Abstract
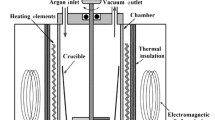
The Al-B4C composites are interestingly used for neutron shielding due to its low weight, high strength, and neutron absorbing. However, during manufacturing process of Al-B4C composites, high content of B4C which leads to aggregation is main problem, as well as the low content resulting in poor neutron absorbing. To solve these problems, this study tries to improve the stirring systems by applying a magnetic field based on traditional mechanical stirring and changing the number and shape of the blade of impeller to enhance the flow of the turbulent kinetic energy to maximizes molten aluminum stirring effects. Compared to the traditional mechanical stirring, simulation, and experimentation showed magnetic-mechanical coupled stirring has the higher turbulent kinetic energy, and the dead region is greatly reduced. From the numerical investigations and experiments in the present work, an optimal configuration was selected based on the particle distribution in the magnetic-mechanical coupled stirring. When the stirring time is 30-40 min, the Al-31 wt.% B4C composites were successfully manufactured and with the B4C particles homogeneously distributed in matrix.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Prăvălie and G. Bandoc, Nuclear Energy: Between Global Electricity Demand, Worldwide Decarbonisation Imperativeness, and Planetary Environmental Implications, J. Environ. Manage., 2018, 209, p 81–92.
P. Liu, P. Chu and J. Hou, Accommodation Issue of Nuclear Power in China: Status Quo, Barriers and Solutions, Energy Strat. Rev., 2018, 22, p 166–178.
Z.G. Xu, L.T. Jiang, Q. Zhang, J. Qiao and G.H. Wu, The Microstructure and Influence of Hot Extrusion on Tensile Properties of (Gd+B4C)/Al Composite, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 729, p 1234–1243.
B. Tozkoparan, B. Dikici, M. Topuz et al., Al-5Cu/B4Cp Composites: The Combined Effect of Artificially Aging (T6) and Particle Volume Fractions on the Corrosion Behaviour, Adv. Powder Technol., 2020, 31(7), p 2833–2842.
J. Hashim, L. Looney and M.S.J. Hashmi, Metal Matrix Composites: Production by the Stir-Casting Method, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1999, 92–93, p 1–7.
C. Wu, S. **e, Y. Li, H. Xu and Y. Chen, Effects of Al Addition on the Phase Transformation and Interfacial Evolution in Multilayer Ti-B4C Composite, Ceram. Int., 2018, 44, p 4121–4125.
G. Burlak, M. Vlasova, P. Aguilar et al., Optical Percolation in Ceramics Assisted by Porous Clusters, Opt. Commun., 2009, 282(14), p 2850–2856.
G. Burlak, A. Díaz-De-Anda, Y. Karlovich et al., Critical Behavior of Nanoemitter Radiation in a Percolation Material, Phys. Lett. A, 2009, 373(16), p 1492–1499.
N.K. Sharma, R.K. Misra and S. Sharma, Experimental Characterization and Numerical Modeling of Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Al-B4C Composites, Ceram. Int., 2017, 43, p 513–522.
B. Chandra Kandpal, J. Kumar and H. Singh, Manufacturing and Technological Challenges in Stir-Casting of Metal Matrix Composites: A Review, Mater. Today Proc., 2018, 5, p 5–10.
T. Yamamoto, K. Kato, S.V. Komarov, Y. Ueno, M. Hayashi and Y. Ishiwata, Investigation of Melt Stirring in Aluminum Melting Furnace Through Water Model, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2018, 259, p 409–415.
J.F. Bilodeau, C. Lakroni and Y. Kocaefe, Modeling of Rotary Injection Process for Molten Aluminum Processing, Light Metals, 2001, 2001, p 1009–1015.
R. Panneerselvam, S. Savithri and G.D. Surender, CFD Simulation of Hydrodynamics of Gas–Liquid–Solid Fluidised Bed Reactor, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2009, 64, p 1119–1135.
S. Fashu and R. Khan, Comparison Between Axial and Radial Melt Stirring on Purification of Industrial Aluminum During Ohno Continuous Casting, Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J., 2016, 19, p 2100–2108.
A.T. Thomas, R. Parameshwaran, A. Muthukrishnan and M.A. Kumaran, Development of Feeding & Stirring Mechanisms for Stir-casting of Aluminium Matrix Composites, Procedia Mater. Sci., 2014, 5, p 1182–1191.
M. Jensen and Y. Yue, Effect of stirring on striae in glass melts, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2012, 358, p 349–353.
S. Louhenkilpi, Chapter 1.8: Continuous Casting of Steel, Treatise on Process Metallurgy. S. Seetharaman Ed., Elsevier, Boston, 2014, p 373–434
U.K.G.B. Annigeri Veeresh Kumar, Method of Stir-Casting of Aluminum metal matrix Composites: A review, Mater. Today Proc., 2017, 4, p 1140–1146.
A. Kumar, S. Kumar and N.K. Mukhopadhyay, Introduction to Magnesium Alloy Processing Technology and Development of Low-Cost Stir-Casting Process for Magnesium Alloy and Its Composites, J. Magn. Alloys., 2018, 6, p 245–254.
B.J. Smith, P.A. Warke, J.P. McGreevy and H.L. Kane, Salt-Weathering Simulations Under Hot Desert Conditions: Agents of Enlightenment or Perpetuators of Preconceptions, Geomorphology, 2005, 67, p 211–227.
R.Q. Liang, J.H. Ji, F.S. Yan and J.C. He, Numerical Study on Flow Characteristics in a Stirring Vessel, Appl. Mech. Mater., 2012, 130–134, p 3050–3053.
H. Su, W. Gao, H. Zhang, H. Liu, J. Lu and Z. Lu, Optimization of Stirring Parameters Through Numerical Simulation for the Preparation of Aluminum Matrix Composite by Stir-casting Process, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 2010, 132, p 061007.
P.K. Rohatgi, J. Sobczak, R. Asthana and J.K. Kim, Inhomogeneities in Silicon Carbide Distribution in Stirred Liquids: A Water Model Study for Synthesis of Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1998, 252, p 98–108.
J. Zhang, Z. Gao, Y. Cai, H. Cao, Z. Cai and Y. Bao, Power Consumption and Mass Transfer in a Gas-Liquid-Solid Stirred Tank Reactor with Various Triple-Impeller Combinations, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2017, 170, p 464–475.
M. Hernández-Hernández, J.L. Camacho-Martínez, C. González-Rivera and M.A. Ramírez-Argáez, Impeller Design Assisted by Physical Modeling and Pilot Plant Trials, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2016, 236, p 1–8.
T.T. Tran, T.T. Vo, S.C. Cho, H.L. Dong and W.R. Hwang, A Stir-Casting System for Drawdown of Light Particles in Manufacturing of Metal Matrix Composites, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2018, 257, p 123–131.
R. Harichandran and N. Selvakumar, Effect of Nano/Micro B4C Particles on the Mechanical Properties of Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites Fabricated by Ultrasonic Cavitation-Assisted Solidification Process, Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng., 2016, 16, p 147–158.
J. Campbell, Chapter 17: Controlled Solidification Techniques, Complete Casting Handbook, 2nd ed., J. Campbell Ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, 2015, p 883–891
J. Zhao and Q. Li, Study on Interfacial Phenomena in Aluminum-Aluminum Bimetal Fabricated by Extrusion at Different Temperatures, J. Mater. Eng. Perf., 2019, 28, p 1122–1131.
S. Mohan, Influence of Stirring Speed and Stirring Time on Distribution of Particles in Cast Metal Matrix Composite, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, 171, p 268–273.
Y. Li, Q. Li, W. Liu and G. Shu, Effect of Ti Content and Stirring Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Al-B4C Composites, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 684, p 496–503.
Acknowledgment
This work was financially support by the Joint funds of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U530108) and the Program for Innovative Research Team of Huizhou University (IRTHZU). The authors sincerely acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for their insights and comments to the further improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Li, Q. Effect of Magnetic-Mechanical Coupled Stirring on the Distribution of B4C Particles in Al-B4C Composites. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 907–917 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06294-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06294-y