Abstract
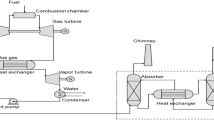
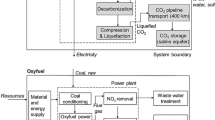
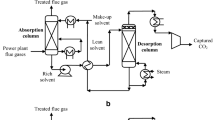
A pre-combustion CO2 capture system was modelled with three different membranes. It comprised an amine absorber for the elimination of H2S, high- and low-temperature water gas shift reactors for the conversion of CO to CO2 and a membrane to keep over 90% of the CO2 in the retentate. The absorber and equilibrium reactors were modelled using rigorous models, while the partial least squares model was used for three different types of membranes to predict the experimental results. The effectiveness of the modelling of the reactors and membranes was tested through comparison of simulated results with experimental data. The effects of operating pressure and membrane type are also discussed, and it was found that using a smaller membrane under high pressure lowered the membrane’s cost but also lowered energy recovery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Davison, Energy, 32, 1163 (2007).
H. J. Herzog, Environ. Sci. Techonol., 35, 148 (2001).
J. Franz and V. Scherer, J. Membr. Sci., 359, 173 (2010).
J. Gibbins and H. Chalmers, Energ. Policy, 36, 4317 (2008).
A. A. Olajire, Energy, 35, 2610 (2010).
W. J. Koros and G. K. Fleming, J. Membr. Sci., 83, 1 (1993).
M. Bracht, P. T. Alderliesten, R. Kloster, R. Pruschek, G. Haupt, E. Xue, J. R.H. Ross, M.K. Koukou and N. Papayannakos, Energy Convers. Mange., 38, S159 (1997).
S. Shelly, Chem. Eng. Prog., 105, 42 (2009).
C. A. Scholes, K. H. Smith, S. E. Kentish and G.W. Stevens, Int. J. Greenh. Gas Con., 4, 739 (2010).
P. Geladi and B. R. Kowalski, Anal. Chim. Acta, 185, 1 (1986).
M.A. Sharaf, D. L. Illman and B. R. Kowalski, Chemometrics, Wiley, New York (1986).
G. Baffi, E.B. Martin and A. J. Morris, Comput. Chem. Eng., 23, 395 (1999).
M.-J. Park, M. T. Dokucu and F. J. Doyle III, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 43, 7227 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.H., Park, MJ., Kim, J. et al. Modelling and analysis of pre-combustion CO2 capture with membranes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 30, 1187–1194 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0042-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0042-7