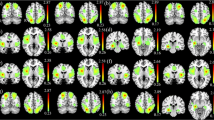
Abstract
Betel quid (BQ) is the fourth most commonly consumed psychoactive substance in the world. However, comprehensive functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies exploring the neurophysiological mechanism of BQ addiction are lacking. Betel-quid-dependent (BQD) individuals (n = 24) and age-matched healthy controls (HC) (n = 26) underwent fMRI before and after chewing BQ. Multivariate pattern analysis (MVPA) was used to explore the acute effects of BQ-chewing in both groups. A cross-sectional comparison was conducted to explore the chronic effects of BQ-chewing. Regression analysis was used to investigate the relationship between altered circuits of BQD individuals and the severity of BQ addiction. MVPA achieved classification accuracies of up to 90% in both groups for acute BQ-chewing. Suppression of the default-mode network was the most prominent feature. BQD showed more extensive and intensive within- and between-network dysconnectivity of the default, frontal-parietal, and occipital regions associated with high-order brain functions such as self-awareness, inhibitory control, and decision-making. In contrast, the chronic effects of BQ on the brain function were mild, but impaired circuits were predominately located in the default and frontal-parietal networks which might be associated with compulsive drug use. Simultaneously quantifying the effects of both chronic and acute BQ exposure provides a possible neuroimaging-based BQ addiction foci. Results from this study may help us understand the neural mechanisms involved in BQ-chewing and BQ dependence.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Reidler, J. S., Huang, C., & Buckner, R. L. (2010a). Evidence for the default network's role in spontaneous cognition. Journal of Neurophysiology, 104(1), 322–335.
Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Reidler, J. S., Sepulcre, J., Poulin, R., & Buckner, R. L. (2010b). Functional-anatomic fractionation of the brain's default network. Neuron, 65(4), 550–562.
Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Smallwood, J., & Spreng, R. N. (2014). The default network and self-generated thought: Component processes, dynamic control, and clinical relevance. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1316, 29–52.
Bogdanov, M., Ruff, C. C., & Schwabe, L. (2017). Transcranial stimulation over the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex increases the impact of past expenses on decision-making. Cerebral Cortex, 27(2), 1094–1102.
Boucher, B. J., & Mannan, N. (2002). Metabolic effects of the consumption of Areca catechu. Addiction Biology, 7(1), 103–110.
Brooks, S. J., Ipser, J., & Stein, D. J. (2017). Chronic and acute nicotine exposure versus placebo in smokers and nonsmokers: A systematic review of resting-state fMRI studies. In Addictive Substances and Neurological Disease (p. 319-338). Academic press.
Buckner, R. L., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., & Schacter, D. L. (2008). The brain's default network: Anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1124, 1–38.
Bullmore, E., & Sporns, O. (2012). The economy of brain network organization. Nature reviews. Neuroscience, 13(5), 336–349.
Burges, C. J. C. (1998). A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2(2), 121–167.
Chen, F., Zhong, Y., Zhang, Z., Xu, Q., Liu, T., Pan, M., Li, J., & Lu, G. (2015). Gray matter abnormalities associated with betel quid dependence: A voxel-based morphometry study. American Journal of Translational Research, 7(2), 364–374.
Cheng, Wei; Rolls, Edmund T.; Robbins, Trevor W.; Gong, Weikang; Liu, Zhaowen; Lv, Wujun et al. (2019): Decreased brain connectivity in smoking contrasts with increased connectivity in drinking. eLife 8.
Cole, D. M., Beckmann, C. F., Long, C. J., Matthews, P. M., Durcan, M. J., & Beaver, J. D. (2010). Nicotine replacement in abstinent smokers improves cognitive withdrawal symptoms with modulation of resting brain network dynamics. Neuroimage, 52(2), 590–599.
Cole, M. W., Reynolds, J. R., Power, J. D., Repovs, G., Anticevic, A., & Braver, T. S. (2013). Multi-task connectivity reveals flexible hubs for adaptive task control. Nature Neuroscience, 16(9), 1348–1355. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3470.
Ding, X., Yang, Y., Stein, E. A., & Ross, T. J. (2015). Multivariate classification of smokers and nonsmokers using SVM-RFE on structural MRI images. Human Brain Map**, 36(12), 4869–4879.
Dodds, C. M., Zamir, M., Robbins, S., & Trevor, W. (2011). Dissociating inhibition, attention, and response control in the frontoparietal network using functional magnetic resonance imaging. Cerebral cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991), 5, 21, 1155–1165.
Dosenbach, Nico, U. F., Nardos, B., Cohen, A. L., Fair, D. A., Power, J. D., Church, J. A., et al. (2010). Prediction of individual brain maturity using fMRI. Science (New York, N.Y.), 329(5997), 1358–1361.
Doyle, L. W., Cheong, J., Hunt, R. W., Lee, K. J., Thompson, D. K., Davis, P. G., Rees, S., Anderson, P. J., & Inder, T. E. (2010). Caffeine and brain development in very preterm infants. Annals of Neurology, 68(5), 734–742.
Esterman, M., Tamber-Rosenau, B. J., Chiu, Y.-C., & Yantis, S. (2010). Avoiding non-independence in fMRI data analysis: Leave one subject out. Neuroimage, 50(2), 572–576.
Fedota, J. R., & Stein, E. A. (2015). Resting-state functional connectivity and nicotine addiction: Prospects for biomarker development. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1349, 64–82.
Fox, M. D., Snyder, A. Z., Vincent, J. L., Corbetta, M., van Essen, D. C., & Raichle, M. E. (2005). The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(27), 9673–9678.
Fransson, P., & Marrelec, G. (2008). The precuneus/posterior cingulate cortex plays a pivotal role in the default mode network: Evidence from a partial correlation network analysis. Neuroimage, 42(3), 1178–1184.
Goldstein, R. Z., & Volkow, N. D. (2011). Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: Neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(11), 652–669.
Goldstein, R. Z., & Volkow, N. D. (2002). Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: Neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. The American journal of psychiatry n., 10(159), 1642–1652.
Golland, P., & Fischl, B. (2003). Permutation tests for classification: Towards statistical significance in image-based studies. Information Processing in Medical Imaging, 18, 330–341.
Greicius, M. D., Flores, B. H., Menon, V., Glover, G. H., Solvason, H. B., Kenna, H., Reiss, A. L., & Schatzberg, A. F. (2007). Resting-state functional connectivity in major depression: Abnormally increased contributions from subgenual cingulate cortex and thalamus. Biological Psychiatry, 62(5), 429–437.
Greicius, M. D., Supekar, K., Menon, V., & Dougherty, R. F. (2008). Resting-state functional connectivity reflects structural connectivity in the default mode network. Cerebral Cortex, 1(19), 72–78.
Guo, S., Kendrick, K. M., Yu, R., Wang, H.-L. S., & Feng, J. (2014). Key functional circuitry altered in schizophrenia involves parietal regions associated with sense of self. Human Brain Map**, 35(1), 123–139.
Guo, S., Palaniyappan, L., Liddle, P. F., & Feng, J. (2016). Dynamic cerebral reorganization in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia: A MRI-derived cortical thickness study. Psychological Medicine, 46(10), 2201–2214.
Guo, S., Huang, C.-C., Zhao, W., Yang, A. C., Lin, C.-P., Nichols, T., & Tsai, S.-J. (2018). Combining multi-modality data for searching biomarkers in schizophrenia. PLoS One, 13(2), e0191202.
Gupta, P. C., & Warnakulasuriya, S. (2002). Global epidemiology of areca nut usage. Addiction Biology, 7(1), 77–83.
Hobkirk, A. L., Nichols, T. T., Foulds, J., Yingst, J. M., Veldheer, S., Hrabovsky, S., Richie, J., Eissenberg, T., & Wilson, S. J. (2018). Changes in resting state functional brain connectivity and withdrawal symptoms are associated with acute electronic cigarette use. Brain Research Bulletin, 138, 56–63.
Huang, W., King, J. A., Ursprung, W., Sanouri, W., Zheng, S., Zhang, N., Kennedy, D. N., et al. (2014). The development and expression of physical nicotine dependence corresponds to structural and functional alterations in the anterior cingulate-precuneus pathway. Brain and behavior, 4(3), 408–417.
Huang, X., Liu, Z., Mwansisya, T. E., Pu, W., Zhou, L., Liu, C., Chen, X., Rohrbaugh, R., Marienfeld, C., Xue, Z., & Liu, H. (2017a). Betel quid chewing alters functional connectivity in frontal and default networks: A resting-state fMRI study. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI, 45(1), 157–166.
Huang, X., Pu, W., Liu, H., Li, X., Greenshaw, A. J., Dursun, S. M., Xue, Z., & Liu, Z. (2017b). Altered brain functional connectivity in betel quid-dependent chewers. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 8, 239.
Killingsworth, M. A., & Gilbert, D. T. (2010). A wandering mind is an unhappy mind. Science n., 6006(330), 932.
Kober, H., Mende-Siedlecki, P., Kross, E. F., Weber, J., Mischel, W., Hart, C. L., & Ochsner, K. N. (2010). Prefrontal-striatal pathway underlies cognitive regulation of craving. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(33), 14811–14816.
Lee, C.-Y., Chang, C.-S., Shieh, T.-Y., & Chang, Y.-Y. (2012). Development and validation of a self-rating scale for betel quid chewers based on a male-prisoner population in Taiwan: The betel quid dependence scale. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 121(1–2), 18–22.
Lee, C.-H., Chiang, S.-L., Ko, A. M.-S., Hua, C.-H., Tsai, M.-H., Warnakulasuriya, S., et al. (2014). Betel-quid dependence domains and syndrome associated with betel-quid ingredients among chewers: an Asian multi-country evidence. Addiction (Abingdon, England), 7, 109, 1194–1204.
Lerman, C., Gu, H., Loughead, J., Ruparel, K., Yang, Y., & Stein, E. A. (2014). Large-scale brain network coupling predicts acute nicotine abstinence effects on craving and cognitive function. JAMA Psychiatry, 71(5), 523–530.
Leshner, A. I. (1997). Addiction is a brain disease, and it matters. Science (New York, N.Y.), 278(5335), 45–47.
Li, Q., Liu, J., Wang, W., Wang, Y., Li, W., Chen, J., Zhu, J., Yan, X., Li, Y., Li, Z., Ye, J., & Wang, W. (2018). Disrupted coupling of large-scale networks is associated with relapse behaviour in heroin-dependent men. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience, 43(1), 48–57.
Liang, X., He, Y., Salmeron, B. J., Gu, H., Stein, E. A., & Yang, Y. (2015). Interactions between the salience and default-mode networks are disrupted in cocaine addiction. The Journal of Neuroscience, 35(21), 8081–8090.
Liao, W., Li, J., Duan, X., Cui, Q., Chen, H., & Chen, H. (2018). Static and dynamic connectomics differentiate between depressed patients with and without suicidal ideation. Human Brain Map**, 39(10), 4105–4118.
Lin, F., Wu, G., Zhu, L., & Lei, H. (2015). Altered brain functional networks in heavy smokers. Addiction Biology, 20(4), 809–819.
Liu, T., Li, J., Zhang, Z., Xu, Q., Lu, G., Huang, S., Pan, M., & Chen, F. (2016a). Altered long-and short-range functional connectivity in patients with betel quid dependence: A resting-state functional MRI study. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 40(6), 1626–1636.
Liu, T., Li, J., Zhao, Z., Zhong, Y., Zhang, Z., Xu, Q., Yang, G., Lu, G., Pan, S., & Chen, F. (2016b). Betel quid dependence is associated with functional connectivity changes of the anterior cingulate cortex: A resting-state fMRI study. Journal of Translational Medicine, 14, 33.
Liu, T., Li, J.-J., Zhao, Z.-Y., Yang, G.-S., Pan, M.-J., Li, C.-Q., Pan, S.-y., & Chen, F. (2016c). Altered spontaneous brain activity in betel quid dependence: A resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Medicine, 95(5), e2638.
Loos, E., Egli, T., Coynel, D., Fastenrath, M., Freytag, V., Papassotiropoulos, A., de Quervain, D. J.-F., & Milnik, A. (2019). Predicting emotional arousal and emotional memory performance from an identical brain network. Neuroimage, 189, 459–467.
Markett, S., Reuter, M., Montag, C., Voigt, G., Lachmann, B., Rudorf, S., et al. (2014). Assessing the function of the fronto-parietal attention network: Insights from resting-state fMRI and the attentional network test. Human Brain Map**, 4(35), 1700–1709.
Meier, T. B., Desphande, A. S., Vergun, S., Nair, V. A., Song, J., Biswal, B. B., Meyerand, M. E., Birn, R. M., & Prabhakaran, V. (2012). Support vector machine classification and characterization of age-related reorganization of functional brain networks. Neuroimage, 60(1), 601–613.
Nicholas, B., & Turk, B. (2013). Functional interactions as big data in the human brain. Science (New York, N.Y.), 342(6158), 580–584.
Norman, K. A., Polyn, S. M., Detre, G. J., & Haxby, J. V. (2006). Beyond mind-reading: Multi-voxel pattern analysis of fMRI data. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 10(9), 424–430.
Osborne, P. G., Chou, T.-S., & Shen, T.-W. (2011). Characterization of the psychological, physiological and EEG profile of acute betel quid intoxication in naïve subjects. PLoS One, 6(8), e23874.
Osborne, P. G., Ko, Y.-C., Wu, M.-T., & Lee, C.-H. (2017). Intoxication and substance use disorder to Areca catechu nut containing betel quid: A review of epidemiological evidence, pharmacological basis and social factors influencing quitting strategies. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 179, 187–197.
Pereira, F., Mitchell, T., & Botvinick, M. (2009). Machine learning classifiers and fMRI: A tutorial overview. Neuroimage, 45(1 Suppl), S199–S209.
Posner, J., Hellerstein, D. J., Gat, I., Mechling, A., Klahr, K., Wang, Z., McGrath, P. J., Stewart, J. W., & Peterson, B. S. (2013). Antidepressants normalize the default mode network in patients with dysthymia. JAMA Psychiatry, 70(4), 373–382.
Raichle, M. E. (2015). The brain's default mode network. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 38, 433–447.
Rose, J. E., McClernon, F. J., Froeliger, B., Behm, F. M., Preud'homme, X., & Krystal, A. D. (2011). Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the superior frontal gyrus modulates craving for cigarettes. Biological Psychiatry, 70(8), 794–799.
Sariah, A., Liu, Z., Pu, W., Liu, H., Xue, Z., & Huang, X. (2019). Structural and functional alterations in betel-quid chewers: A systematic review of neuroimaging findings. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 10, 16.
Tanabe, J., Nyberg, E., Martin, L. F., Martin, J., Cordes, D., Kronberg, E., & Tregellas, J. R. (2011). Nicotine effects on default mode network during resting state. Psychopharmacology, 216(2), 287–295.
Tomasi, D., & Volkow, N. D. (2010). Functional connectivity density map**. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(21), 9885–9890.
Wang, K., Yang, J., Zhang, S., Wei, D., Hao, X., Tu, S., & Qiu, J. (2014). The neural mechanisms underlying the acute effect of cigarette smoking on chronic smokers. PLoS One, 9(7), e102828.
Weiland, B. J., Sabbineni, A., Calhoun, V. D., Welsh, R. C., & Hutchison, K. E. (2015). Reduced executive and default network functional connectivity in cigarette smokers. Human Brain Map**, 36(3), 872–882.
Weng, J.-C., Chou, Y.-S., Huang, G.-J., Tyan, Y.-S., & Ho, M.-C. (2018). Map** brain functional alterations in betel-quid chewers using resting-state fMRI and network analysis. Psychopharmacology, 235(4), 1257–1271.
Woodward, N. D., Rogers, B., & Heckers, S. (2011). Functional resting-state networks are differentially affected in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 130(1–3), 86–93.
**a, M., Wang, J., & He, Y. (2013). BrainNet viewer: A network visualization tool BrainNet viewer: A network visualization for human brain Connectomics. PLoS One, 8(7).
Yan, C.-G., Wang, X.-D., Zuo, X.-N., & Zang, Y.-F. (2016). DPABI: Data Processing & Analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics, 14(3), 339–351.
Yuan, F., Kong, L., Zhu, X., Jiang, C., Fang, C., & Liao, W. (2017a). Altered gray-matter volumes associated with betel quid dependence. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 8, 139.
Yuan, F., Zhu, X., Kong, L., Shen, H., Liao, W., & Jiang, C. (2017b). White matter integrity deficit associated with betel quid dependence. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 8, 201.
Zahr, N. M., Kaufman, K. L., & Harper, C. G. (2011). Clinical and pathological features of alcohol-related brain damage. Nature reviews. Neurology, 7(5), 284–294.
Zhang, R., & Volkow, N. D. (2019). Brain default-mode network dysfunction in addiction. NeuroImage, 200, 313–331.
Zhao, W., Guo, S., Linli, Z., Yang, A. C., Lin, C.-P., & Tsai, S.-J. (2019). Functional, anatomical, and morphological networks highlight the role of basal ganglia-thalamus-cortex circuits in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia bulletin.
Zhu, X., Zhu, Q., Jiang, C., Shen, H., Wang, F., Liao, W., & Yuan, F. (2017). Disrupted resting-state default mode network in betel quid-dependent individuals. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 84.
Acknowledgements
Zhening Liu is supported by the China Precision Medicine initiative grant (No. 2016YFC0906300) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grant (No.81561168021). Shuixia Guo is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grant (No.11671129, 31671134). All the work of the study was done by the authors. The authors were responsible for the authenticity of the data and related results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants followed the ethical standards of the institutional or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 765 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linli, Z., Huang, X., Liu, Z. et al. A multivariate pattern analysis of resting-state functional MRI data in Naïve and chronic betel quid chewers. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 1222–1234 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00322-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00322-6