Abstract
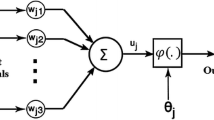
Three important factors influencing directly the dissolved oxygen (DO) of river including the outflow, the water temperature and the pH, were used as input parameters to set up a BP neural network based on Levenberg-Marquant algorithm. The neural network model was proposed to evaluate DO in water. The model contains two parts: firstly, the learning sample is unified; secondly, the neural network is used to train the unified samples to ensure the best node number of hidden layer. The proposed model is applied to assessing the DO concentration of the Yellow River in Lanzhou city. The evaluation result is compared with that by the neural network method and the reported result in Lanzhou city. The comparison result indicates that the performance of the neural network model is practically feasible in the assessment of DO. At the same time, the linear interpolation method can add the number of network’s learning sample to improve the prediction precision of the network.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
MA Rui-jie, LI **n, LIU **ao-duan, XU Qing. An application study of connection model between reservoir organic pollutant BOD-DO and temperature [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2005, 24(2): 105–108. (in Chinese)
GUO **-song, HUO Guo-you, LONG Teng-rui. Study on BOD-DO coupling for water quality simulation with artificial neural network [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2001, 21(2): 140–143.
GUO Lian-xi, DENG Chang-hui. Prediction model for dissolved oxygen in fish pond based on fuzzy neural network [J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2006, 30(2): 225–229. (in Chinese)
YANG **ao-ming, LI Ming-huan, YANG Pu, JIA Ming-xing. Dissolved oxygen prediction model and its error revision [J]. Control Engineering of China, 2004, 11(2): 127–129, 137.
FU Guo-wei, et al. Water pollution control planning [M]. Bei**g: Tsinghua University Press, 1985: 185–187. (in Chinese)
YANG Mei-ni, LI Ding-fang. FANN-based surface water quality evaluation model and its application in the Shaoguan area [J]. Geo-spatial Information Science, 2007, 10(4): 303–310.
WAN You-chuan, XIE Hong-yu, WU Zheng-bing, SHEN **ao-li. Application of artificial neural network and GIS to water quality evaluation [J]. Journal of Wuhan University: Engineering, 2003, 36(3): 7–12.
GUO Zhong-yang, CHEN Zhong-yuan, LI Lu-qian, SONG Bao-**, LU Yan. Artificial neural network and its application in regime prediction of ground water quality [J]. Journal of East China Normal University: Science, 2001(1): 84–89. (in Chinese)
CHEN Shou-yu, LI Ya-wei. Water quality evaluation based on fuzzy artificial neural network [J]. Advances in Water Science, 2005, 16(1): 88–91.
SHU **. Using neural network model to predict water quality [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2006, 31(1): 44–46. (in Chinese)
KUO Yi-ming, LIU Chen-ying, LIN Kao-hong. Evaluation of the ability of an artificial neural network model to assess the variation of groundwater quality in an area of Blackfoot disease in Taiwan [J]. Water Research, 2004, 36(1): 148–158.
LIU Lian-fang, WEI Li-hong, LI Ai-ming. Neural network apply in water evaluation of the Liao River [J]. Urban Environment and Urban Ecology, 2003, 16(6): 251–253. (in Chinese)
CHEN Li-hua, CHANG Qin-chun, CHEN **ng-guo. Application of BP networks to predict water quality of the Yellow River [J]. Journal of Lanzhou University: Natural Science, 2003, 39(2): 53–56. (in Chinese)
SOVAN L, GUEGAN J F. Artificial neural networks as a tool in ecological modeling, an introduction [J]. Ecological Modeling, 1999, 120(2): 65–73.
ABRAHART R J, LINDA S. Comparing neural network and autoregressive moving average techniques for the provision of continuous river flow forecasts in two contrasting catchments [J]. Hydrological Processes, 2000, 14(1): 2157–2172.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Lh., Li, L. Evaluation of dissolved oxygen in water by artificial neural network and sample optimization. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 15 (Suppl 2), 416–420 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0498-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0498-5