Abstract
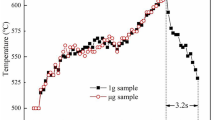
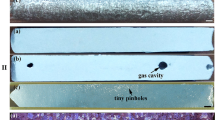
Marangoni convection significantly affects the solidification structure as it controls the bubble behavior and mass transfer in the melt. Sn-3.5Ag/Sn-17Bi-0.5Cu (wt pct) alloy with different surface tension gradients was fabricated and solidified on a Cu ring substrate under space microgravity condition (SJ-10 satellite) to study the Marangoni convection formation mechanism. The pore and element distributions in the solidified alloy and surface tension gradient in the melt were analyzed. The differences between the microstructures of alloys solidified under microgravity and normal gravity conditions were also investigated. The surface tension gradient induced by Bi concentration difference resulted in the formation of Marangoni convection from the right to left of the melt under the microgravity condition. In the left (Bi-scarce) part of the melt, Marangoni convection induced by the Cu concentration difference flowed from outside to inside. Driven by bubble-agitation convection, Cu mainly migrated from the substrate to the right part of the melt. Therefore, dendrite-like CuxSny was distributed along a gradient. Under the normal gravity condition, significant gravity-induced convection resulted in an even distribution of Bi and Cu, which decreased the contact angle and reduced the surface tension, thus promoting nucleation of the alloy. Therefore, fine dendrite-like CuxSny with larger number density were uniformly distributed in the melt.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Ruan, Q.Q. Wang, and S. Chang, B. Wei: Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 141, pp. 456-465.
K. L. Scotti, E. E. Northard, A. Plunk, B. C. Tappan, and D. C. Dunand: Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 124, pp. 608-619.
Z. Lu, Y. Fautrelle, and X. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018, vol. 49, pp. 4383-4388.
C.R. Heiple, and J.R. Roper: Weld. J., 1982, vol. 61, pp. 97-102.
L. G. Napolitano: Science, 1984, vol. 225, pp. 197-198.
T. Yano, K. Nishino, H. Kawamura, I. Ueno, S. Matsumoto, M. Ohnishi, and M. Sakurai: Exp. Fluids, 2012, vol. 53, pp. 9-20.
X. Zou, D. Zhao, J. Sun, C. Wang, and H. Matsuura: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 481-489.
S. Sun, Q. Hu, W. Lu, Z. Ding, M. **a, and J. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018 vol. 49, pp. 4429-4434.
Q. Wang, X. Zou, H. Matsuura, and C. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 18-22.
W. Lu, S. Zhang, W. Zhang, Q. Hu, J. Yu, Y. Fu, and J. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, vol. 48, pp. 2701-2705.
F. Dai, Y. Wu, W. Wang, and B. Wei: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018, vol. 49, pp. 5478-5487.
L. E. Scriven, and C. V. Sternling: Nature, 1960, vol. 187, pp. 186-188.
H.E. Jeffes: Physical chemistry of process metallurgy, Institution of Mining and Metallurgy, Bei**g, 1974.
F. Czerwinski: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48, pp. 367-393.
H. Fujii, N. Sogabe, and K. Nogi: Materials Science Forum, 2006, vol. 521, pp. 301-304.
L. Zang, Z. Yuan, H. Xu, and B. Xu: Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, vol. 257 (11), pp. 4877-4884.
B. Xu, Z. Yuan, and Y. Wu: Colloids Surf. A, 2014, vol. 441(1), pp. 217-225.
L. Zang, Z. Yuan, Y. Zhu, B. Xu, H. Matsuura, and F. Tsukihashi: Colloids Surf. A, 2012, vol. 414, pp. 57-65.
Z. Zhang, X. Hu, X. Jiang, and Y. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2019, vol. 50, pp. 480-492.
P. Sungkhaphaitoon, and T. Plookphol: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018, vol. 49, pp. 652-660.
B. Xu, J. Chen, Z. Yuan, L. Zhang, L. Zhang, and Y. Wu: Microgravity Sci. Technol., 2016, vol. 28, pp. 115-122.
Q. Kang, and W. Hu: Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016, vol. 31(5), pp. 574-580.
W. Hu, J. Zhao, M. Long, X. Zhang, Q. Liu, M. Hou, Q. Kang, Y. Wang, S. Xu, W. Kong, H. Zhang, S. Wang, Y. Sun, H. Hang, Y. Huang, W. Cai, Y. Zhao, J. Dai, H. Zheng, E. Duan, and J. Wang: Microgravity Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 26(3), pp. 159-169.
W. Hu, B. Tang, and Q. Kang: Aeron Aero Open Access J1, 2017, pp. 125-127.
Y. Wang, H. Zhao, Y. Zhang, J. Qiu, X. Mao, and X. Wang: Aerospace China, 2016, vol. 4, pp. 3-13.
X. Yu, M. Wang, Z. Wang, X. Gong, and Z. Guo: Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, vol. 360, pp. 502-509.
X. Yu, M. Wang, Z. Wang, X. Gong, and Z. Guo: Electrochim. Acta, 2016, vol. 211, pp. 900-910.
Z. Yuan, W. Huang, and K. Mukai: Appl. Phys. A, 2004, vol. 78, pp. 617-622.
Z. Yuan, and K. Mukai: J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2004, vol. 270(1), 140-145.
X. Yu, M. Wang, Z. Wang, X. Gong, and Z. Guo: J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, vol. 121, pp. 16792-16802.
Y. Ruan, Q.Q. Wang, S. Chang, and B. Wei: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 4405-4413.
H. Jiang, J. He, and J. Zhao: Sci. Rep., 2015, 5:12680. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12680
N. D. Nikolic, K. I. Popov, J Lj, and M. G. Pavlovic: J. Electroanal. Chem., 2006, vol. 588, pp. 88-98.
T. Cool, and P.W. Voorhees: Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 127, pp. 359-367.
H. Jiang, Q. Sun, L. Zhao, and J. Zhao: J. Alloy Compd., 2018, vol. 748, pp. 774-782.
Q. Sun, H. Jiang, J. Zhao, and J. He: Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 129, pp. 321-330.
E. Yablonovitch, and T. Gmitter: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1984, vol. 131, pp. 2625-2630.
Z. Q. Cui, Principles of Metallography and heat treatment, Harbin Institute of Technology Press, Harbin, 2008.
W. Yao, C. Yang, X. Han, M. Chen, B. Wei, and Z. Guo: Acta Phys. Sin., 2003, vol. 52, pp. 448-452.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U1738101 and 51804023), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. FRF-TP-18-007A1 and FRF-MP-18-007), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 2019M650489 and 2019T120046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted November 21, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Z., Wang, R. & Yu, X. Marangoni-Convection-Driven Bubble Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Sn-3.5Ag/Sn-17Bi-0.5Cu (Wt Pct) Alloy Solidified on Cu Substrate Under Space Microgravity Condition. Metall Mater Trans A 50, 5210–5220 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05424-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05424-5