Abstract
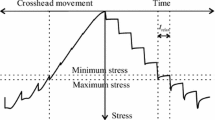
By studying and summarizing the characteristics of wood rheology, the mathematic models of creep and mechano-sorptive creep of wood were analyzed. Rheology behaviors in process, especially drying stress and deformation set were discussed. Application of wood rheology in woodcraft process was elaborated and the research prospects and orientation were forecasted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG Feng-hu. The rheology of wood materials [M]. Harbin: North-east Forestry University Press. 2005: 11–15. (in Chinese)
DIAO Hai-lin, LIANG Bing-zhao. Creep characteristic constants of woods of Pinus masoniana and Eucalyptus urophyllo camaldulensis [J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2003, 10(2): 150–153. (in Chinese)
SHAO Zhuo-**. The study on variable coefficients rheological model of wood [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2003, 39(3): 106–110. (in Chinese)
ARMSTRONG L D, KINGSTON R S T. Effect of moisture changes on creep of wood [J]. Nature, 1960, 185: 862–863.
SALIN J G. Numerical predication of checking during timber drying and a new mechano-sorptive creep model [J]. Holz.als Roh-und Werkstoff, 1992, 50(5): 195–200.
CHANG Jian-ming, HU Song-tao. Study on non-contact method for measuring drying stresses of wood [J]. China Forestry Products Industry, 1998, 25(5): 7–10. (in Chinese)
LI Da-gang, GU Lian-bai. Study on rheological behavior of surface layer of poplar during high-temperature drying [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 1999, 35(1): 83–89. (in Chinese)
CHEN Tai-an. Rheology behavior during conditioning of Eucalyptus camaldulensis lumber in laboratory kiln [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2007, 43(3): 84–89. (in Chinese)
DIAO **u-ming, HE Ling-zhi. Study on drying stress of hardwood timber [J]. Forestry Science & Technology, 1994, 19(2): 37–41. (in Chinese)
TOKUMOTO M. Casehardening and drying set in the kiln-drying of wood III, Changes of set in slices from the outside to the center of wood pieces during conditioning [J]. Mokuzai Gakkaishi, 1989, 35(3): 392–399.
LIU Ying-an. The mathematics models of wood-drying stress [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 1998, 26(5): 56–59. (in Chinese)
HU Chuan-kun. Preliminary exploration on the detection method of stress and strain in the process of wood drying [J]. Journal of Anhui Agri Sci, 2008, 36(6): 2323–2326. (in Chinese)
GONG Ren-mei, WANG Li-yu. Effect of vapor treatment on dry wood stress [J]. Forestry Science & Technology, 21(5): 40–42. (in Chinese)
CHENG Wan-li, LIU Yi-xing. Characteristics of shrinkage stress of wood during drying under high temperature and high pressure steam conditions [J]. Journal of Bei**g Forestry University, 2005, 27(2): 101–106. (in Chinese)
TAKANORI A. Recovery of wood after mechano-sorptive deformation. II. Effects of drying conditions while clamped [J]. Mokuzai Gakkaishi, 1979, 25(7): 469–475
SHUICHI K. Computation of drying stresses resulting from moisture gradients in wood during drying I. Computative method [J]. Mokuzai Gakkaish, 1979, 25(2): 103–110.
TOKUMOTO M. Creep and set of wood in the non-equilibrium states of moisture [J]. Mokuzai Gakkaishi, 1994, 40(11): 256–264.
LIDA I, NORIMOTO M. Recovery of compression set [J]. Mokuzai Gakkaishi, 1987, 33(12): 929–933.
NORIMOTO M. Wood bending utilizing microwave heating [J]. Journal of the society of rhelogy, 1980(4): 166–171.
NORIMOTO M. Wood bending of Sugi and Hinoki from the thinning operation [J]. Wood Research, 1983(18): 93–102.
INOUE M, NORIMOTO M. Surface compression of coniferous wood lumber II: Permanent set of compression wood by low molecular weight phenolic resin and some physical properties of the products [M]. Mokuzai Gakkaishi, 1991, 37(3): 227–233.
NORIMOTO M. Surface compression of coniferous wood lumber III: Permanent set of the surface compressed layer by a water solution of low molecular weight phenolic resin [J]. Mokuzai Gakkaishi, 1991, 37(3): 234–240.
DWIANTO W, INOUE M, Misato Norimoto. Fixation of compressive deformation by heat treatment [J]. Mokuzai Gakkaishi, 1997, 43(4): 303–309.
ZHOU Li, LU **ao-ning, DING Hui. Effect of hydrothermal treatment on londitudinal compression properties of poplar [J]. Journal of Nan**g Forestry University, 2008, 32(1): 61–64. (in Chinese)
XIE Gui-jun, LIU Lei. Research of heat treatment on masson pine [J]. Guangxi Forestry & Technology, 2007, 23(4): 6–10. (in Chinese)
WANG Jie-ying, ZHAO Guang-jie. Creep of compressed wood of Chinese fir heat treated in air. [J]. Journal of Bei**g Forestry University, 2002, 24(2): 52–58. (in Chinese)
LI Jian, LIU Yi-xing. Study on the fixation of compressive deformation of wood in the transverse direction by high temperature steam treatment [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2000, 28(4): 4–8. (in Chinese)
LI Da-gang, LI Jian. Effects of heat treatment on permanent fixation bending deformation in wood of fraxinus mandshurica [J]. Journal of Nan**g Forestry University, 2004, 28(3): 23–26. (in Chinese)
LI Yan-jun, TANG Rong-qiang. The preliminary study on high temperature heat-treatment technology of wood [J]. China Forest Products Industry, 2008, 35(2): 16–18. (in Chinese)
XIE Man-hua, ZHAO Guang-jie. Structural change of wood molecules and chemo-rheological behavior during chemical treatment [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2005, 41(3): 158–162. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(30871983) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Yr., Luo, Ys. & Li, Xj. Advances and expectations of study on wood rheology. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 15 (Suppl 1), 545–549 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0418-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0418-8