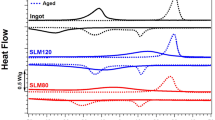
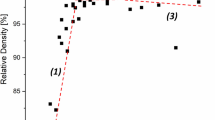
Abstract
NiTi shape memory alloy (SMA) with nominal composition of Ni 50.8 at% and Ti 49.2 at% was additively manufactured (AM) by selective laser melting (SLM) and laser directed energy deposition (DED) for a comparison study, with emphasis on its phase composition, microstructure, mechanical property and deformation mechanism. The results show that the yield strength and ductility obtained by SLM are 100 MPa and 8%, respectively, which are remarkably different from DED result with 700 MPa and 2%. The load path of SLM sample presents shape memory effect, corresponding to martensite phase detected by XRD; while the load path of DED presents pseudo-elasticity with austenite phase. In SLM sample, fine grain and hole provide a uniform deformation during tensile test, resulting in a better elongation. Furthermore, the nonequilibrium solidification was studied by a temperature field simulation to understand the difference of the two 3D printing methods. Both temperature gradient G and growth rate R determine the microstructure and phase in the SLM sample and DED sample, which leads to similar grain morphologies because of similar G/R. While higher G×R of SLM leads to a finer grain size in SLM sample, providing enough driving force for martensite transition and subsequently changing texture compared to DED sample.
摘要
利用激光增材制造技术成形了Ni50.8Ti49.2 形状记忆合金,对比分析选区激光熔化(SLM)成形试样与激光定向能量沉积(DED)成形试样的物相分布、微观结构、力学性能与变形机理。结果表明SLM试样具有100 MPa 的屈服**度和8%的伸长率,而DED 试样的屈服**度高达700 MPa 但仅有2%的伸长率。SLM 试样的变形行为主要体现为形状记忆效应,DED 试样的变形行为体现为伪弹性。XRD 结果表明SLM 基体为马氏体态而DED 试样为奥氏体态。分析发现非**衡凝固和激光定向凝固过程导致激光增材试样存在明显的熔池行为,但由于SLM 工艺的扫描速度明显高于DED 工艺的,其存在更高的温度梯度和生长速度,形成了更小的晶粒尺寸分布和更**的织构**度,且形成的气孔缺陷较为均匀,使得材料的均匀变形更易发生,具有较高的伸长率。Ni 元素的挥发以及更**的晶界界面能使得SLM试样具有足够的驱动力发生马氏体相变,改变了SLM 试样的**织构方向和变形方式。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
OTSUKA K, WAYMAN C M. Shape memory materials [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998.
ZHANG Yan-qiu, JIANG Shu-yong, ZHAO Ya-nan, ZHU **ao-ming. Simulation of isothermal precision extrusion of NiTi shape memory alloy pipe coupling by combining finite element method with cellular automaton [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(3): 506–514. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3453-5.
DADBAKHSH S, SPEIRS M, KRUTH J P, VAN HUMBEECK J. Influence of SLM on shape memory and compression behaviour of NiTi scaffolds [J]. CIRP Annals, 2015, 64(1): 209–212. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2015.04.039.
HABERLAND C, ELAHINIA M, WALKER J M, MEIER H, FRENZEL J. On the development of high quality NiTi shape memory and pseudoelastic parts by additive manufacturing [J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2014, 23(10): 104002. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/23/10/104002.
HABERLAND C, ELAHINIA M, WALKER J, MEIER H. Visions, concepts and strategies for smart nitinol actuators and complex nitinol structures produced by additive manufacturing [C]// Proceedings of ASME 2013 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems. Snowbird, Utah, USA, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/SMASIS2013-3072.
YANG **n, REN Yao-jia, LIU Shi-feng, WANG Qing-juan, SHI Ming-jun. Microstructure and tensile property of SLM 316L stainless steel manufactured with fine and coarse powder mixtures [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(2): 334–343. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4299-9.
TAHERI ANDANI M, SAEDI S, TURABI A S, KARAMOOZ M R, HABERLAND C, KARACA H E, ELAHINIA M. Mechanical and shape memory properties of porous Ni50.1Ti49.9 alloys manufactured by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2017, 68: 224–231. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.01.047.
VAN HUMBEECK J. Additive manufacturing of shape memory alloys [J]. Shape Memory and Superelasticity, 2018, 4(2): 309–312. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-018-0174-z.
YABLOKOVA G, SPEIRS M, VAN HUMBEECK J, KRUTH J P, SCHROOTEN J, CLOOTS R, BOSCHINI F, LUMAY G, LUYTEN J. Rheological behavior of β-Ti and NiTi powders produced by atomization for SLM production of open porous orthopedic implants [J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 283: 199–209. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2015.05.015.
BORMANN T, SCHUMACHER R, MÜLLER B, MERTMANN M, WILD M. Tailoring selective laser melting process parameters for NiTi implants [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2012, 21(12): 2519–2524. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0318-9.
LI Rui-di, WANG Min-bo, LI Zhi-ming, CAO Peng, YUAN Tie-chui, ZHU Hong-bin. Develo** a high-strength Al-Mg-Si-Sc-Zr alloy for selective laser melting: Crack-inhibiting and multiple strengthening mechanisms [J]. Acta Materialia, 2020, 193: 83–98. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.03.060.
LU H Z, YANG C, LUO X, MA H W, SONG B, LI Y Y, ZHANG L C. Ultrahigh-performance TiNi shape memory alloy by 4D printing [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019, 763: 138166. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138166.
SAEDI S, SHAYESTEH MOGHADDAM N, AMERINATANZI A, ELAHINIA M, KARACA H E. On the effects of selective laser melting process parameters on microstructure and thermomechanical response of Ni-rich NiTi [J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 144: 552–560. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.10.072.
HABERLAND C, ELAHINIA M, WALKER J, MEIER H, FRENZEL J. Additive manufacturing of shape memory devices and pseudoelastic components [M]// ASME 2013 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems-Volume 1: Development and Characterization of Multifunctional Materials; Modeling, Simulation and Control of Adaptive Systems; Integrated System Design and Implementation. New York: Amer Soc Mechanical Engineers, 2014.
HABERLAND C, ELAHINIA M, WALKER J, MEIER H, FRENZEL J. Additive manufacturing of shape memory devices and pseudoelastic components [C]// ASME 2013 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, SMASIS 2013. 2013, 1: 1–8.
SAEDI S, SAGHAIAN S E, JAHADAKBAR A, SHAYESTEH MOGHADDAM N, TAHERI ANDANI M, SAGHAIAN S M, LU Y C, ELAHINIA M, KARACA H E. Shape memory response of porous NiTi shape memory alloys fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2018, 29(4): 1–12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-018-6044-6.
SAEDI S, TURABI A S, ANDANI M T, MOGHADDAM N S, ELAHINIA M, KARACA H E. Texture, aging, and superelasticity of selective laser melting fabricated Ni-rich NiTi alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 686: 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.01.008.
YANG Y, ZHAN J B, LI B, LIN J X, GAO J J, ZHANG Z Q, REN L, CASTANY P, GLORIANT T. Laser beam energy dependence of martensitic transformation in SLM fabricated NiTi shape memory alloy [J]. Materialia, 2019, 6: 100305. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2019.100305.
WEN Shi-feng, LIU Yang, ZHOU Yan, ZHAO Ai-guo, YAN Chun-ze, SHI Yu-sheng. Effect of Ni content on the transformation behavior and mechanical property of NiTi shape memory alloys fabricated by laser powder bed fusion [J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 134: 106653. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106653.
SPEIRS M, WANG X, BAELEN S, AHADI A, DADBAKHSH S, KRUTH J P, HUMBEECK J. On the transformation behavior of NiTi shape-memory alloy produced by SLM [J]. Shape Memory and Superelasticity, 2016, 2(4): 310–316. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-016-0083-y.
ZHAO Chun-yang, LIANG Hai-long, LUO Shun-cun, YANG **g-**g, WANG Ze-min. The effect of energy input on reaction, phase transition and shape memory effect of NiTi alloy by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 817: 153288. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153288.
NIU Peng-da, LI Rui-di, ZHU Shu-ya, WANG Min-bo, CHEN Chao, YUAN Tie-chui. Hot cracking, crystal orientation and compressive strength of an equimolar CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy printed by selective laser melting [J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2020, 127: 106147. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106147.
HAMILTON R F, BIMBER B A, TAHERI ANDANI M, ELAHINIA M. Multi-scale shape memory effect recovery in NiTi alloys additive manufactured by selective laser melting and laser directed energy deposition [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 250: 55–64. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.06.027.
LI Lan-bo, LI Rui-di, YUAN Tie-chui, CHEN Chao, ZHANG Zhi-jian, LI **ao-feng. Microstructures and tensile properties of a selective laser melted Al-Zn-Mg-Cu (Al7075) alloy by Si and Zr microalloying [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020, 787: 139492. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139492.
PENG Hao-**, XIE Si-yao, NIU Peng-da, ZHANG Zhi-jian, YUAN Tie-chui, REN Zhi-qiang, WANG **ao-ming, ZHAO Yang, LI Rui-di. Additive manufacturing of Al0.3CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy by powder feeding laser melting deposition [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 862: 158286. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158286.
ABIOYE T E, FARAYIBI P K, KINNEL P, CLARE A T. Functionally graded Ni-Ti microstructures synthesised in process by direct laser metal deposition [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 79(5–8): 843–850. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6878-8.
BIMBER B A, HAMILTON R F, KEIST J, PALMER T A. Anisotropic microstructure and superelasticity of additive manufactured NiTi alloy bulk builds using laser directed energy deposition [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 674: 125–134. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.07.059.
HAMILTON R F, PALMER T A, BIMBER B A. Spatial characterization of the thermal-induced phase transformation throughout as-deposited additive manufactured NiTi bulk builds [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 101: 56–59. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.01.018.
WANG C, TAN X P, DU Z, CHANDRA S, SUN Z, LIM C W J, TOR S B, LIM C S, WONG C H. Additive manufacturing of NiTi shape memory alloys using pre-mixed powders [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 271: 152–161. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.03.025.
TAN Zhao-qiang, ZHANG Qing, GUO Xue-yi, ZHAO Wei-jiang, ZHOU Cheng-shang, LIU Yong. New development of powder metallurgy in automotive industry [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(6): 1611–1623. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4394-y.
SHISHKOVSKY I, YADROITSEV I, SMUROV I. Direct selective laser melting of nitinol powder [J]. Physics Procedia, 2012, 39: 447–454. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.10.060.
CALLISTER W D. Fundamentals of materials science and engineering: An integrated approach [M]. 2nd edition. New York: John Wiley and Sons Ltd, 2005.
GOLLERTHAN S, YOUNG M L, BARUJ A, FRENZEL J, SCHMAHL W W, EGGELER G. Fracture mechanics and microstructure in NiTi shape memory alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(4): 1015–1025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2008.10.055.
WANG J, SEHITOGLU H. Martensite modulus dilemma in monoclinic NiTi-theory and experiments [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2014, 61: 17–31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2014.05.005.
KOU S. Welding metallurgy [M]. Wisconsi: John Wiley and Son, InC, 2003.
KOK Y, TAN X P, WANG P, NAI M L S, LOH N H, LIU E, TOR S B. Anisotropy and heterogeneity of microstructure and mechanical properties in metal additive manufacturing: A critical review [J]. Materials & Design, 2018, 139: 565–586. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.11.021.
THOMASOVÁ M, SEINER H, SEDLÁK P, FROST M, ŠEVČÍK M, SZURMAN I, KOCICH R, DRAHOKOUPIL J, ŠITTNER P. Evolution of macroscopic elastic moduli of martensitic polycrystalline NiTi and NiTiCu shape memory alloys with pseudoplastic straining [J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 123: 146–156. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.10.024.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The overarching research goals were developed by LI Rui-di, YUAN Tie-chui and SONG Bo. ZHENG Dan and XIONG Yi provided the measured mechanical properties data, and analyzed the measured data. ZHENG Dan, XIONG Yi and WANG Jia-xing established the microstructure and calculated the predicted model of temperature field simulations. LI Rui-di and SU Ya-dong analyzed the calculated results. The initial draft of the manuscript was written by ZHENG Dan, LI Rui-di and SONG Bo. All authors replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the final version.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
ZHENG Dan, LI Rui-di, YUAN Tie-chui, XIONG Yi, SONG Bo, WANG Jia-xing, SU Ya-dong declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Foundation item: Project(2020JJ2046) supported by the Science Fund for Hunan Distinguished Young Scholars, China; Project(S2020GXKJGG0416) supported by the Special Project for Hunan Innovative Province Construction, China; Project (2018RS3007) supported by the Huxiang Young Talents, China; Project(GuikeAB19050002) supported by the Science Project of Guangxi, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, D., Li, Rd., Yuan, Tc. et al. Microstructure and mechanical property of additively manufactured NiTi alloys: A comparison between selective laser melting and directed energy deposition. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 1028–1042 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4677-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4677-y
Key words
- Ni50.8Ti49.2 shape memory alloy
- additive manufacturing
- selective laser melting
- laser directed energy deposition
- mechanical properties