Abstract
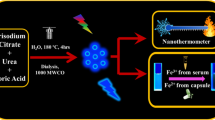
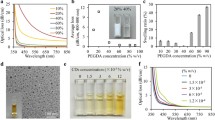
In this paper, a nontoxic and biocompatible hydrogel optic fiber Fe3+ sensor is presented. Nitrogen carbon dots (NCDs) as fluorescence indicators are prepared by a one-step hydrothermal method using citric acid as the carbon source and urea as the nitrogen source. Transmission electron microscopy images and x-ray diffraction analysis show that the average size of the NCDs is 3.94 nm, and they have an amorphous structure. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy shows that nitrogen is effectively doped into the framework of the NCDs. The hydrogel optical fiber with a core-cladding structure is fabricated using different concentrations of polyethylene glycol diacrylate as precursor. The NCDs were incorporated into the core of the hydrogel fiber for Fe3+ sensing. NCDs were selectively quenched by Fe3+ diffused into the hydrogel fiber. The sensitivity of the system was optimized by varying the concentration of doped NCDs. The fluorescence intensity decreased with the increase in temperature, with the greatest sensitivity at 24°C. By measuring the fluorescence intensity, the quantitative and selective detection of iron ions was realized in the range of 0–60 um, and the detection limit was 0.802 um. It has good application prospects in the detection of Fe3+ and can realize the detection of implanted biological Fe3+ in vivo.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.W. Hentze, M.U. Muckenthaler, B. Galy, and C. Camaschella, Two to tango: regulation of Mammalian iron metabolism. Cell 142, 24 (2010).
G. Weiss and L.T. Goodnough, Anemia of chronic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 1011 (2005).
L.T. Goodnough, E. Nemeth, and T. Ganz, Detection, evaluation, and management of iron-restricted erythropoiesis. Blood 116, 4754 (2010).
L. Thomas and C. Thomas, Detection of iron restriction in anaemic and non-anaemic patients: new diagnostic approaches. Eur. J. Haematol. 99, 262 (2017).
G.A. Antunes, H.S. dos Santos, Y.P. da Silva, M.M. Silva, C.M.S. Piatnicki, and D. Samios, Determination of Iron, Copper, Zinc, Aluminum, and Chromium in Biodiesel by flame atomic absorption spectrometry using a microemulsion preparation method. Energy Fuels 31, 2944 (2017).
H. Hu, Y. Tang, H. Ying, M. Wang, P. Wan, and X.J. Yang, The effect of copper on iron reduction and its application to the determination of total iron content in iron and copper ores by potassium dichromate titration. Talanta 125, 425 (2014).
Y. Zhu, D. Pan, X. Hu, H. Han, M. Lin, and C. Wang, An electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide/gold nanoparticles modified electrode for determination of iron in coastal waters. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 243, 1 (2017).
B. Peng, Y. Shen, Z. Gao, M. Zhou, Y. Ma, and S. Zhao, Determination of total iron in water and foods by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with microvolume UV-vis spectrophotometry. Food Chem. 176, 288 (2015).
W. Ming, X. Wang, W. Lu, Z. Zhang, X. Song, J. Li, and L. Chen, Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the fluorescent detection of trace 17β-estradiol in environmental water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 238, 1309 (2017).
Y. Cai, M. Li, M. Wang, J. Li, Y.-N. Zhang, and Y. Zhao, Optical fiber sensors for metal ions detection based on novel fluorescent materials. Front. Phys. 8, 598209 (2020).
V.M. Naik, S.V. Bhosale, and G.B. Kolekar, A brief review on the synthesis, characterisation and analytical applications of nitrogen doped carbon dots. Anal. Methods 14, 877 (2022).
Y. Wang, T. Lv, K. Yin, N. Feng, X. Sun, J. Zhou, and H. Li, Carbon dot-based hydrogels: preparations properties and applications. Small 19, e2207048 (2023).
L. Ðorđević, F. Arcudi, and M. Prato, Preparation, functionalization and characterization of engineered carbon nanodots. Nat. Protoc. 14, 2931 (2019).
X.C. Li, S.J. Zhao, B.L. Li, K. Yang, M.H. Lan, and L.T. Zeng, Advances and perspectives in carbon dot-based fluorescent probes: mechanism, and application. Coord. Chem. Rev. 431, 213686 (2021).
Y.F. Wang and A.G. Hu, Carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 6921 (2014).
W. Su, R. Guo, F. Yuan, Y. Li, X. Li, Y. Zhang, S. Zhou, and L. Fan, Red-emissive carbon quantum dots for nuclear drug delivery in cancer stem cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11, 1357 (2020).
R. Atchudan, T.N.J.I. Edison, S. Perumal, N. Muthuchamy, and Y.R. Lee, Hydrophilic nitrogen-doped carbon dots from biowaste using dwarf banana peel for environmental and biological applications. Fuel 275, 117821 (2020).
L. Wang, J. Jana, J.S. Chung, and S.H. Hur, High quantum yield aminophenylboronic acid-functionalized N-doped carbon dots for highly selective hypochlorite ion detection. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 260, 119895 (2021).
Z. Kang and S.T. Lee, Carbon dots: advances in nanocarbon applications. Nanoscale 11, 19214 (2019).
Z.-A. Qiao, Y. Wang, Y. Gao, H. Li, T. Dai, Y. Liu, and Q. Huo, Commercially activated carbon as the source for producing multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots by chemical oxidation. Chem. Commun. 46, 8812 (2010).
S. Mohapatra, M.K. Bera, and R.K. Das, Rapid “turn-on” detection of atrazine using highly luminescent N-doped carbon quantum dot. Sens. Actuators B CHEM 263, 459 (2018).
P. Yang, Z. Zhu, T. Zhang, M. Chen, Y. Cao, W. Zhang, X. Wang, X. Zhou, and W. Chen, Facile synthesis and photoluminescence mechanism of green emitting xylose-derived carbon dots for anti-counterfeit printing. Carbon 146, 636 (2019).
X. Gong, Q. Zhang, Y. Gao, S. Shuang, M.M.F. Choi, and C. Dong, Phosphorus and nitrogen dual-doped hollow carbon dot as a nanocarrier for doxorubicin delivery and biological imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 11288 (2016).
X. Gong, Y. Liu, Z. Yang, S. Shuang, Z. Zhang, and C. Dong, An “on-off-on” fluorescent nanoprobe for recognition of chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid based on phosphorus/nitrogen dual-doped carbon quantum dot. Anal. Chim. Acta 968, 85 (2017).
Z. Peng, C. Ji, Y. Zhou, T. Zhao, and R.M. Leblanc, Polyethylene glycol (PEG) derived carbon dots: preparation and applications. Appl. Mater. Today 20, 100677 (2020).
C. Ding, A. Zhu, and Y. Tian, Functional surface engineering of C-dots for fluorescent biosensing and in vivo bioimaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 47, 20 (2014).
H.J. Kalinowski, J.L. Fabris, W.J. Bock, S.P. Wren, T. Sun, K.T.V. Grattan, A fluorescent optical fibre chemosensor for mercury detection, International Conference on Optical Fibre Sensors(OFS24) International Society for Optics and Photonics, (2015).
T.-W. Sung and Y.-L. Lo, Highly sensitive and selective sensor based on silica-coated CdSe/ZnS nanoparticles for Cu2+ ion detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 165, 119 (2012).
M. Elsherif, M.U. Hassan, A.K. Yetisen, and H. Butt, Hydrogel optical fibers for continuous glucose monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 137, 25 (2019).
N. Gogoi, M. Barooah, G. Majumdar, and D. Chowdhury, Carbon dots rooted agarose hydrogel hybrid platform for optical detection and separation of heavy metal ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 3058 (2015).
J. Guo, M. Zhou, and C. Yang, Fluorescent hydrogel waveguide for on-site detection of heavy metal ions. Sci. Rep. 7, 7902 (2017).
F.A. Permatasari, A.H. Aimon, F. Iskandar, T. Ogi, and K. Okuyama, Role of C-N configurations in the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots synthesized by a hydrothermal route. Sci. Rep. 6, 21042 (2016).
Z.F. Pu, Q.L. Wen, Y.J. Yang, X.M. Cui, J. Ling, P. Liu, and Q.E. Cao, Fluorescent carbon quantum dots synthesized using phenylalanine and citric acid for selective detection of Fe(3+) ions. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 229, 117944 (2020).
M. Zulfajri, G. Gedda, C.J. Chang, Y.P. Chang, and G.G. Huang, Cranberry beans derived carbon dots as a potential fluorescence sensor for selective detection of Fe3+ ions in aqueous solution. ACS Omega 4, 15382 (2019).
Y. Liu, Y. Liu, S.J. Park, Y. Zhang, T. Kim, S. Chae, M. Park, and H.Y. Kim, One-step synthesis of robust nitrogen-doped carbon dots: acid-evoked fluorescence enhancement and their application in Fe3+ detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 17747 (2015).
L. Zhang, Z. Bian, A. Hu, J. Li, L. Liu, and F. Chu, Iodine ions sensing based on fluorescence quenching method and hydrogel fiber doped with fluorescein. Opt. Commun. 475, 126225 (2020).
J. Xu, Y. Guo, T. Gong, K. Cui, L. Hou, and C. Yuan, B, N co-doped carbon dots based fluorescent test paper and hydrogel for visual and efficient dual ion detection. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 145, 110047 (2022).
W. Wu, X. Wu, M. He, X. Yuan, J. Lai, and H. Sun, A novel carbon dot/polyacrylamide composite hydrogel film for reversible detection of the antibacterial drug ornidazole. RSC Adv. 11, 22993 (2021).
M. Nagaraj, S. Ramalingam, C. Murugan, S. Aldawood, J.O. **, I. Choi, and M. Kim, Detection of Fe3+ ions in aqueous environment using fluorescent carbon quantum dots synthesized from endosperm of Borassus flabellifer. Environ. Res. 212, 113273 (2022).
W. Lukosz and P. Pliska, Determination of thickness and refractive index of SiO2 films on silicon wafers using an Abbe refractometer. Opt. Commun. 85, 381 (1991).
Y. Chen, H. Lian, Y. Wei, X. He, Y. Chen, B. Wang, Q. Zeng, and J. Lin, Concentration-induced multi-colored emissions in carbon dots: origination from triple fluorescent centers. Nanoscale 10, 6734 (2018).
H.K. Sadhanala, S. Senapati, and K.K. Nanda, Temperature sensing using sulfur-doped carbon nanoparticles. Carbon 133, 200 (2018).
G. Li, N. Lv, W. Bi, J. Zhang, and J. Ni, Nitrogen-doped carbon dots as a fluorescence probe suitable for sensing Fe3+ under acidic conditions. New J. Chem. 40, 10213 (2016).
K. Qu, J. Wang, J. Ren, and X. Qu, Carbon dots prepared by hydrothermal treatment of dopamine as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for the label-free detection of iron(III) ions and dopamine. Chem. Eur. J. 19, 7243 (2013).
A. Zhao, C. Zhao, M. Li, J. Ren, and X. Qu, Ionic liquids as precursors for highly luminescent, surface-different nitrogen-doped carbon dots used for label-free detection of Cu2+/Fe3+ and cell imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 809, 128 (2014).
H.T. Lin, J. Huang, and L.Y. Ding, A recyclable optical fiber sensor based on fluorescent carbon dots for the determination of ferric ion concentrations. J. Lightwave Technol. 37, 4815 (2019).
L.S. Laxmeshwar, M.S. Jadhav, J.F. Akki, P. Raikar, J. Kumar, O. Prakash, R. Mahakud, and U.S. Raikar, Quantification of chloride and iron in sugar factory effluent using long period fiber grating chemical sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 258, 850 (2018).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62205195) and the Local College Capacity Building Project of the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission (No. 20020500700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, Z., Xu, Q., Chu, F. et al. Fe3+ Sensing Based on Hydrogel Optical Fiber Doped with Nitrogen Carbon Dots. J. Electron. Mater. 53, 642–651 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10821-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10821-z