Abstract
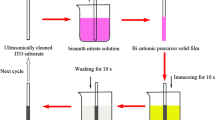
Ni-doped bismuth oxide (Bi2O4:Ni) thin films with varying Ni concentrations of 1–5 wt.% were successfully fabricated by the dip-coating method. The monoclinic Bi2O4 phase of all thin films was confirmed by the XRD spectra. The average crystallite size of pure Bi2O4 was 45.98 nm, which was reduced to 39.23–33.39 nm after Ni do** (1–5 wt.%). It was revealed from SEM images that pure and Ni-doped bismuth oxide thin films showed an increase in grain size ranging from 11 nm to 21 nm. The band-gap value varied from 2.00 eV to 1.77 eV. The optical properties and crystallite size were correlated with each other. Among all Ni-doped Bi2O4, 2 wt.% Ni has very strong antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa and S. aureus with a zone of inhibition of 30 ± 0.7 mm and 30 ± 2.12 mm, respectively. The effect of Ni do** on the photocatalytic activity of Bi2O4 thin films is reported. Prepared catalysis can play a very important role in the treatment of polluted air and water. The hop** mechanism justified the dielectric parameters which follow Koop’s theory and the Maxwell–Wagner model. The thin films have been to be found ferromagnetic. High-frequency devices find the low values of dielectric constants beneficial for them.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data not available / The data that has been used is confidential.
References
F. Ghasemzadeh and M. E. Shayan, Nanotechnol Environ. 59 (2020)
K. Gurunathan, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 29, 933 (2004).
C. Jiang, S.J.A. Moniz, A. Wang, and T. Zhang, J. Tang. Chem. Soc. Rev. 15, 4645 (2017).
T.D. Moustakas, Phys. Status Solidi A. 210, 169 (2013).
M.M. Khin, A.S. Nair, V.J. Babu, R. Murugan, and S. Ramakrishna, Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 8075 (2012).
M. Napari, T.N. Huq, R.L.Z. Hoye, and J.L.M. Driscoll, InfoMat. 3, 576 (2021).
X. Wu, Z. Wei, L. Zhang, X. Wang, H. Yang, and J. Jiang, J. Nanomater. 6, 45 (2014).
Z.N. Kayani, H.A. Shafiq, S. Riaz, and S. Naseem, J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 155, 110104 (2021).
S. Vempati, A. Shetty, P. Dawson, K.K. Nanda, and S.B. Krupanidhi, Thin Solid Films 524, 137 (2012).
M. Anwar, Z.N. Kayani, and A. Hassan, Opt. Mater. 118, 111276 (2021).
J. Sharma, B. Hamid, A. Kumar, and A.K. Srivastava, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 1107 (2018).
Q. Meng, and Z. Yin, Mendeleev. Commun. 29, 672 (2019).
N. Goswami, and N. Sahai, Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 351 (2013).
D.P. Dutta, M. Roy, and A.K. Tyagi, Dalton Trans. 34, 10248 (2012).
Z.N. Kayani, and H. Aslam, Adv. Powder Technol. 32, 2358 (2021).
Z.N. Kayani, A. Altaf, R. Sagheer, S. Riaz, and S. Naseem, Mater. Chem. Phys. 282, 125944 (2022).
M.M. Viana, V.F. Soares, and N.D.S. Mohallem, Ceram. Int. 36, 2047 (2010).
B. Pal, S. Dhara, P.K. Giri, and D. Sarkar, J. Alloys Compd. 647, 558 (2015).
Z.N. Kayani, S.R. Maria, and S. Naseem, Ceram. Int. 46, 381 (2020).
Z.N. Kayani, M. Sahar, S. Riaz, S. Naseem, and Z. Saddiqe, Opt. Mater. 108, 110 (2019).
A. Hassan, Z.N. Kayani, and M. Anwar, J. Mater. Sci. 22, 14398 (2021).
S. Thakur, and V. Kaur Singh, J Non Cryst Solids. 512, 60 (2019).
N. Kaur, S.K. Shahi, J.S. Shahi, S. Sandhu, R. Sharma, and V. Singh, Vacuum 178, 109429 (2020).
S. Xue, J. Wang, Q. Wu, L. Zhang, R. Dai, B. Tian, W. Wang, W. Zhang, and F. Zhang, Results Phys. 19, 103596 (2020).
G. Viruthagiri, and P. Kannan, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 127 (2019).
D. Kaur, T. Sharma, and C. Madhu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 9917 (2022).
I. Boukhris, I. Kebaili, M.S. Al-Buriahi, B. Tonguc, M.M. AlShammari, and M.I. Sayyed, Ceram Int. 46, 22888 (2020).
L. Wu, X. Liu, G. Wan, X. Peng, Z. He, S. Shi, and G. Wang, J. Chem. Eng. 448, 137600 (2022).
S. Vinoth, A.M.S. Arulanantham, S. Saravanakumar, R.S.R. Isaac, N. Soundaram, N. Chidhambaram, D. Alagarasan, S. Varadharajaperumal, M. Shkir, and S. AlFaify, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 27060 (2021).
B.R. Kumar, B.H. Rajesh, and T.S. Rao, J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Dev. 3, 433 (2018).
E. Lim, T. Manaka, R. Tamura, and M. Iwamoto, JJAP. 45, 3712 (2006).
K.N. Devi, S.A. Devi, W.J. Singh, and K.J. Singh, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 8745 (2021).
I. Khan, I. Khan, M. Usman, M. Imran, and K. Saeed, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 8985 (2020).
K. Yang, R. Li, C. Zhu, and J. Pei, J. Mater. Res. 36, 2936 (2021).
C. Regmi, Y.K. Kshetri, T.H. Kim, R.P. Pandey, S.K. Ray, and S.W. Lee, Appl. Surf. Sci. 413, 265 (2017).
M. Shkir, B. Palanivel, A. Khan, M. Kumar, J.H. Chang, A. Mani, and S. AlFaify, Chemosphere 291, 132687 (2022).
H. Su, S. Li, L. Xu, C. Liu, R. Zhang, and W. Tan, J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 170, 110954 (2022).
Z.N. Kayani, M. Ashfaq, S. Riaz, and S. Naseem, Opt. Mater. 132, 112809 (2022).
J. Sun, S. Yu, Z. Cui, L. Hu, B. Sun, and B. Chen, J. Mater. Sci. 32, 15276 (2022).
B.L.D. Silva, B.L. Caetano, B.G.C. Andréo, R.C.L.R. Pietro, and L.A. Chiavacci, Colloids Surf. B. 177, 440 (2019).
M.J. Hajipour, A. Akbar, D. Ashkarran, J. Aberasturi, I.R. Larramendi, T. Rojo, V. Serpooshan, W.J. Parak, and M. Mahmoudi, Trends Biotechnol. 30, 499 (2012).
R. Elilarassi, and G. Chandrasekaran, Mater. Chem. Phys. 123, 450 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS: Investigation; Formal analysis, Prof. Dr. ZNK: Conceptualization; Writing—Original Draft; Supervision; Project administration, Dr. SR: discussions, VSM analysis, Prof. Dr. SN: Writing—Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical Approval
This manuscript is original, has not been published before, and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. The Corresponding Author is the sole contact for the Editorial process. She is responsible for communicating with the other authors about progress, submissions of revisions, and final approval of proofs. The manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed. The order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sahar, M., Kayani, Z.N., Riaz, S. et al. Role of Ni Do** on Bi2O4 Thin Films for Optical, Dielectric and Photocatalytic Applications. JOM 75, 3385–3399 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05942-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05942-z