Abstract
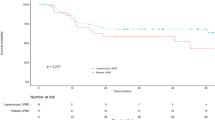
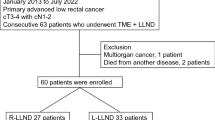
The treatment of lateral pelvic lymph node (LPLN) metastasis of rectal cancer has evolved because of technical difficulties from open surgery to laparoscopy and, recently, robot-assisted surgery. This study aimed to evaluate the technical feasibility and short- and long-term outcomes of robot-assisted LPLN dissection (LPND) following total mesorectal excision (TME) in advanced rectal cancer. Clinical data of 65 patients who underwent robotic-assisted TME with LPND from April 2014 to July 2022 were reviewed. Data regarding operative details, postoperative morbidity (within 90 postoperative days) for short-term outcomes and lateral recurrence as long-term outcomes were analyzed. Among the 65 patients with LPND, preoperative chemoradiotherapy was performed in 49 (75.4%). The mean operative time was 306.8 (range 191–477) min, and the mean time of unilateral LPND was 38.6 (range 16–66) min. LPND was bilaterally performed in 19 (29.2%) patients. The mean number of each side of harvested LPLNs was 6.8. Lymph node metastasis was observed in 15 (23.0%) patients, and 10 (15.4%) patients had postoperative complications. Lymphocele (n = 3) and pelvic abscess (n = 3) were the most common, followed by voiding difficulty, erectile dysfunction, obturator neuropathy, and sciatic neuropathy (all n = 1). During the 25 months of median follow-up, no lateral recurrence of the LPND site was noted. Robot-assisted LPND following TME is safe and feasible and showed acceptable short- and long-term outcomes. Despite some study limitations, we may be able to apply this strategy more widely through subsequent prospective controlled studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The dataset are available from corresponding author, Yong Sik Yoon, upon reasonable request.
References
Sugihara K, Kobayashi H, Kato T, Mori T, Mochizuki H, Kameoka S, Shirouzu K, Muto T (2006) Indication and benefit of pelvic sidewall dissection for rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 49:1663–1672
Ueno M, Oya M, Azekura K, Yamaguchi T, Muto T (2005) Incidence and prognostic significance of lateral lymph node metastasis in patients with advanced low rectal cancer. Br J Surg 92:756–763. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15838895. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Hashiguchi Y, Muro K, Saito Y, Ito Y, Ajioka Y, Hamaguchi T, Hasegawa K, Hotta K, Ishida H, Ishiguro M, Ishihara S, Kanemitsu Y, Kinugasa Y, Murofushi K, Nakajima TE, Oka S, Tanaka T, Taniguchi H, Tsuji A, Uehara K et al (2020) Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (JSCCR) guidelines 2019 for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 25:1–42. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31203527. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Kobayashi H, Mochizuki H, Kato T, Mori T, Kameoka S, Shirouzu K, Sugihara K (2009) Outcomes of surgery alone for lower rectal cancer with and without pelvic sidewall dissection. Dis Colon Rectum 52:567–576. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19404054. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Song SH, Choi GS, Kim HJ, Park JS, Park SY, Lee SM, Choi JA, Seok KA (2021) Long-term clinical outcomes of total mesorectal excision and selective lateral pelvic lymph node dissection for advanced low rectal cancer: a comparative study of a robotic versus laparoscopic approach. Tech Coloproctol 25:413–423. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33594627. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Lanfranco AR, Castellanos AE, Desai JP, Meyers WC (2004) Robotic surgery: a current perspective. Ann Surg 239:14–21. https://journals.lww.com/annalsofsurgery/Fulltext/2004/01000/Robotic_Surgery__A_Current_Perspective.3.aspx. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Luca F, Valvo M, Ghezzi TL, Zuccaro M, Cenciarelli S, Trovato C, Sonzogni A, Biffi R (2013) Impact of robotic surgery on sexual and urinary functions after fully robotic nerve-sparing total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Ann Surg 257:672–678. https://journals.lww.com/annalsofsurgery/Fulltext/2013/04000/Impact_of_Robotic_Surgery_on_Sexual_and_Urinary.14.aspx. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Hu C, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Liu R, Yan J, Sun Q, Wang G, She J (2022) Robot-assisted total mesorectal excision and lateral pelvic lymph node dissection for locally advanced middle-low rectal cancer. J Vis Exp. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35225257. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Kagawa H, Kinugasa Y, Shiomi A, Yamaguchi T, Tsukamoto S, Tomioka H, Yamakawa Y, Sato S (2015) Robotic-assisted lateral lymph node dissection for lower rectal cancer: short-term outcomes in 50 consecutive patients. Surg Endosc 29:995–1000. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25135444. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Kim HJ, Choi GS, Park JS, Park SY, Lee HJ, Woo IT, Park IK (2018) Selective lateral pelvic lymph node dissection: a comparative study of the robotic versus laparoscopic approach. Surg Endosc 32:2466–2473. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29124406. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Peacock O, Limvorapitak T, Bednarski BK, Kaur H, Taggart MW, Dasari A, Holliday EB, Minsky BD, You YN, Chang GJ (2020) Robotic lateral pelvic lymph node dissection after chemoradiation for rectal cancer: a Western perspective. Colorectal Dis 22:2049–2056. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.15350
Yamaguchi T, Kinugasa Y, Shiomi A, Tomioka H, Kagawa H (2016) Robotic-assisted laparoscopic versus open lateral lymph node dissection for advanced lower rectal cancer. Surg Endosc 30:721–728. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26092002. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Ogura A, Konishi T, Cunningham C, Garcia-Aguilar J, Iversen H, Toda S, Lee IK, Lee HX, Uehara K, Lee P, Putter H, van de Velde CJH, Beets GL, Rutten HJT, Kusters M, Lateral Node Study C (2019) Neoadjuvant (Chemo)radiotherapy with total mesorectal excision only is not sufficient to prevent lateral local recurrence in enlarged nodes: results of the multicenter lateral node study of patients with low cT3/4 rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 37:33–43. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30403572. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Park JA, Choi GS, Park JS, Park SY (2012) Initial clinical experience with robotic lateral pelvic lymph node dissection for advanced rectal cancer. J Korean Soc Coloproctol 28:265–270. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23185707. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Baek SJ, Kim CH, Cho MS, Bae SU, Hur H, Min BS, Baik SH, Lee KY, Kim NK (2015) Robotic surgery for rectal cancer can overcome difficulties associated with pelvic anatomy. Surg Endosc 29:1419–1424. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25159651. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Kim MJ, Park SC, Park JW, Chang HJ, Kim DY, Nam BH, Sohn DK, Oh JH (2018) Robot-assisted versus laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer: a phase ii open label prospective randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg 267:243–251. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28549014. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Fantus RJ, Cohen A, Riedinger CB, Kuchta K, Wang CH, Yao K, Park S (2019) Facility-level analysis of robot utilization across disciplines in the National Cancer Database. J Robot Surg 13:293–299. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30062641. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Cheng H, Clymer JW, Po-Han Chen B, Sadeghirad B, Ferko NC, Cameron CG, Hinoul P (2018) Prolonged operative duration is associated with complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Surg Res 229:134–144. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29936980. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Yamaguchi T, Konishi T, Kinugasa Y, Yamamoto S, Akiyoshi T, Okamura R, Ito M, Nishimura Y, Shiozawa M, Yamaguchi S, Hida K, Sakai Y, Watanabe M (2017) Laparoscopic versus open lateral lymph node dissection for locally advanced low rectal cancer: a subgroup analysis of a large multicenter cohort study in Japan. Dis Colon Rectum 60:954–964. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28796734. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Tokuhara K, Hishikawa H, Yoshida T, Ueyama Y, Yoshioka K, Sekimoto M (2021) Short-term outcomes of laparoscopic lateral pelvic node dissection for advanced lower rectal cancer. Surg Endosc 35:1572–1578. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32246236. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Ochiai K, Kaneko M, Nozawa H, Kawai K, Hata K, Tanaka T, Nishikawa T, Shuno Y, Sasaki K, Hiyoshi M, Emoto S, Murono K, Sonoda H, Ishihara S (2020) Incidence of and risk factors for lymphocele formation after lateral pelvic lymph node dissection for rectal cancer: a retrospective study. Colorectal Dis 22:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.14831
Ma X, Wang Y, Fan A, Dong M, Zhao X, Zhang X, Xue F (2018) Risk factors, microbiology and management of infected lymphocyst after lymphadenectomy for gynecologic malignancies. Arch Gynecol Obstet 298:1195–1203. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30269216. Accessed 8 Oct 2022
Funding
No funding was received to assist in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study design and analysis. Material preparation was performed by Eon Bin Kim, Yong Sik Yoon, In Ja Park, ** Cheon Kim. Data collection, analysis and the first draft of the manuscript was written by Eon Bin Kim and all authors revised critically and commented on the previous version of the manuscript. All authors participated and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration. The study protocol was approved by institutional review board of Asan Medical Center (Date 18 Sep 2022/IRB no. 2022–1264).
Informed consent
The review board waived the requirements for informed consent, as this study was a retrospective analysis.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, E.B., Yoon, Y.S., Kim, M.H. et al. Robot-assisted lateral pelvic lymph node dissection in patients with advanced rectal cancer: a single-center experience of 65 cases. J Robotic Surg 17, 1697–1703 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-023-01570-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-023-01570-6