Abstract
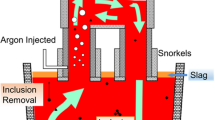
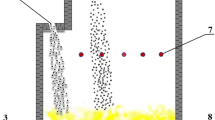
In situ formation micro-phase molten steel purification technology is a new inclusions control technology. In this study, to increase the purification efficiency of the composite particles in the Ruhrstahl–Heraeus (RH) reactor, a water model was used to simulate the addition process of the spherical particles. The effects of gas flow rate and immersion depth on particle motion behavior were carefully investigated. The settling process of the particles in the reactor was further analyzed with kinetic theory. Industrial trials in a 180-t RH were also conducted to validate the effect of the composite particle treatment on steel quality. The results show that the small-size particles disperse more in the liquid steel. The gas flow rate is positively correlated with the settling displacement in this experimental range. The optimal gas flow rate is 4.1 m3 h−1, and the optimal immersion depth increases with increasing particle size. The results of the industrial trials also show that the quality of the steel treated with composite particles is significantly improved. The T·[O] content was reduced by 8.78 ppm. The inclusions number density was reduced by 3.55 pieces/mm2. The percentage of inclusions smaller than 3 μm was increased from 27.02% to 73.96%.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.F. Chen, H. Lei, H.C. Hou, C.Y. Ding, H. Zhang, and Y. Zhao, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 15, 5141 (2021).
H. Wang, Y.P. Bao, J.G. Zhi, C.Y. Duan, S. Gao, and M. Wang, ISIJ Int. 61, 657 (2021).
B.S. Liu, G.S. Zhu, H.X. Li, B.H. Li, and A.M. Cui, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 17, 22 (2010).
X.G. Ai, Y.P. Bao, W. Jiang, J.H. Liu, P.H. Li, and T.Q. Li, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 17, 17 (2010).
F. Jiang, and G.G. Cheng, Ironmak. Steelmak. 39, 386 (2012).
Y.H. Li, Y.P. Bao, R. Wang, L.F. Ma, and J.S. Liu, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 25, 153 (2018).
F.P. Tang, Z. Li, X.F. Wang, B.W. Chen, and P. Fei, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 18, 144 (2011).
F.P. Tang, X.F. Wang, Z. Li, Y. Lin, B.W. Chen, and P. Fei, Ironmak. Steelmak. 38, 285 (2011).
L. Wang, H.G. Lee, and P. Hayes, ISIJ Int. 36, 7 (1996).
S. Chang, Z. Zou, B. Li, M. Isac, and R.I. Guthrie, Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 53, 526 (2022).
R. Guthrie, and M. Isac, In Extraction. 729, 1 (2018).
S. Chang, X. Cao, C.H. Hsin, Z. Zou, M. Isac, and R. Guthrie, ISIJ Int. 56, 1188 (2016).
L. Wang, S. Yang, J. Li, S. Zhang, and J. Ju, Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 48, 805 (2017).
Y. **ao, G. Wang, H. Lei, and S. Sridhar, J. Alloy Compd. 813, 1543 (2020).
B. Zhu, K. Chattopadhyay, X. Hu, B. Zhang, Q. Liu, and Z. Chen, Vacuum 152, 30 (2018).
X. Li, X. Wang, Y.P. Bao, J. Gong, and M. Wang, JOM. 72, 3628 (2020).
J. Dong, C. Feng, R. Zhu, G. Wei, J. Jiang, and S. Chen, Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 52, 2127 (2021).
C. Yao, M. Wang, Y.J. Ni, J. Gong, L.D. **ng, H.B. Zhang, and Y.P. Bao, JOM. 1, 1 (2022).
R.D. Wang, Y. **, and H. Cui, Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 53, 342 (2022).
J.J.M. Peixoto, W.V. Gabriel, T.A.S. de Oliveira, C.A. da Silva, I.A. da Silva, and V. Seshadri, Metall. Mater. Trans B. 49, 2421 (2018).
W.B. Rauen, B. Lin, R.A. Falconer, and E.C. Teixeira, Chem. Eng. J. 137, 550 (2008).
C.A. Da Silva, I.A. Da Silva, E.M. de Castro Martins, V. Seshadri, C.A. Perim and G.A. Vargas Filho, Ironmak Steelmak. 31, 37 (2004).
B. Dahya, and M.E. Weber, J. Fluid Mech. 105, 61 (1981).
F.P. Tang, Z. Li, X.F. Wang, W.S. Liu, and B.W. Chen, Iron Steel. 45, 28 (2010).
A.N. Ernest, J.S. Bonner, and R.L. Autenrieth, J. Environ. Eng. 121, 320 (1995).
M.E. ONeill, Chem Eng Sci. 23, 1293 (1968).
S. Taniguchi, ISIJ Int. 36, 117 (1999).
H. Matsuno, CAMP. 10, 103 (1997).
D.Y. Liu, Bei**g: Higher Education Press. (1993).
S.H. Huang, W. Li, and L.J. Cheng, Appl. Math. Mech. 21, 265 (2000).
C.Y. Dong, W.L. Luan, S.T. Zhou, and Q. Zhang, J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.). 31, 55 (2007).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51574019). The authors wish to express their gratitude to the foundation for providing financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Bao, Yp., Gu, C. et al. Simulation of Centimeter-Level Particle Motion Behavior in the Ruhrstahl–Heraeus Reactor Based on Situ Formation Micro-phase Molten Steel Purification Technology. JOM 75, 3724–3733 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05943-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05943-y