Abstract
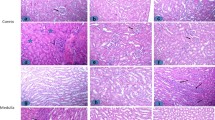
Despite the promising effect of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs) on controlling the chronic symptoms of different diseases, their toxicity has restricted the long-term administration of these agents. The lack of suitable substitution provides opportunities for innovation of combined-modality strategies that could reduce the toxic side effects of these drugs. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the protective effect of ellagic acid, a phenolic compound found in plants, on diclofenac-induced nephrotoxicity. The results of the treatment of 32 Wistar rats with diclofenac (0 mg/Kg) and/or ellagic acid (10 mg/Kg) for seven days showed that, unlike diclofenac that shifted the ratio of the redox system in favor of oxidative stress, ellagic acid reduced the tissue levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), protein carbonyl (PC) and diminished serum nitrite content. Moreover, through upregulating nuclear factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), ellagic acid might increase the activity and the tissue levels of several antioxidant enzymes such as catalase (CAT), superoxidase dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and glutathione (GSH) in diclofenac-treated rats. This phenolic agent also prevented diclofenac-mediated inflammatory responses by suppressing the expression of nuclear factor (NK)-κB/tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and reducing the number of infiltrated lymphocytes in the kidney tissue. Taken together, our study demonstrated that ellagic acid may produce a protective effect against diclofenac-induced renal failure by exerting both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. This finding indicates that this agent might be a valuable candidate to be used alongside NSAIDs such as diclofenac to alleviate their side effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- COX:
-
cyclooxygenase
- PG:
-
prostaglandin
- NSAID:
-
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
catalase
- GPx:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- BUN:
-
blood urea nitrogen
- CR:
-
creatinine
- UA:
-
uric acid
- sGOT:
-
serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase
- PAC:
-
plasma antioxidant capacity
- TPTZ:
-
trypyridyl-s-triazine
- NO:
-
nitrite oxide
- PC:
-
protein carbonyl
- DNPH:
-
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
- NBT:
-
nitro blue tetrazolium
- DTNB:
-
5,5-dithiobis-2- nitrobenzoic acid. TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor-κB
- HO-1:
-
heme oxygenase 1
- Nrf2:
-
nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
References
Abiola TS, Adebayo OC, Babalola O (2019) Diclofenac-Induced Kidney Damage in Wistar Rats: Involvement of Antioxidant Mechanism. J Biosci Med 7:44. https://doi.org/10.4236/jbm.2019.712005
Ahmad I, Kumar A, Shukla S, Prasad Pandey H, Singh C (2008) The involvement of nitric oxide in maneb-and paraquat-induced oxidative stress in rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Free Radic Res 42:849–862. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760802513733
Ahmed SMU, Luo L, Namani A, Wang XJ, Tang X (2017) Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease. 1863:585–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.11.005
Alabi QK, Akomolafe RO, Adefisayo MA, Olukiran OS, Nafiu AO, Fasanya MK, Oladele AA (2018) Kolaviron attenuates diclofenac-induced nephrotoxicity in male Wistar rats. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 43:956–968. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2017-0788
Ateşşahín A, Çeríbaşi AO, Yuce A, Bulmus Ö, Çikim G (2007) Role of ellagic acid against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 100:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.00015.x
Aycan İÖ, Elpek Ö, Akkaya B, Kıraç E, Tuzcu H, Kaya S, Coşkunfırat N, Aslan M (2018) Diclofenac induced gastrointestinal and renal toxicity is alleviated by thymoquinone treatment. Food Chem Toxicol 118:795–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.06.038
Ayhanci A, Cengiz M, Kutlu HM, Vejselova D (2016) Protective effects of ellagic acid in D-galactosamine-induced kidney damage in rats. Cytotechnology 68:1763–1770
Bharathi E, Jagadeesan G (2014) Antioxidant potential of hesperidin and ellagic acid on renal toxicity induced by mercuric chloride in rats. Biomed Prev Nutr 4:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bionut.2013.12.007
Bondeson J, Berglund S (1991) Diclofenac-induced thrombocytopenic purpura with renal and hepatic involvement. J Intern Med 230:543–547. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.1991.tb00487.x
Cengiz M, Ali JH, Kutlu HM, Vejselova D, Ayhanci A (2017) Potential recruiting and hepatoprotective effects of ellagic acid in D-galactosamine-induced liver damage in rats. 49:1–10. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.pjz/2017.49.4.1251.1259
Dhanvijay P, Misra AK, Varma SK (2013) Diclofenac induced acute renal failure in a decompensated elderly patient. J Pharmacol pharmacotherapeutics 4:155. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-500X.110916
Ding X, Jian T, Wu Y, Zuo Y, Li J, Lv H, Ma L, Ren B, Zhao L, Li W (2019) Ellagic acid ameliorates oxidative stress and insulin resistance in high glucose-treated HepG2 cells via miR-223/keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 110:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.018
Ding Y, Zhang B, Zhou K, Chen M, Wang M, Jia Y, Song Y, Li Y, Wen A (2014) Dietary ellagic acid improves oxidant-induced endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis: role of Nrf2 activation. Int J Cardiol 175:508–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.06.045
Ebrahimi R, Sepand MR, Seyednejad SA, Omidi A, Akbariani M, Gholami M, Sabzevari O (2019) Ellagic acid reduces methotrexate-induced apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction via up-regulating Nrf2 expression and inhibiting the IĸBα/NFĸB in rats. DARU J Pharm Sci 27:721–733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-019-00309-9
Ejaz P, Bhojani K, Joshi V (2004) NSAIDs and kidney. Japi 52:371. https://doi.org/10.1.1.1066.7269
El-Garhy AM, Abd El-Raouf OM, El-Sayeh BM, Fawzy HM, Abdallah DM (2014) Ellagic acid antiinflammatory and antiapoptotic potential mediate renoprotection in cisplatin nephrotoxic rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 28:472–479. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.21587
Ellman (1959) GL. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Francois H, Facemire C, Kumar A, Audoly L, Koller B, Coffman T (2007) Role of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:1466–1475. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2006040343
Giridharan R, Lavinya U, Sabina EP (2017) Suppressive effect of Spirulina fusiformis on diclofenac-induced hepato-renal injury and gastrointestinal ulcer in Wistar albino rats: a biochemical and histological approach. Biomed Pharmacother 88:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.032
Goetz FW, Planas JV, MacKenzie S (2004) Tumor necrosis factors. Dev Comp Immunol 28:487–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2003.09.008
Heidarian E, Saffari J, Jafari-Dehkordi E (2014) Hepatoprotective action of Echinophora platyloba DC leaves against acute toxicity of acetaminophen in rats. J Diet supplements 11:53–63. https://doi.org/10.3109/19390211.2013.859217
Hickey E, Raje R, Reid V, Gross S, Ray S (2001) Diclofenac induced in vivo nephrotoxicity may involve oxidative stress-mediated massive genomic DNA fragmentation and apoptotic cell death. Free Radic Biol Med 31:139–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00560-3
Islas-Flores H, Gómez-Oliván LM, Galar-Martínez M, Colín-Cruz A, Neri-Cruz N, García-Medina S (2013) Diclofenac-induced oxidative stress in brain, liver, gill and blood of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 92:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.01.025
Jordão JBR, Porto HKP, Lopes FM, Batista AC, Rocha ML (2017) Protective effects of ellagic acid on cardiovascular injuries caused by hypertension in rats. Planta Med 83:830–836. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-103281
Jung S-H, Lee W, Park S-H, Lee K-Y, Choi Y-J, Choi S, Kang D, Kim S, Chang T-S, Hong S-S (2020) Diclofenac impairs autophagic flux via oxidative stress and lysosomal dysfunction: Implications for hepatotoxicity. Redox Biol 37:101751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101751
Khan KNM, Paulson SK, Verburg KM, Lefkowith JB, Maziasz TJ (2002) Pharmacology of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition in the kidney. Kidney Int 61:1210–1219. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00263.x
Ma Q (2013) Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:401–426. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011112-140320
Moradi A, Abolfathi M, Javadian M, Heidarian E, Roshanmehr H, Khaledi M, Nouri A (2021) Gallic Acid Exerts Nephroprotective, Anti-Oxidative Stress, and Anti-Inflammatory Effects Against Diclofenac-Induced Renal Injury in Malerats. Arch Med Res 52:380–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.12.005
Muñoz-Peñuela M, Nostro FLL, Gomes ADO, Tolussi CE, Branco GS, Pinheiro JPS, de Godoi FGA, Moreira RG (2021) Diclofenac and caffeine inhibit hepatic antioxidant enzymes in the freshwater fish Astyanax altiparanae (Teleostei: Characiformes). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part. Toxicol Pharmacol 240:108910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108910
Ng LE, Halliwell B, Wong KP (2008) Nephrotoxic cell death by diclofenac and meloxicam. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369:873–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.02.116
Priyadarsini KI, Khopde SM, Kumar SS, Mohan H (2002) Free radical studies of ellagic acid, a natural phenolic antioxidant. J Agric Food Chem 50:2200–2206. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf011275g
Qi Z, Hao C-M, Langenbach RI, Breyer RM, Redha R, Morrow JD, Breyer MD (2002) Opposite effects of cyclooxygenase-1 and-2 activity on the pressor response to angiotensin II. J Clin Investig 110:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI14752
Ramezannezhad P, Nouri A, Heidarian E (2019) Silymarin mitigates diclofenac-induced liver toxicity through inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress in male rats. J Herbmed Pharmacol 8:231–237. https://doi.org/10.15171/jhp.2019.34
Reznick AZ, Packer L (1994) Oxidative damage to proteins: spectrophotometric method for carbonyl assay, Methods in enzymology. Elsevier, pp 357–363
Sembulingam K, Sembulingam P (2012) Essentials of medical physiology. JP Medical Ltd.
Turnbull N, Callan M, Staughton R (2014) Diclofenac-induced pseudoporphyria; an under-recognized condition? Clin Exp Dermatol 39:348–350. https://doi.org/10.1111/ced.12313
Ungprasert P, Cheungpasitporn W, Crowson CS, Matteson EL (2015) Individual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur J Intern Med 26:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2015.03.008
Wadhwa N, Mathew BB, Jatawa S, Tiwari A (2012) Lipid peroxidation: mechanism, models and significance. Int J Curr Sci 3:29–38
Wardyn JD, Ponsford AH, Sanderson CM (2015) Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways. Biochem Soc Trans 43:621–626. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20150014
Zhang X, Donnan PT, Bell S, Guthrie B (2017) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug induced acute kidney injury in the community dwelling general population and people with chronic kidney disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol 18:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-017-0673-8
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Iran university of medical sciences for contributing financially. Declarations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Saeed Karimi-Matloub and Rasoul Namavari these authors are considered as the first author.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karimi-Matloub, S., Namavari, R., Hatefi-Hesari, F. et al. The nephroprotective effect of ellagic acid against diclofenac-induced renal injury in male rats: role of Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB/TNF-α pathways. Biologia 77, 3633–3643 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01217-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01217-1