Abstract
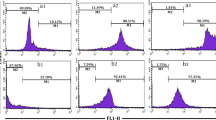
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (S. maltophilia) is a spoilage microorganism widely distributed in vegetables, dairy products, and various environments and can cause serious foodborne illnesses. Renowned for its environmentally friendly, safe, and non-toxic properties, rose essential oil (REO) is widely recognized as an exceptional natural antibacterial agent. In the present study, we conducted a comprehensive analysis to elucidate the inhibition mechanism of REO against S. maltophilia at both cellular and metabolic levels. The results demonstrated that REO treatment of cells resulted in the disruption of cell structure and leakage of cellular contents. Remarkable changes in the morphology of bacterial cells were observed under both scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. At the metabolic level, multiple metabolic pathways were disrupted after REO treatment, including amino acid metabolism, nucleotide metabolism, and aminoacyl tRNA biosynthesis. These results shed new light to the inhibition mechanism of REO against S. maltophilia and provide a theoretical basis for the development of effective essential oil preservatives.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Androutsopoulou, C., Christopoulou, D., Hahalis, S. P., Kotsalou, C., Lamari, F. N., & Vantarakis, A. (2021). Evaluation of essential oils and extracts of rose geranium and rose petals as natural preservatives in terms of toxicity, antimicrobial, and antiviral activity. Pathogens, 10, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10040494
Cebi, N., Arici, M., & Sagdic, O. (2021). The famous Turkish rose essential oil: Characterization and authenticity monitoring by FTIR, Raman and GC–MS techniques combined with chemometrics. Food Chemistry, 354, 129495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129495
Chanyi, R. M., Koval, S. F., & Brooke, J. S. (2016). Stenotrophomonas maltophilia biofilm reduction by Bdellovibrio exovorus. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 8, 343–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12384
Chazelas, E., Pierre, F., Druesne-Pecollo, N., Esseddik, Y., de Edelenyi, F. S., Agaesse, C., De Sa, A., Lutchia, R., Gigandet, S., Srour, B., Debras, C., Huybrechts, I., Julia, C., Kesse-Guyot, E., Allès, B., Zelek, L., Galan, P., Hercberg, S., Deschasaux-Tanguy, M., & Touvier, M. (2022). Abstract P1–09–01: Breast and prostate cancer risk associated with nitrites and nitrates from food additives: Results from the NutriNet-Santé cohort. Cancer Research, 82, P1–09–01. https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.Sabcs21-p1-09-01
Cheng, M., Yan, X., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Zhao, P., & Wang, J. (2023). Fabrication, characterization, and antifungal assessment of oregano essential oil-loaded nano-silica against Curvularia lunata in brown rot of Agaricus bisporus storage. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03125-x
Cui, H., Zhang, C., Li, C., & Lin, L. (2018). Antimicrobial mechanism of clove oil on Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control, 94, 140–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.07.007
Dallagnol, A. M., Barrio, Y., Cap, M., Szerman, N., Castellano, P., Vaudagna, S. R., & Vignolo, G. (2017). Listeria inactivation by the combination of high hydrostatic pressure and Lactocin AL705 on cured-cooked pork loin slices. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10, 1824–1833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1956-6
Dinkova, R., Vardakas, A., Dimitrova, E., Weber, F., Passon, M., Shikov, V., & Schieber, & A., Mihalev, K. (2022). Valorization of rose (Rosa damascena Mill.) by-product: Polyphenolic characterization and potential food application. European Food Research and Technology, 248, 2351–2358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-022-04051-6
El Khetabi, A., Lahlali, R., Ezrari, S., Radouane, N., Lyousfi, N., Banani, H., Askarne, L., Tahiri, A., El Ghadraoui, L., Belmalha, S., & Barka, E. A. (2022). Role of plant extracts and essential oils in fighting against postharvest fruit pathogens and extending fruit shelf life: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 120, 402–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2022.01.009
Erickson, M. C., & Doyle, M. P. (2017). The challenges of eliminating or substituting antimicrobial preservatives in foods. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 8, 371–390. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-food-030216-025952
Gateva, S., Jovtchev, G., Angelova, T., Dobreva, A., & Mileva, M. (2022). The anti-genotoxic activity of wastewaters produced after water-steam distillation of bulgarian Rosa damascena Mill. and Rosa alba L. Essential Oils. Life, 12(3), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030455
Gibb, J., & Wong, D. W. (2021). Antimicrobial treatment strategies for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A focus on novel therapies. Antibiotics, 10(10), 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10101226
Guo, F., Liang, Q., Zhang, M., Chen, W., Chen, H., Yun, Y., Zhong, Q., & Chen, W. (2021). Antibacterial activity and mechanism of linalool against Shewanella putrefaciens. Molecules, 26, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010245
Gupta, S., Cox, S., Rajauria, G., Jaiswal, A. K., & Abu-Ghannam, N. (2012). Growth inhibition of common food spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms in the presence of brown seaweed extracts. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5, 1907–1916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0502-6
Hao, J., Wu, T., Li, H., & Liu, H. (2017). Differences of bactericidal efficacy on Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtilis of slightly and strongly acidic electrolyzed water. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10, 155–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1801-3
Heydari, N., Abootalebi, M., Jamalimoghadam, N., Kasraeian, M., Emamghoreishi, M., & Akbarzaded, M. (2018). Evaluation of aromatherapy with essential oils of Rosa damascena for the management of premenstrual syndrome. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics, 142, 156–161. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.12534
Ju, J., **e, Y., Guo, Y., Cheng, Y., Qian, H., & Yao, W. (2019). The inhibitory effect of plant essential oils on foodborne pathogenic bacteria in food. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 59, 3281–3292. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1488159
Kant, R., & Kumar, A. (2022). Review on essential oil extraction from aromatic and medicinal plants: Techniques, performance and economic analysis. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 30, 100829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2022.100829
Katekar, V. P., Rao, A. B., & Sardeshpande, V. R. (2022). Review of the rose essential oil extraction by hydrodistillation: An investigation for the optimum operating condition for maximum yield. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 29, 100783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2022.100783
Kumar, N., Rahul, K., Gniewosz, M., & Kieliszek, M. (2023). Characterization of aloe vera gel-based edible coating with orange peel essential oil and its preservation effects on button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03107-z
Lee, C. H., Woo, H. J., Kang, J. H., & Song, K. B. (2021). Electrostatic spraying of passion Fruit (Passiflora Edulis L.) peel extract for inactivation of Escherichia Coli O157: H7 and Listeria monocytogenes on fresh-cut lollo rossa and beetroot leaves. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14, 898–908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02608-z
Li, Q., & Hoppe, T. (2023). Role of amino acid metabolism in mitochondrial homeostasis. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 11, 1127618. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2023.1127618
Li, D., Wong, C. H., Seet, M. F., & Kuan, N. (2019). Isolation, characterization, and inactivation of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia from leafy green vegetables and urban agriculture systems. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 2718. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02718
Li, J., Li, C., Shi, C., Aliakbarlu, J., Cui, H., & Lin, L. (2022). Antibacterial mechanisms of clove essential oil against Staphylococcus aureus and its application in pork. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 380, 109864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109864
Liang, C., Huang, S., Geng, Y., Huang, X., Chen, D., Lai, W., Guo, H., Deng, H., Fang, J., Yin, L., & Ouyang, P. (2021). A study on the antibacterial mechanism of thymol against Aeromonas hydrophila in vitro. Aquaculture International, 30, 115–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-021-00789-0
Lin, L., Gu, Y., Li, C., Vittayapadung, S., & Cui, H. (2018). Antibacterial mechanism of ε -poly-lysine against Listeria monocytogenes and its application on cheese. Food Control, 91, 76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.03.025
Liu, Y., Pang, X., Song, J., Liu, X., Song, J., Yuan, Y., & Zhao, C. (2019). Exploring the membrane toxicity of decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE): Based on cell membranes and lipid membranes model. Chemosphere, 216, 524–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.140
Naganuma, T., Iinuma, Y., Nishiwaki, H., Murase, R., Masaki, K., & Nakai, R. (2018). Enhanced bacterial growth and gene expression of D-amino acid dehydrogenase with D-glutamate as the sole carbon source. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 2097. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02097
Ni, Z. J., Wang, X., Shen, Y., Thakur, K., Han, J., Zhang, J. G., Hu, F., & Wei, Z. J. (2021). Recent updates on the chemistry, bioactivities, mode of action, and industrial applications of plant essential oils. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 110, 78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.070
Ning, Y., Hou, L., Ma, M., Li, M., Zhao, Z., Zhang, D., Wang, Z., & Jia, Y. (2022). Synergistic antibacterial mechanism of sucrose laurate combined with nisin against Staphylococcus aureus and its application in milk beverage. LWT, 158, 113145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113145
Nonato, F. R., Santana, D. G., de Melo, F. M., dos Santos, G. G., Brustolim, D., Camargo, E. A., de Sousa, D. P., Soares, M. B., & Villarreal, C. F. (2012). Anti-inflammatory properties of rose oxide. International Immunopharmacology, 14, 779–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2012.10.015
Patra, J. K., & Baek, K. H. (2016). Antibacterial activity and action mechanism of the essential oil from Enteromorpha linza L. against foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Molecules, 21, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030388
Qiu, L., Zhang, M., Adhikari, B., & Chang, L. (2023). Microencapsulation of rose essential oil using perilla protein isolate-sodium alginate complex coacervates and application of microcapsules to preserve ground beef. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 16(2), 368–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02944-8
Rocha, V. F. D., Cavalcanti, T. P., Azevedo, J., Leal, H. F., Silva, G. E. O., Malheiros, A. R. X., Ataide, L. A., Lima, J. A., Almeida, A. R. P., Khouri, N. D., Reis, M. G., & Reis, J. N. (2021). Outbreak of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Burkholderia cepacia bloodstream infections at a hemodialysis Center. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 104, 848–853. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.20-1035
Shiratsuchi, H., Chang, S., Wei, A., El-Ghorab, A. H., & Shibamoto, T. (2020). Biological activities of low-molecular weight compounds found in foods and plants. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 20. https://doi.org/10.38212/2224-6614.2131
Shu, H., Zhang, W., Yun, Y., Chen, W., Zhong, Q., Hu, Y., Chen, H., & Chen, W. (2020). Metabolomics study on revealing the inhibition and metabolic dysregulation in Pseudomonas fluorescens induced by 3-carene. Food Chemistry, 329, 127220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127220
Simons, K. (2016). Cell membranes: A subjective perspective. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 1858, 2569–2572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.01.023
Sweet, R., Kroon, P. A., & Webber, M. A. (2022). Activity of antibacterial phytochemicals and their potential use as natural food preservatives. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2121255
Tang, Z., Chen, H., Zhang, M., Fan, Z., Zhong, Q., Chen, W., Yun, Y. H., & Chen, W. (2021). Antibacterial mechanism of 3-carene against the meat spoilage bacterium Pseudomonas lundensis and its application in pork during refrigerated storage. Foods, 11(1), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010092
Teixeira, J. S., Seeras, A., Sanchez-Maldonado, A. F., Zhang, C., Su, M. S.-W., & Gänzle, M. G. (2014). Glutamine, glutamate, and arginine-based acid resistance in Lactobacillus reuteri. Food Microbiology, 42, 172–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2014.03.015
Tian, L., Wang, X., Liu, R., Zhang, D., Wang, X., Sun, R., Guo, W., Yang, S., Li, H., & Gong, G. (2021). Antibacterial mechanism of thymol against Enterobacter sakazakii. Food Control, 123, 107716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107716
Ul Hoque, M. I., Chowdhury, A. N., Islam, M. T., Firoz, S. H., Luba, U., Alowasheeir, A., Rahman, M. M., Rehman, A. U., Ahmad, S. H. A., Holze, R., Hossain, M. S. A., Rahman, S., Donne, S. W., & Kaneti, Y. V. (2021). Fabrication of highly and poorly oxidized silver oxide/silver/tin(IV) oxide nanocomposites and their comparative anti-pathogenic properties towards hazardous food pathogens. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 408, 124896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124896
Wang, K., Ge, Q., Shao, X., Wei, Y., Zhang, X., Wang, H., & Xu, F. (2023). The antifungal efficacy of flavonoids from sedum aizoon L. on grapes. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03165-3
Yi, F., Sun, J., Bao, X., Ma, B., & Sun, M. (2019). Influence of molecular distillation on antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of rose essential oils. Lwt, 102, 310–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.12.051
Yuan, H., Xu, Y., Chen, Y., Zhan, Y., Wei, X., Li, L., Wang, D., He, P., Li, S., & Chen, S. (2019). Metabolomics analysis reveals global acetoin stress response of Bacillus licheniformis. Metabolomics, 15, 25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1492-7
Yuan, Y. H., Liu, L. X., Guo, L., Wang, L., Hao, J. W., & Liu, Y. G. (2022). Changes of bacterial communities and volatile compounds developed from the spoilage of white Hypsizygus marmoreus under different storage conditions. Lwt, 168, 113906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113906
Zeinhom, M. M. A., Hassan, G. M., Salem, H. A. M., & Corke, H. (2021). Prevalence and survival of Stenotrophomonas species in milk and dairy products in egypt. Foodborne Pathogens and Disease, 18, 337–345. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2020.2893
Zengin, N., Yuzbasioglu, D., Unal, F., Yilmaz, S., & Aksoy, H. (2011). The evaluation of the genotoxicity of two food preservatives: Sodium benzoate and potassium benzoate. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 49, 763–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.11.040
Zhai, Q., **ao, Y., Narbad, A., & Chen, W. (2018). Comparative metabolomic analysis reveals global cadmium stress response of Lactobacillus plantarumstrains. Metallomics, 10, 1065–1077. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8mt00095f
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Program in Shandong Province (No. 2019YYSP026), Linyi Key Research and Development Project (No. 2020ZX028), and the Central Funds for Guiding the Local Scientific and Technological development (No. YDZX2023036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu-Han Yuan: conceptualization, methodology, and writing—original draft. Wen-Liang Wang: investigation and formal analysis. Ling-**ao Liu: formal analysis and writing—original draft. Li Guo: visualization and supervision. **ng-Jiang Li: resources and investigation. Yun-Guo Liu: conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, supervision, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, YH., Wang, WL., Liu, LX. et al. Anti-Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Mechanism of Rose Essential Oil: A Metabolomic Study. Food Bioprocess Technol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03285-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03285-w