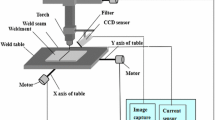
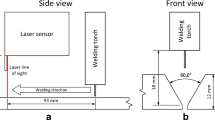
Abstract
Welding distortions, assembly errors, and deviation correction between the welding torch and weld beads play a significant role in the automatic welding system of the boiler tube wall cladding. As a result, this paper proposes a seam tracking system comprised of two parts: a contact displacement sensor for data acquisition and an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) controller along with the backpropagation (BP) algorithm for controlling the position and posture of the welding torch. The results showed that the proposed ANFIS controller achieves a faster rise time of up to 0.06 s, settling time of about 0.1 s, overshooting up to 1.5%, and amplitude stability with the lowest training error up to 2 × 10−4 mm. In contrast, the fuzzy logic controller achieves a rise time of up to 0.075 s, a settling time of around 0.3 s, and a 0.5% overshoot. Also, the proportional–integral–derivative (PID) controller executes a lower rise time of up to 0.035 s, a settling time of about 0.25 s, and an overshoot of up to 9.34%. According to the results, the ANFIS controller performs better than the PID and fuzzy logic controllers. Thus, the proposed system offers a much-improved functionality in terms of flexibility, consistency, and cladding layer surface finish of the treated components. It fully meets the requirements of the welding torch control motion for seam tracking. It can also be used to create automatic seam tracking systems for other types of surface treatment.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rout, A., Deepak, B.B.V.L., Biswal, B.B.: Advances in weld seam tracking techniques for robotic welding: a review. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 56, 12–37 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2018.08.003
Chen, S., Liu, J., Chen, B., Suo, X.: Universal fillet weld joint recognition and positioning for robot welding using structured light. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2021.102279
Geng, Y., Zhang, Y., Tian, X., Shi, X., Wang, X., Cui, Y.: A novel welding path planning method based on point cloud for robotic welding of impeller blades. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 119, 8025–8038 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08573-3
Tian, S., Xu, F., Zhang, G., Saifan, A., Saleh, B., Li, X.: Influence of post-weld heat treatment on microstructure and toughness properties of 13MnNiMoR high strength low alloy steel weld joint. Materials (Basel). 14, 5336 (2021)
Liu, Y., Liu, J., Tian, X.: An approach to the path planning of intersecting pipes weld seam with the welding robot based on non-ideal models. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 55, 96–108 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2018.07.010
Liu, J., Jiao, T., Li, S., Wu, Z., Chen, Y.F.: Automatic seam detection of welding robots using deep learning. Autom. Constr. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104582
Lu, S., Shi, X., Tian, X., Liu, Y.: Weld seam extraction of intersecting pipelines based on point cloud entropy. In: 11th data driven control and learning systems conference, August 5–7, (2022), Emeishan, China, pp. 385–390
Xu, F., Xu, Y., Zhang, H., Chen, S.: Application of sensing technology in intelligent robotic arc welding: a review. J. Manuf. Process. 79, 854–880 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.05.029
Songya, T., Saifan, A., Pengqian, G., Dawy, I., Saleh, B.: Development of an automatic welding system for the boiler tube walls weld overlay. Metals (Basel). 10, 1–16 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091241
Dutra, J.C., Bonacorso, N.G., Silva, R.H.G.E., Carvalho, R.S., Silva, F.C.: Development of a flexible robotic welding system for weld overlay cladding of thermoelectrical plants’ boiler tube walls. Mechatronics 24, 416–425 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechatronics.2014.03.002
Gao, F., Chen, Q., Guo, L.: Study on arc welding robot weld seam touch sensing location method for structural parts of hull. In: ICCAIS 2015 - 4th international conference on control, automation and information science, (2015), pp. 42–46
Bae, K.Y., Park, J.H.: A study on development of inductive sensor for automatic weld seam tracking. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 176, 111–116 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.02.020
Jeong, S.K., Lee, G.Y., Lee, W.K., Kim, S.B.: Development of high speed rotating arc sensor and seam tracking controller for welding robots. In: IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics, (2001), pp. 845–850
Mahajan, A., Figueroa, F.: Intelligent seam tracking using ultrasonic sensors for robotic welding. Robotica 15, 275–281 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0263574797000313
Mao, Y., Xu, G.: A real-time method for detecting weld deviation of corrugated plate fillet weld by laser vision sensor. Optik (Stuttg) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.168786
Dinham, M., Fang, G.: Autonomous weld seam identification and localisation using eye-in-hand stereo vision for robotic arc welding. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 29, 288–301 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2013.01.004
Xue, K., Wang, Z., Shen, J., Hu, S., Zhen, Y., Liu, J., Wu, D., Yang, H.: Robotic seam tracking system based on vision sensing and human-machine interaction for multi-pass MAG welding. J. Manuf. Process. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.02.026
Fang, Z., Weng, W., Wang, W., Zhang, C., Yang, G.: A vision-based robotic laser welding system for insulated mugs with fuzzy seam tracking control. Symmetry (Basel). 11, 1–15 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111385
Fan, J., **g, F., Yang, L., Long, T., Tan, M.: A precise seam tracking method for narrow butt seams based on structured light vision sensor. Opt. Laser Technol. 109, 616–626 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.08.047
Xu, Y., Yu, H., Zhong, J., Lin, T., Chen, S.: Real-time seam tracking control technology during welding robot GTAW process based on passive vision sensor. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212, 1654–1662 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.03.007
Shen, H., Lin, T., Chen, S., Li, L.: Real-time seam tracking technology of welding robot with visual sensing. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. Theory Appl. 59, 283–298 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-010-9403-1
Jiang, R., Shankaran, R., Wang, S., Chao, T.: A proportional, integral and derivative differential evolution algorithm for global optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117669
K. Wang, J. Zhang, B. Zhao, D. Tang, Research on control technology of trajectory tracking for robotic welding, in: Int. Conf. Comput. Intell. Softw. Eng. CiSE 2010, 2010: pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/CISE.2010.5676764.
Morgan, A.A.A., Al-Mufadi, F.A.: A novel method to improve weld uniformity by automatic control of current intensity. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 8, 17–25 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3844/ajeassp.2015.17.25
Fallaha, C.J., Saad, M., Kanaan, H.Y., Al-Haddad, K.: Sliding-mode robot control with exponential reaching law. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58, 600–610 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2010.2045995
Zhang, H., Ding, X., Chen, M., Da, B., Zou, C.: The seam tracking system for submerged arc welding. In: Tarn, T.-J., Zhou, C., Chen, S.-B. (eds.) Robotic Welding, Intelligence and Automation, pp. 144–151. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Fang, Z., Xu, D., Tan, M.: A vision-based self-tuning fuzzy controller for fillet weld seam tracking. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatr. 16, 540–550 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMECH.2010.2045766
Chen, S.B., Zhao, D.B., Lou, Y.J., Wu, L.: Computer vision sensing and intelligent control of welding pool dynamics. In: Tarn, T.-J., Zhou, C., Chen, S.-B. (eds.) Robotic Welding, Intelligence and Automation, pp. 25–55. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Zhang, T., Li, K., Yang, J.: Seam tracking control for mobile welding robot based on vision sensor. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 17, 1320–1326 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-010-0637-7
Kaneko, Y., Yamane, S., Kubota, T., Ohshima, K.: Neural network and fuzzy control in the welding robots using CCD camera and touch sensor. In: Proceedings 1993 international joint conference neural networks neural, (1993), pp. 677–680
Zou, Y., Wang, Y., Zhou, W., Chen, X.: Real-time seam tracking control system based on line laser visions. Opt. Laser Technol. 103, 182–192 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.01.010
Xu, F., Lv, Y., Liu, Y., Shu, F., He, P., Xu, B.: Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Inconel 625 alloy during pulsed plasma Arc deposition process. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29, 480–488 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.02.010
Balamurugan, S., Umarani, A.: Study of discrete PID controller for DC motor speed control using MATLAB. In: 2020 international conference computer information technology ICCIT 2020, (2020) pp. 358–363
Duarte-Galvan, C., Torres-Pacheco, I., Guevara-Gonzalez, R.G., Romero-Troncoso, R.J., Contreras-Medina, L.M., Rios-Alcaraz, M.A., Millan-Almaraz, J.R.: Review. Advantages and disadvantages of control theories applied in greenhouse climate control systems, Spanish. J. Agric. Res. 10, 926 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5424/sjar/2012104-487-11
Jiang, Y., Yang, C., Ma, H.: A review of fuzzy logic and neural network based intelligent control design for discrete-time systems. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7217364
Jang, J.-S.R.: ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 23, 665–685 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/21.256541
Omar, B.A.A., Haikal, A.Y.M., Areed, F.F.G.: Design adaptive neuro-fuzzy speed controller for an electro-mechanical system. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2, 99–107 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2011.07.003
Petković, D., Ćojbašić, Ž, Nikolić, V., Shamshirband, S., Kiah, M.L.M., Anuar, N.B., Wahab, A.W.A.: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy maximal power extraction of wind turbine withcontinuously variable transmission. Energy. 64, 868–874 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.10.094
Petković, D., Issa, M., Pavlović, N.D., Zentner, L., Ćojbašić, Ž: Adaptive neuro fuzzy controller for adaptive compliant robotic gripper. Expert Syst. Appl. 39, 13295–13304 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.05.072
Shamshirband, S., Petković, D., Anuar, N.B., Kiah, M.L.M., Akib, S., Gani, A., Ćojbašić, Ž, Nikolić, V.: Sensorless estimation of wind speed by adaptive neuro-fuzzy methodology. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 62, 490–495 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2014.04.065
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance provided by the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and Hohai University during this work. We also thank the ANSO scholarship for young talents and the UCAS scholarship for international students for their support.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saifan, A., Chen, S., Saifan, S. et al. Seam tracking control for weld cladding of boiler tubes in thermal power plants. Int J Interact Des Manuf 18, 1709–1729 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-023-01205-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-023-01205-y