Abstract
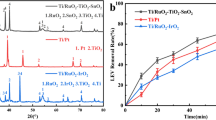
The interest in new emerging pollutants (NEPs) does not only focus on the main compounds but also the degradation or intermediate products. It is important to have an effective primary treatment for the removal/degradation of NEPs from hospital and clinical wastewater to protect the environment. In this study, nifedipine degradation was performed by an electro-oxidation method using titanium-based mixed metal oxide (MMO) electrode. The determination of nifedipine was carried out by differential pulse voltammetry at hanging mercury drop electrode using Britton–Robinson buffer (BRB). The nifedipine oxidation peak was observed at + 0.7 V at a scan rate of 20 mV s−1 in BRB pH 8. Titanium-based electrodes with different metal oxide compositions were assessed as an anode material for nifedipine degradation as follows: TiO2/Ti, IrO2–TiO2/Ti, RuO2–TiO2/Ti, and IrO2–RuO2–TiO2/Ti. The electro-oxidation of nifedipine was monitored using cyclic voltammetric techniques, and the degradation intermediates were confirmed using LC–MS. Approximately 65–83% of nifedipine degradation was achieved using RuO2–TiO2/Ti and IrO2–TiO2/Ti electrodes. Interestingly, RuO2–IrO2–TiO2 electrode showed complete (100%) electro-oxidation of nifedipine at 30 min. Two nifedipine degradation intermediates were identified, namely 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid (compound I) and 2,6-dimethyl-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarbaldehyde (compound II) during the electro-oxidation process using RuO2–IrO2–TiO2 electrode. Finally, the degradation pathway of nifedipine by MMO electrode was proposed. This is the first report on the nifedipine degradation using MMO titanium electrode by the electro-oxidation process.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhmal Saadon S, Sathishkumar P, Mohd Yusoff AR, Wirzal MDH, Rahmalan MT, Nur H (2016) Photocatalytic activity and reusability of ZnO layer synthesised by electrolysis, hydrogen peroxide and heat treatment. Environ Technol 37:1875–1882. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2015.1135989
Al-Qaim FF, Abdullah MP, Othman MR, Latip J, Zakaria Z (2014) Multi-residue analytical methodology-based liquid chromatography-time-of-flight-mass spectrometry for the analysis of pharmaceutical residues in surface water and effluents from sewage treatment plants and hospitals. J Chromatogr A 1345:139–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.04.025
Al-Qaim FF, Abdullah MP, Othman MR, Mussa ZH, Zakaria Z, Latip J, Afiq WM (2015) Investigation of the environmental transport of human pharmaceuticals to surface water: a case study of persistence of pharmaceuticals in effluent of sewage treatment plants and hospitals in Malaysia. J Braz Chem Soc 26:1124–1135. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20150075
Alshahrani LA, Liu L, Sathishkumar P, Nan J, Gu FL (2018) Copper oxide and carbon nano-fragments modified glassy carbon electrode as selective electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of catechol and hydroquinone in real-life water samples. J Electroanal Chem 815:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.03.004
Amiri M, Niasari MS, Akbari A (2017) A magnetic CoFe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposite fabricated by the sol-gel method for electrocatalytic oxidation and determination of L-cysteine. Microchim Acta 184:825–833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2064-4
Ardakani MM, Sadrabadi EA, Khoshroo A, Niasari MS (2015) Electrocatalytic properties of vanadyl complex in graphite nanocomposite and its enhanced electrochemical catalysis properties for levodopa oxidation. J Inorg Organomet Polym 25:1576–1581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-015-0277-3
Azhari S, Sathishkumar P, Ahamad R, Ahmad F, Yusoff ARM (2016) Fabrication of a composite modified glassy carbon electrode: a highly selective, sensitive and rapid electrochemical sensor for silver ion detection in river water samples. Anal Methods 8:5712–5721. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY01336H
Bagastyo AY, Radjenovic Y, Yang M, Rozendal AR, Batstone DJ, Rabaey K (2011) Electrochemical oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrate on mixed metal oxide (MMO) titanium coated electrodes. Water Res 45:4951–4959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.06.039
Bai H, He P, Pan J, Chen J, Chen Y, Dong F, Li H (2017) Boron-doped diamond electrode: preparation, characterization and application for electrocatalytic degradation of m-dinitrobenzene. J Colloid Interface Sci 497:422–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.03.017
Cao J, Zhao Y, Zhu Y, Yang X, Shi P, **ao H, Du N, Hou W, Qi G, Liu J (2017) Preparation and photovoltaic properties of CdS quantum dot-sensitized solar cell based on zinc tin mixed metal oxides. J Colloid Interface Sci 498:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.03.061
Esmaili Z, Cheshmberah F, Nazar ARS, Farhadian M (2017) Treatment of florfenicol of synthetic trout fish farm wastewater through nanofiltration and photocatalyst oxidation. Environ Technol 38:2040–2047. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1245359
Falfushynska H, Gnatyshyna L, Horyn O, Sokolova I, Stoliar O (2017) Endocrine and cellular stress effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and nifedipine in marsh frogs Pelophylax ridibundus. Aquat Toxicol 185:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.02.009
Fathi MJ, Jasni M, Arulkumar M, Sathishkumar P, Yusoff ARM, Buang NA, Gu FL (2017a) Electrospun nylon 6,6 membrane as a reusable nano-adsorbent for bisphenol A removal: adsorption performance and mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 508:591–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.08.075
Fathi MJ, Jasni M, Sathishkumar P, Sornambikai S, Yusoff ARM, Ameen F, Buang NA, Kadir MRA, Yusop Z (2017b) Fabrication, characterization and application of laccase-nylon 6,6/Fe3+ composite nanofibrous membrane for 3,3′-dimethoxybenzidine detoxification. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1686-6
Handa T, Singh S, Singh IP (2014) Characterization of a new degradation product of nifedipine formed on catalysis by atenolol: a typical case of alteration of degradation pathway of one drug by another. J Pharm Biomed Anal 89:6–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2013.10.024
Hojaghan HS, Niasari MS (2017) Degradation of methylene blue as a pollutant with N-doped graphene quantum dot/titanium dioxide nanocomposite. J Clean Prod 148:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.169
Jarrah N, Muazua ND (2016) Simultaneous electro-oxidation of phenol, CN−, S2−and NH4+ in synthetic wastewater using boron doped diamond anode. J Environ Chem Eng 4:2656–2664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.04.011
Kumar S, Singh S, Srivastava VC (2015) Electro-oxidation of nitrophenol by ruthenium oxide coated titanium electrode: parametric, kinetic and mechanistic study. Chem Eng J 263:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.051
Maafi W, Maafi M (2013) Modelling nifedipine photodegradation, photostability and actinometric properties. Int J Pharm 456:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.07.075
Maryskova M, Ardao I, Garcia-Gonzalez CA, Martinova L, Rotkova J, Sevcu A (2016) Polyamide 6/chitosan nanofibers as support for the immobilization of Trametes versicolor laccase for the elimination of endocrine disrupting chemicals. Enzyme Microb Technol 89:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2016.03.001
Peterson JW, Petrasky LJ, Seymour MD, Burkhart RS, Schuiling AB (2012) Adsorption and breakdown of penicillin antibiotic in the presence of titanium oxide nanoparticles in water. Chemosphere 87:911–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.044
Qureshi MS, Mohd Yusoff AR, Wirzal MDH, Sirajuddin BJ, Afridi HI, Üstündag Z (2016) Methods for the determination of endocrine disrupting phthalate esters. Crit Rev Anal Chem 46:146–159. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2015.1004157
Rocha RS, Valim RB, Trevelin LC, Silva FL, Steter JR, Zaiat M, Lanza MRV (2017) New operational mode of an electrochemical reactor and its application to the degradation of levofloxacin. J Environ Chem Eng 5:4441–4446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.08.041
Safajou H, Khojasteh H, Niasari MS, Derazkola SM (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene/Pd/TiO2 nanocomposites: TiO2 nanowires versus TiO2 nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 498:423–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.03.078
Sarkka H, Vepsalainen M, Pulliainen M, Sillanpaa M (2008) Electrochemical inactivation of paper mill bacteria with mixed metal oxide electrode. J Hazard Mater 156:208–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.011
Sathishkumar P, Mythili A, Hadibarata T, Jayakumar R, Kanthimathi MS, Palvannan T, Ponraj M, Salim MR, Yusoff ARM (2014) Laccase mediated diclofenac transformation and cytotoxicity assessment on mouse fibroblast 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. RSC Adv 4:11689–11697. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA46014B
Shim SC, Pae AN, Lee YL (1988) Mechanistic studies on the photochemical degradation of nifedipine. Bull Korean Chem Soc 2:271–332
Stone PH, Antman EM, Muller JE, Braunwald E (1980) Calcium channel blocking agent in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders. Part II: hemodynamic effects and clinical applications. Ann Intern Med 93:886–904. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-93-6-886
Waller DG, Renwick AG, Gruchy BS, George CF (1984) The first pass metabolism of nifedipine in man. Br J Clin Pharm 18:951–954. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02569.x
Wirzal MDH, Yusoff ARM, Zima J, Barek J (2013) Degradation of ampicillin and penicillin G using anodic oxidation. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:8978–8988
Wirzal MDH, Yusoff ARM, Zima J, Barek J (2015) Voltammetric determination of nifedipine at a hanging mercury drop electrode and a mercury meniscus modified silver amalgam electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 10:4571–4584
Wu J, He Z, Du X, Zhang C, Fu D (2016) Electrochemical degradation of acid orange II dye using mixed metal oxide anode: role of supporting electrolytes. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 59:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.08.008
Zhang W, Zhou L, Shi J, Deng H (2017) Fabrication of novel visible-light-driven AgI/g-C3N4 composites with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for diclofenac degradation. J Colloid Interface Sci 496:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.02.022
Zhou M, Sarkka H, Sillanpaa M (2011) A comparative experimental study on methyl orange degradation by electrochemical oxidation on BDD and MMO electrodes. Sep Purif Technol 78:290–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.02.013
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Ministry of Education Malaysia (LRGS Grant: 203/PKT/6720006) and Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM Vot. No.: 4L810).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wirzal, M.D.H., Sathishkumar, P., Alshahrani, L.A. et al. Nifedipine degradation by an electro-oxidation process using titanium-based RuO2–IrO2–TiO2 mixed metal oxide electrode. Chem. Pap. 75, 681–690 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01243-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01243-w