Abstract
Purpose of Review
Peyronie’s disease (PD) is a scarring condition of the tunica albuginea. Various graft materials are used to fill defects following plaque incision (PIG) or partial excision (PEG), but the optimal graft material remains unknown. This systematic review compares outcomes of different grafts, performed with or without concurrent penile prosthesis implantation (PPI).
Recent Findings
Studies reported quantitative curvature assessment, with adequate follow-up to assess straightening, change in penile length, postoperative erectile dysfunction (ED), and patient satisfaction. From a total of 41 study arms, 1732 patients underwent PEG/PIG without and 302 with PPI. For PIG/PEG without PPI, the most frequently used grafts are cadaveric human pericardium (38.3%), autologous saphenous vein (21.2%), and porcine small intestinal submucosa (13.5%) with reported mean preoperative curvature of 69.3° and curvature recurrence ≥ 30° in 6.6%, 5.4%, and 15.4%, respectively. Grafts used most commonly with PPI include hemostatic patches (36.4%), bovine pericardium (34.8%), with similar mean preoperative curvature of 70.0° (p < 0.01). Satisfaction rates for PIG/PEG without PPI ranged from 70 to 100% with lowest satisfaction rates associated with dermis (70%) and human pericardium (73.4%). In the prosthesis cohort, satisfaction rates exceeded 88% with all grafts.
Summary
Human pericardium seems to be the most commonly used graft when PPI is not indicated, with low rates of curvature recurrence, an acceptable rate of ED and satisfaction. Hemostatic patches are the most favorable graft choice with concurrent PPI. In general, the PD treatment literature is limited to low evidence grade retrospective studies, and further prospective investigation is warranted.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Available upon request.
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Arafa M, Eid A, Ezz-Eldine K, Shamloul R. The prevalence of Peyronie’s disease in diabetic patients with erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2007;19:213–7.
Dibenedetti DB, Nguyen D, Zografos L, Ziemiecki R, Zhou X. A population-based study of Peyronie’s disease: prevalence and treatment patterns in the United States. Ther Adv Urol. 2011;2011:282503.
Levine L, Lenting EL. A surgical algorithm for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Urology. 1997;158:2149–52.
Ralph D, Gonzalez-Cadavid N, Mirone V, Perovic S, Sohn M, Usta M, et al. The management of Peyronie’s disease: evidence-based 2010 guidelines. J Sex Med. 2010;7(7):2359–74.
Hatzichristou DG, Hatzimouratidis K, Apostolidis A, Tzortzis V, Bekos A, Ioannidis E. Corporoplasty using tunica albuginea free grafts for penile curvature: surgical technique and long-term results. J Urol. 2002;167:1367–70.
Lowsley OS, Boyce WH. Further experiences with an operation for the cure of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 1950;63:888–902.
Garcia-Gomez B, Ralph D, Levine L, Moncada-Iribarren I, D**ovic R, Albersen M, et al. Grafts for Peyronie’s disease: a comprehensive review. Andrology. 2018;6(1):117–26.
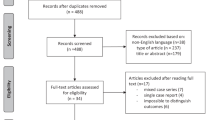
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336–41.
Innovation VH. Covidence systematic review software. www.covidence.org. Accessed 16 May 2020 to 27 Oct 2020.
Center for Evidence Based Medicine. www.cebm.net. Published 2016. Accessed July 5, 2020.
Adeniyi AA, Grooney SR, Pryor JP, Ralph DJ. The Lue procedure: an analysis of the outcome in Peyronis’ disease. Brit J Urol Int. 2002;89:404–8.
Backhaus BO, Muller SC, Albers P. Corporoplasty for advanced Peyronie’s disease using venous and/or dermis patch grafting: new surgical technique and long-term patient satisfaction. J Urol. 2003;169(3):981–4.
Bokarica P, Parazajder J, Mazuran B, Gilja I. Surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease based on penile length and degree of curvature. Int J Impot Res. 2005;17(2):170–4.
Breyer BN, Brant WO, Garcia MM, Bella AJ, Lue TF. Complications of porcine small intestine submucosa graft for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2007;177(2):589–91.
Cormio L, Mancini V, Massenio P, d’Altilia N, Selvaggio O, di Fino G, et al. Combined plaque incision, buccal mucosa grafting, and additional tunica albuginea plication for Peyronie’s disease. Sex Med. 2019;7(1):48–53.
Cormio L, Zucchi A, Lorusso F, Selvaggio O, Fioretti F, Porena M, et al. Surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease by plaque incision and grafting with buccal mucosa. Eur Urol. 2009;55(6):1469–75.
De Stefani S, Savoca G, Ciampalini S, Gattuccio I, Scieri F, Belgrano E. Saphenous vein harvesting by ‘strip**’ technique and ‘W’-shaped patch covering after plaque incision in treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res. 2000;12:293–301.
Flores S, Choi J, Alex B, Mulhall JP. Erectile dysfunction after plaque incision and grafting: short-term assessment of incidence and predictors. J Sex Med. 2011;8(7):2031–7.
• Hatzichristodoulou G. Introducing the ventral sealing technique using collagen fleece for surgical therapy of patients with ventral Peyronie’s curvature: initial experience. Int J Impot Res. 2018;30(6):306–11. This paper is one of the first to describe using collagen fleece hemostatic patches for Peyronie’s reconstruction.
Hauck EW, Bschleipfer T, Diemer T, Manning M, Schroeder-Printzen I, Weidner W. Long-term results of plaque thinning with carbide burs, small incision and venous grafting for correcting complex penile curvature in Peyronie’s disease: poor results of an “ideal” approach. J Urol. 2002;167:2070–3.
Hellstrom WJ, Reddy S. Application of pericardial graft in the surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2000;163:1445–7.
Hsu GL, Chen HS, Hsieh CH, Chen RM, Wen HS, Liu LJ, et al. Long-term results of autologous venous grafts for penile morphological reconstruction. J Androl. 2007;28(1):186–93.
Kadioglu A, Sanli O, Akman T, Cakan M, Erol B, Mamadov F. Surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease: a single center experience with 145 patients. Eur Urol. 2008;53(2):432–9.
Kalsi J, Minhas S, Christopher N, Ralph D. The results of plaque incision and venous grafting (Lue procedure) to correct the penile deformity of Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2005;95(7):1029–33.
Kalsi JS, Christopher N, Ralph DJ, Minhas S. Plaque incision and fascia lata grafting in the surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2006;98(1):110–4 discussion 114-115.
Knoll LD. Use of porcine small intestinal submucosal graft in the surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. Urology. 2001;57:753–7.
Knoll LD. Use of small intestinal submucosa graft for the surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2007;178(6):2474–8 discussion 2478.
Kovac JR, Brock GB. Surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction after dermal, pericardial, and small intestinal submucosal grafting for Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med. 2007;4(5):1500–8.
Leungwattanakij S, Bivalacqua TJ, Reddy S, Hellstrom WJ. Long-term follow-up on use of pericardial graft in the surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res. 2001;13:183–6.
Levine LA, Estrada CR. Human cadaveric pericardial graft for the surgical correction of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2003;170(6 Pt 1):2359–62.
Liu B, Li Q, Cheng G, Song N, Gu M, Wang Z. Surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease with autologous tunica vaginalis of testis. BMC Urol. 2016;16:1.
Montorsi F, Salonia A, Maga T, et al. Evidence based assessment of long-term results of plaque incision and vein grafting for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2000;163:1704–8.
Mulhall J, Anderson M, Parker M. A surgical algorithm for men with combined Peyronie’s disease and erectile dysfunction: functional and satisfaction outcomes. J Sex Med. 2005;2:132–8.
Rybak J, Papagiannopoulos D, Levine L. A retrospective comparative study of traction therapy vs. no traction following tunica albuginea plication or partial excision and grafting for Peyronie’s disease: measured lengths and patient perceptions. J Sex Med. 2012;9(9):2396–403.
Sansalone S, Garaffa G, D**ovic R, Pecoraro S, Silvani M, Barbagli G, et al. Long-term results of the surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease with Egydio’s technique: a European multicentre study. Asian J Androl. 2011;13(6):842–5.
Shioshvili TJ, Kakonashvili AP. The surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease: replacement of plaque by free autograft of buccal mucosa. Eur Urol. 2005;48(1):129–33 discussion 134-125.
Taylor FL, Abern MR, Levine LA. Predicting erectile dysfunction following surgical correction of Peyronie’s disease without inflatable penile prosthesis placement: vascular assessment and preoperative risk factors. J Sex Med. 2012;9(1):296–301.
Taylor FL, Levine LA. Surgical correction of Peyronie’s disease via tunica albuginea plication or partial plaque excision with pericardial graft: long-term follow up. J Sex Med. 2008;5(9):2221–8 discussion 2229-2230.
Usta MF, Bivalacqua TJ, Sanabria J, Koksal IT, Moparty K, Hellstrom WJG. Patient and partner satisfaction and long-term results after surgical treatment for Peyronie’s disease. Urology. 2003;62(1):105–9.
Valente P, Gomes C, Tomada N. Small intestinal submucosa grafting for Peyronie disease: outcomes and patient satisfaction. Urology. 2017;100:117–24.
Yafi FA, Diao L, DeLay KJ, et al. Multi-institutional prospective analysis of intralesional injection of collagenase clostridium histolyticum, tunical plication, and partial plaque excision and grafting for the management of Peyronie’s disease. Urology. 2018;120:138–42.
Yafi FA, Hatzichristodoulou G, Wang J, Anaissie J, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJ. Outcomes of surgical management of men with Peyronie’s disease with hourglass deformity. Urology. 2016;91:119–23.
Yurkanin JP, Dean R, Wessells H. Yurkanin-2001-Effect of incision and saphenous.pdf. J Urol. 2001;166:1769–73.
Zucchi A, Silvani M, Pastore AL, Fioretti F, Fabiani A, Villirillo T, et al. Corporoplasty using buccal mucosa graft in Peyronie disease: is it a first choice? Urology. 2015;85(3):679–83.
Wimpissinger F, Parnham A, Gutjahr G, Maksys S, Baierlein M, Stackl W. 10 years’ plaque incision and vein grafting for Peyronie’s. J Sex Med. 2016;13:120–8.
Chow AK, Sidelsky SA, Levine L. Surgical outcomes of plaque excision and grafting and supplemental tunica albuginea plication for treatment of Peyronie’s disease with severe compound curvature. J Sex Med. 2018;15:1021–9.
• Farrell MR, Abdelsayed GA, Ziegelmann MJ, Levine LA. A comparison of hemostatic patches versus pericardium allograft for the treatment of complex Peyronie’s disease with penile prosthesis and plaque incision. Urology. 2019;129:113–8. This is a comparison of multiple hemostatic patch types which compared Tachosil to pericardial grafting in men with penile prosthesis.
Pathak AS, Chang JH, Parekh AR, Aboseif SR. Use of rectus fascia graft for corporeal reconstruction during placement of penile implant. Urology. 2005;65(6):1198–201.
Egydio PH, Kuehhas FE, Sansalone S. Penile length and girth restoration in severe Peyronie’s disease using circular and longitudinal grafting. BJU Int. 2013;111(4 Pt B):E213–9.
Falcone M, Preto M, Ceruti C, Timpano M, Garaffa G, Sedigh O, et al. A comparative study between 2 different grafts used as patches after plaque incision and inflatable penile prosthesis implantation for end-stage Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med. 2018;15:848–52.
•• Hatzichristodoulou G, Yang DY, Ring JD, Herbert KJ, Ziegelmann MJ, Kohler TS. Multicenter experience using collagen fleece for plaque incision with grafting to correct residual curvature at the time of inflatable penile prosthesis placement in patients with Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med. 2020;17:1168–74. This is the first multicenter study looking at collagen fleece hemostatic patch grafting.
Ziegelmann MJ, Trost LW, Russo GI, Levine L. Peyronie’s disease intervention studies: an exploration of modern-era challenges in study design and evaluating treatment outcomes. J Sex Med. 2020;17:364–77.
Sansalone S, Garaffa G, D**ovic R, Egydio P, Vespasiani G, Miano R, et al. Simultaneous penile lengthening and penile prosthesis implantation in patients with Peyronie’s disease, refractory erectile dysfunction, and severe penile shortening. J Sex Med. 2012;9(1):316–21.
Egydio P, Kuehhas F. The multiple-slit technique (MUST) for penile length and girth restoration. J Sex Med. 2018;15:261–9.
Egydio P, Kuehhas F, Valenzuela RJ. Modified sliding technique (MoST) for penile lengthening with insertion of inflatable penile prosthesis. J Sex Med. 2015;12:1100–4.
Wilson SK, Mora-Estaves C, Egydio P, Ralph D, Habous M, Love C, et al. Glans necrosis following penile prosthesis implantation: prevention and treatment suggestions. Urology. 2017;107:144–8.
Reed-Maldonado AB, Alwaal A, Lue TF. The extra-tunical grafting procedure for Peyronie’s disease hourglass and indent deformities. Transl Androl Urol. 2018;7(Suppl 1):S1–6.
Nehra A, Alterowitz R, Culkin DJ, Faraday MM, Hakim LS, Heidelbaugh JJ, et al. Peyronie’s disease: AUA guideline. J Urol. 2015;194(3):745–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
LAL is a consultant for Absorption Pharmaceuticals, Boston Scientific, Coloplast, and Gesiva Medical.
The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Male Sexual Dysfunction and Disorder
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bajic, P., Siebert, A.L., Amarasekera, C.A. et al. Comparing Outcomes of Grafts Used in Peyronie’s Disease Surgery: a Systematic Review. Curr Sex Health Rep 12, 236–243 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11930-020-00283-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11930-020-00283-3