 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.06.018
Bradley, C., Wong, Y.S.: Surface texture indicators of tool wear - a machine vision approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 17(6), 435–443 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001700170161
Bagga, P.J., Makhesana, M.A., Patel, K., Patel, K.M.: Tool wear monitoring in turning using image processing techniques. Mater. Today: Proc. 44, 771–775 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.680
Selvaraj, T., Balasubramani, C., Vignesh, S.H., Prabakaran, M.P.: Tool wear monitoring by image processing. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2(8), 10 (2013)
Moldovan, O., Dzitac, S., Moga, I., Vesselenyi, T., Dzitac, I.: Tool-wear analysis using image processing of the tool flank. Symmetry 9(12), 296 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/sym9120296
Chethan, Y.D., Ravindra, H., Gowda, Y.T.K., Kumar, S.B.: Machine Vision for Tool Status Monitoring in Turning Inconel 718 using Blob Analysis. Undefined (2015). Accessed: Oct. 18, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Machine-Visionfor-Tool-Status-Monitoring-in-718-Chethan-Ravindra/4fcaaae6248444d531e06f08971bf4bb354f7e80
Žuvela, P., Lovrić, M., Yousefian-Jazi, A., Liu, J.J.: Ensemble learning approaches to data imbalance and competing objectives in design of an industrial machine vision system. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05766
Patel, D.R., Kiran, M.B., Vakharia, V.: Modeling and prediction of surface roughness using multiple regressions: a noncontact approach. Eng. Rep. 2(2), e12119 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/eng2.12119
Dhanasekar, B., Ramamoorthy, B.: Restoration of blurred images for surface roughness evaluation using machine vision. Tribol. Int.. Int. 43(1–2), 268–276 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2009.05.030
Yuan, Y., et al.: Crack length measurement using convolutional neural networks and image processing. Sensors 21(17), 5894 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21175894
Patel, D.R., Vakharia, V., Kiran, M.B.: Texture classification of machined surfaces using image processing and machine learning techniques. FME Trans. 47(4), 865–872 (2019). https://doi.org/10.5937/fmet1904865P
Xu, L.M., Fan, F., Hu, Y.X., Zhang, Z., Hu, D.J.: A vision-based processing methodology for profile grinding of contour surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405419857401
Mook, W.K., Shahabi, H.H., Ratnam, M.M.: Measurement of nose radius wear in turning tools from a single 2D image using machine vision. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 43(3), 217–225 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1712-1
Kumar, B.M., Ratnam, M.M.: Study on effect of tool nose radius wear on hybrid roughness parameters during turning using vision-based approach. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 530, 012009 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/530/1/012009
Patel, D.R., Kiran, M.B.: Vision based prediction of surface roughness for end milling. Mater. Today Proc. 44, 792–796 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.709
Patel, D.R., Kiran, M.B.: A non-contact approach for surface roughness prediction in CNC turning using a linear regression model. Mater. Today Proc. 26, 350–355 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.12.029
Guardiola, B.A.: Machine vision systems: automated inspection and metrology. p. 88
Shuxia, G., Jiancheng, Z., **aofeng, J., Yin, P., Lei, W.: Mini milling cutter measurement based on machine vision. Procedia Eng. 15, 1807–1811 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2011.08.336
Szydłowski, M., Powałka, B.: Chatter detection algorithm based on machine vision. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 62(5–8), 517–528 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3816-2
Zhou, J., Yu, J.: Chisel edge wear measurement of high-speed steel twist drills based on machine vision. Comput. Ind.. Ind. 128, 103436 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2021.103436
Shahabi, H.H., Ratnam, M.M.: Assessment of flank wear and nose radius wear from workpiece roughness profile in turning operation using machine vision. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 43(1), 11–21 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1688-x
Mahapatra, P.K., Thareja, R., Kaur, M., Kumar, A.: A machine vision system for tool positioning and its verification. Meas. Control (2015). https://doi.org/10.1177/0020294015602499
Li, B.: Research on geometric dimension measurement system of shaft parts based on machine vision. EURASIP J. Image Video Process (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13640-018-0339-x
Dutta, S., Pal, S. K., Mukhopadhyay, S., Sen, R.: Application of digital image processing in tool condition monitoring: a review. Undefined, 2013, Accessed: Oct. 18 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Application-of-digital-imageprocessing-in-tool-A-Dutta-Pal/bd53460cef65cb12f69bfab31bc66d82d30b1e29
Verma, N., Vettivel, S.C., Rao, P.S., Zafar, S.: Processing, tool wear measurement using machine vision system and optimisation of machining parameters of boron carbide and rice husk ash reinforced. Mater. Res. Express 6(8), 86 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab2509
Lins, R.G., de Araujo, P.R.M., Corazzim, M.: In-process machine vision monitoring of tool wear for cyber-physical production systems. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 61, 101859 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2019.101859
Shao, F., Liu, Z., Wan, Y., Shi, Z.: Finite element simulation of machining of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with thermodynamical constitutive equation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 49(5–8), 431–439 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2423-y
Sortino, M.: Application of statistical filtering for optical detection of tool wear,” undefined. Accessed: Oct. 18, 2021. [Online]. (2003) Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Application-of-statistical-filtering-for-optical-ofSortino/cfb523844d543730b40483a7379227acf1ae110b
Castejón, M., Alegre, E., Barreiro, J., Hernández, L.: On-line tool wear monitoring using geometric descriptors from digital images. undefined, .Accessed: Oct. 18, 2021. [Online]. (2007). Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/On-line-tool-wear-monitoringusing-geometric-from-Castej%C3%B3n-Alegre/e4679549606817a97e11e74dcd84e1ba7850165c
Danesh, M., Khalili, K.: Determination of tool wear in turning process using undecimated wavelet transform and textural features. Undefined. Accessed: Oct. 18, 2021. [Online] (2015) Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Determination-of-Tool-Wear-inTurning-Process-Using-Danesh-Khalili/e720a235f30c8d0ad8240d654627cfda6c019dfd
Yu, X., Lin, X., Dai, Y., Zhu, K.: Image edge detection based tool condition monitoring with morphological component analysis. Undefined (2017) Accessed: Oct. 18, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Image-edge-detection-based-toolcondition-with-Yu-Lin/a9845773454d36ee77f4bb3cdb91c64d1a71080e
D’Addona, D.M., Teti, R.: Image data processing via neural networks for tool wear prediction. Procedia CIRP 12, 252–257 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2013.09.044
Yu, J., Cheng, X., Lu, L., Wu, B.: A machine vision method for measurement of machining tool wear. Measurement 182, 109683 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109683
Dawson, T.G., Kurfess, T.: Quantification of tool wear using white light interferometry and three-dimensional computational metrology. Undefined, 2005, Accessed: Oct. 18, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Quantification-of-toolwear-using-white-light-and-Dawson-Kurfess/eacc9a87f117bd8a7b9c36dc50cea28cb580cf90
**ong, G., Liu, J., Avila, A.: Cutting tool wear measurement by using active contour model based image processing. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Bei**g, China, pp. 670–675 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMA.2011.5985741
Prasad, K. N., Ramamoorthy, B.: Tool wear evaluation by stereo vision and prediction by artificial neural network. Undefined, 2001. Accessed: Oct. 18, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Tool-wear-evaluation-by-stereo-vision-and-byneural-Prasad-Ramamoorthy/35359076d898f2d10219cb805828be893653a4ca
Iliyas Ahmad, M., Yusof, Y., Daud, M.E., Latiff, K., AbdulKadir, A.Z., Saif, Y.: Machine monitoring system: a decade in review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 108(11), 3645–3659 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05620-3
Teti, R., Jemielniak, K., O’Donnell, G., Dornfeld, D.: Advanced monitoring of machining operations. CIRP Ann. 59(2), 717–739 (2010)
Thakre, A.A., Lad, A.V., Mala, K.: Measurements of tool wear parameters using machine vision system. Model. Simul. Eng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1876489
Wang, Y., Jia, X., Li, X., Yang, S., Zhao, H., Lee, J.: A machine vision-based monitoring system for the LCD panel cutting wheel degradation. Procedia Manuf. 48, 49–53 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2020.05.019
Fernández-Robles, L., Azzopardi, G., Alegre, E., Petkov, N.: Machine-vision-based identification of broken inserts in edge profile milling heads. Robot. Comput.-Integrated Manuf. 44, 276–283 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2016.10.004
Kurada, S., Bradley, C.: A review of machine vision sensors for tool condition monitoring. Comput. Ind.. Ind. 34(1), 55–72 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-3615(96)00075-9
Choudhary, A. K. , AhmadKhan D.: Introduction to conditioning monitoring of mechanical systems. Soft Comput. Cond. Monit. Diagn. Electr. Mech. Syst. (2020) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1532-3_9
Liu, W., Li, X., Jia, Z., Yan, H., Ma, X.: A three-dimensional triangular vision-based contouring error detection system and method for machine tools. Precis. Eng. 50, 85–98 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2017.04.016
Nath, C.: Integrated tool condition monitoring systems and their applications: a comprehensive review. Procedia Manuf. 48, 852–863 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2020.05.123
Zhang, C., Zhang, J.: On-line tool wear measurement for ball-end milling cutter based on machine vision. Comput. Ind.. Ind. 64(6), 708–719 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2013.03.010
Ge, L., Dan, D., Li, H.: An accurate and robust monitoring method of full-bridge traffic load distribution based on YOLO-v3 machine vision. Struct. Control. Health Monit.. Control. Health Monit. 27(12), e2636 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2636
Chen, M.-C.: Roundness measurements for discontinuous perimeters via machine visions. Comput. Ind.. Ind. 47(2), 185–197 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-3615(01)00143-9
Peng, R., Liu, J., Fu, X., Liu, C., Zhao, L.: Application of machine vision method in tool wear monitoring. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 116(3), 1357–1372 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07522-4
Ambadekar, P.K., Choudhari, C.M.: CNN based tool monitoring system to predict life of cutting tool. SN Appl. Sci. 2(5), 1–11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2598-2
Wong, S.Y., Chuah, J.H., Yap, H.J.: Technical data-driven tool condition monitoring challenges for CNC milling: a review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 107(11), 4837–4857 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05303-z
Hou, Q., Sun, J., Huang, P.: A novel algorithm for tool wear on-line inspection based on machine vision. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 101(9), 2415–2423 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3080-9
Chen, W., Teng, X., Huo, D., Wang, Q.: An improved cutting force model for micro milling considering machining dynamics. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 93(9), 3005–3016 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0706-2
Peng, R., Pang, H., Jiang, H., Hu, Y.: Study of tool wear monitoring using machine vision. Autom. Control. Comput. Sci.. Control. Comput. Sci. 54(3), 259–270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411620030062
García-Ordás, M.T., Alegre, E., González-Castro, V., Alaiz-Rodríguez, R.: A computer vision approach to analyze and classify tool wear level in milling processes using shape descriptors and machine learning techniques. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 90(5), 1947–1961 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9541-0
Sun, W.-H., Yeh, S.-S.: Using the machine vision method to develop an on-machine insert condition monitoring system for computer numerical control turning machine tools. Materials (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101977
Szydłowski, M., Powałka, B., Matuszak, M., Kochmański, P.: Machine vision micro-milling tool wear inspection by image reconstruction and light reflectance. Precis. Eng. 44, 236–244 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.01.003
Čerče, L., Pušavec, F., Kopač, J.: 3D cutting tool-wear monitoring in the process. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 29(9), 3885–3895 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-015-0834-2
Wei, W., Yin, J., Zhang, J., Zhang, H., Lu, Z.: Wear and breakage detection of integral spiral end milling cutters based on machine vision. Materials (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195690
Loizou, J., Tian, W., Robertson, J., Camelio, J.: Automated wear characterization for broaching tools based on machine vision systems. J. Manuf. Syst. 37, 558–563 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2015.04.005
Lee, W.K., Ratnam, M.M., Ahmad, Z.A.: Detection of fracture in ceramic cutting tools from workpiece profile signature using image processing and fast Fourier transform. Precis. Eng. 44, 131–142 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.11.001
Prabhu, S., Karthik Saran, S., Majumder, D., Siva Teja, P.V.: A review on applications of image processing in inspection of cutting tool surfaces. Appl. Mech. Mater. 766–767, 635–642 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.766-767.635
Jywe, W.-Y., Hsieh, T.-H., Chen, P.-Y., Wang, M.-S., Lin, Y.-T.: Evaluation of tool scra** wear conditions by image pattern recognition system. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 105(1), 1791–1799 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04360-3
García-Ordás, M.T., Alegre-Gutiérrez, E., González-Castro, V., Alaiz-Rodríguez, R.: Combining shape and contour features to improve tool wear monitoring in milling processes. Int. J. Prod. Res. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1435919
Kalil, J., Schueller, K., Pinto, F. de A. C., Villibor, G. P.: Monitoring of flank wear and damage on turning cutting tools by image processing. J. Eng. Exact Sci. (2020) https://doi.org/10.18540/jcecvl6iss2pp0098-0106.
Zawawi, M. A. M. , Teoh, S. S., Abdullah, N. B., Mohd Sazali, M. I. S. (Eds.) In: 10th International Conference on Robotics, Vision, Signal Processing and Power Applications: Enabling Research and Innovation Towards Sustainability, vol. 547. Singapore: Springer Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6447-1.
Ho, S.-Y., Lee, K., Chen, S.-S., Ho, S.-J.: Accurate modeling and prediction of surface roughness by computer vision in turning operations using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Undefined (2002). Accessed: Oct. 19, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Accurate-modeling-and-prediction-of-surface-by-in-HoLee/7d476bb348e8a0819605ec31b46f9e2a9afce96d
Kapłonek, W., Nadolny, K.: Laser methods based on an analysis of scattered light for automated, in-process inspection of machined surfaces: a review. Optik 126(20), 2764–2770 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.07.009
Sun, T.-H., Tien, F.-C., Tien, F.-C., Kuo, R.-J.: Automated thermal fuse inspection using machine vision and artificial neural networks. J. Intell. Manuf.Intell. Manuf. 27(3), 639–651 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0902-y
Wang, J., Qian, J., Ferraris, E., Reynaerts, D.: In-situ process monitoring and adaptive control for precision micro-EDM cavity milling. Precis. Eng. 47, 261–275 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.09.001
Priya, P., Ramamoorthy, B.: The influence of component inclination on surface finish evaluation using digital image processing. Undefined, 2007, Accessed: Oct. 19, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-influence-of-componentinclination-on-surface-Priya-Ramamoorthy/e79433a0f6e0fe63dfb01f82822f36cbdc8f93c9
Gadelmawla, E.S., Eladawi, A.E., Abouelatta, O.B., Elewa, I.M.: Investigation of the cutting conditions in milling operations using image texture features. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 222(11), 1395–1404 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1243/09544054JEM1173
Tian, H., Wang, D., Lin, J., Chen, Q., Liu, Z.: Surface defects detection of stam** and grinding flat parts based on machine vision. Sensors 20(16), 4531 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20164531
Fekri-Ershad, S.: Texture image analysis and texture classification methods—a review. vol. 2, p. 29 (2019).
“Image Processing with NI Vision Development Module.” https://www.ni.com/en-lb/innovations/white-papers/06/image-processing-withni-vision-development-module.html (accessed Oct. 19, 2021).
Baaziz, N., Abahmane, O., Missaoui, R.: Texture feature extraction in the spatial-frequency domain for content-based image retrieval. p. 19
Wang, W., Wong, Y.S., Hong, G.S.: Flank wear measurement by successive image analysis. Comput. Ind.. Ind. (2005). https://doi.org/10.5555/1672858.1672934
Ong, P., Lee, W.K., Lau, R.J.H.: Tool condition monitoring in CNC end milling using wavelet neural network based on machine vision. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 104(1), 1369–1379 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04020-6
Ambadekar, P.K., Choudhari, D.C.M.: Application of gray level co-occurrence matrix as a feature extraction technique to monitor wear of cutting tool. p. 9 (2018)
Jurkovic, J., Korosec, M., Kopac, J.: New approach in tool wear measuring technique using CCD vision system. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf 45(9), 1023–1030 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.11.030
Lutz, B., Kisskalt, D., Regulin, D., Reisch, R., Schiffler, A., Franke, J.: Evaluation of deep learning for semantic image segmentation in tool condition monitoring. In: 2019 18th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019, pp. 2008–2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLA.2019.00321.
Li, X.: A brief review: acoustic emission method for tool wear monitoring during turning. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf 42(2), 157–165 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(01)00108-0
Zhang, Y., Qi, X., Wang, T., He, Y.: Tool wear condition monitoring method based on deep learning with force signals. Sensors. 23(10), 4595 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104595
Machikhin, A., Poroykov, A., Bardakov, V., Marchenkov, A., Zhgut, D., Sharikova, M., Barat, V., Meleshko, N., Kren, A.: Combined acoustic emission and digital image correlation for early detection and measurement of fatigue cracks in rails and train parts under dynamic loading. Sensors. 22(23), 9256 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: DRP; Methodology: ADO; Formal analysis and investigation: MK; Writing—original draft preparation: DRP; Writing—DRP and ADO; Supervision: DRP.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, D.R., Oza, A.D. & Kumar, M. Integrating intelligent machine vision techniques to advance precision manufacturing: a comprehensive survey in the context of mechatronics and beyond. Int J Interact Des Manuf (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-023-01635-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-023-01635-8