Abstract
Objective
To study the effect of electroacupuncture (EA) on oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy (OIPN) in rats.
Methods
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were equally divided into 3 groups using a random number table: the control group, the OIPN group, and the EA (OIPN + EA) group, with 10 rats in each. The time courses of mechanical, cold sensitivity, and microcirculation blood flow intensity were determined. The morphology of the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) was observed by electron microscopic examination. The protein levels of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), and the transient receptor potential (TRP) protein family in DRGs were assayed by Western blot.
Results
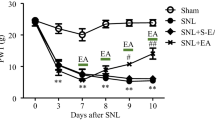
EA treatment significantly reduced mechanical allodynia and cold allodynia in OIPN rats (P<0.01). Notably, oxaliplatin treatment resulted in impaired microcirculatory blood flow and pathomorphological defects in DRGs (P<0.01). EA treatment increased the microcirculation blood flow and attenuated the pathological changes induced by oxaliplatin (P<0.01). In addition, the expression levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 were down-regulated, and the TRP protein family was over-expressed in the DRGs of OIPN rats (P<0.01). EA increased the expression levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 and decreased the level of TRP protein family in DRG (P<0.05 or P<0.01).
Conclusion
EA may be a potential alternative therapy for OIPN, and its mechanism may be mainly mediated by restoring the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson AB, Venook AP, Al-Hawary MM, Cederquist L, Chen YJ, Ciombor KK, et al. Rectal cancer, version 2. 2018, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2018;16:874–901.
Kang L, Tian Y, Xu S, Chen H. Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy: clinical features, mechanisms, prevention and treatment. J Neurol 2021;268:3269–3282.
Gebremedhn EG, Shortland PJ, Mahns DA. The incidence of acute oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy and its impact on treatment in the first cycle: a systematic review. BMC Cancer 2018;18:410.
Storey DJ, Sakala M, McLean CM, Phillips HA, Dawson LK, Wall LR, et al. Capecitabine combined with oxaliplatin (CapOx) in clinical practice: how significant is peripheral neuropathy? Ann Oncol 2010;21:1657–1661.
Griffith KA, Zhu S, Johantgen M, Kessler MD, Renn C, Beutler AS, et al. Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy and identification of unique severity groups in colorectal cancer. J Pain Symptom Manage 2017;54:701–706.
Huang CC, Ho TJ, Ho HY, Chen PY, Tu CH, Huang YC, et al. Acupuncture relieved chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with breast cancer: a pilot randomized sham-controlled trial. J Clin Med 2021;10:3694.
Lu W, Giobbie-Hurder A, Freedman RA, Shin IH, Lin NU, Partridge AH, et al. Acupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled pilot trial. Oncologist 2020;25:310–318.
Nash J, Armour M, Penkala S. Acupuncture for the treatment of lower limb diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review. Acupunct Med 2019;37:3–15.
Chen Z, Liang F, Yang M, Li D, Zhang Y, Ren Y. Effect and safety of CX-DZ-II intelligent electroacupuncture therapeutic instrument for neck pain caused by cervical spondylos: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Chin J Integr Med 2020;26:375–381.
Ali U, Apryani E, Ahsan MZ, Shoaib RM, Ahmad KA, WANG Y. Acupuncture/electroacupuncture as an alternative in current Opioid Crisis. Chin J Integr Med 2020;26:643–647.
Li Y, Yin C, Li X, Liu B, Wang J, Zheng X, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathic pain in rats via suppressing TLR4 signaling and TRPV1 up-regulation in sensory neurons. Int J Mol Sci 2019;20:5917.
Zhang S, Wu T, Zhang H, Yang Y, Jiang H, Cao S, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with malignant tumor: a single-blinded, randomized controlled trial. J Tradit Chin Med 2017;37:179–184.
Greenlee H, Crew KD, Capodice J, Awad D, Buono D, Shi Z, et al. Randomized sham-controlled pilot trial of weekly electro-acupuncture for the prevention of taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy in women with early stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2016;156:453–464.
Wei G, Gu Z, Gu J, Yu J, Huang X, Qin F, et al. Platinum accumulation in oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2021;26:35–42.
Boyette-Davis J, Dougherty PM. Protection against oxaliplatin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia and intraepidermal nerve fiber loss by minocycline. Exp Neurol 2011;229:353–357.
Boyette-Davis J, **n W, Zhang H, Dougherty PM. Intraepidermal nerve fiber loss corresponds to the development of taxol-induced hyperalgesia and can be prevented by treatment with minocycline. Pain 2011;152:308–313.
Ju Z, Cui H, Guo X, Yang H, He J, Wang K. Molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of acupuncture on neuropathic pain. Neural Regen Res 2013;8:2350–2359.
Yu J, Zhao C, Luo X. The effects of electroacupuncture on the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2/P2X3 signal pathway in the spinal cord of rats with chronic constriction injury. Anesth Analg 2013;116:239–246.
**ao WH, Zheng H, Bennett GJ. Characterization of oxaliplatin-induced chronic painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat and comparison with the neuropathy induced by paclitaxel. Neuroscience 2012;203:194–206.
Flatters SJ, Bennett GJ. Ethosuximide reverses paclitaxel-and vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Pain 2004;109:150–161.
Komirishetty P, Areti A, Sistla R, Kumar A. Morin mitigates chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced peripheral neuropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress induced PARP over-activation and neuroinflammation. Neurochem Res 2016;41:2029–2042.
Wu CY, Chan KC, Cheng YJ, Yeh YC, Chien CT. Effects of different types of fluid resuscitation for hemorrhagic shock on splanchnic organ microcirculation and renal reactive oxygen species formation. Crit Care 2015;19:434.
Molassiotis A, Dawkins B, Longo R, Suen LK, Cheng HL, Mok T, et al. Economic evaluation alongside a randomised controlled trial to assess the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of acupuncture in the management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Acupunct Med 2021;39:41–52.
Siegelmann-Danieli N, Michaelis O, Katzir I, Wolner M, Zwang GA. Acupuncture treatment in cancer patients in a community setting: feasibility and positive impact on quality of life. J Altern Complement Med 2020;26:758–759.
** Y, Wang Y, Zhang J, **ao X, Zhang Q. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture against chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-aalysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020;2020:8875433.
Yang Y, Hu L, Wang C, Yang X, Song L, Jiang C, et al. p38/TF/HIF-α signaling pathway participates in the progression of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice. Biomed Res Int 2019;2019:5347804.
Yang Y, Luo L, Cai X, Fang Y, Wang J, Chen G, et al. Nrf2 inhibits oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy via protection of mitochondrial function. Free Radic Biol Med 2018;120:13–24.
Sun H, Guo X, Wang Z, Wang P, Zhang Z, Dong J, et al. Alphalipoic acid prevents oxidative stress and peripheral neuropathy in Nab-paclitaxel-treated rats through the Nrf2 signalling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019;2019:3142732.
Shen Y, Zhang ZJ, Zhu MD, Jiang BC, Yang T, Gao YJ. Exogenous induction of HO-1 alleviates vincristine-induced neuropathic pain by reducing spinal glial activation in mice. Neurobiol Dis 2015;79:100–110.
Singh R, Adhya P, Sharma SS. Redox-sensitive TRP channels: a promising pharmacological target in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2021;25:529–545.
Chukyo A, Chiba T, Kambe T, Yamamoto K, Kawakami K, Taguchi K, et al. Oxaliplatin-induced changes in expression of transient receptor potential channels in the dorsal root ganglion as a neuropathic mechanism for cold hypersensitivity. Neuropeptides 2018;67:95–101.
Lee JH, Ji H, Ko SG, Kim W. JI017 Attenuates oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia via spinal TRPV1 and astrocytes inhibition in mice. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:8811.
Zhang H, Chen H. TRPA1 involved in miR-141-5p-alleviated neuropathic pain induced by oxaliplatin. Neuroreport 2021;32:284–290.
Wu B, Su X, Zhang W, Zhang YH, Feng X, Ji YH, et al. Oxaliplatin depolarizes the IB4(-) dorsal root ganglion neurons to drive the development of neuropathic pain through TRPM8 in mice. Front Mol Neurosci 2021;14:690858.
Yang Y, Luo L, Cai X, Fang Y, Wang J, Chen G, et al. Nrf2 inhibits oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy via protection of mitochondrial function. Free Radic Biol Med 2018;120:13–24.
Loprinzi CL, Lacchetti C, Bleeker J, Cavaletti G, Chauhan C, Hertz DL, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: ASCO Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol 2020;38:3325–3348.
Pozzi E, Fumagalli G, Chiorazzi A, Canta A, Meregalli C, Monza L, et al. The relevance of multimodal assessment in experimental oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. Exp Neurol 2020;334:113458.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to data analysis, drafting or revising the article, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. Ju ZY and Wang K conceived and designed the experiments. Shi S, Wang FJ, Fan SD, Zhang YN and Feng CC performed the tests. Wang YQ, Wang FJ, and Shi S analyzed the results. Wang FJ wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81874506) and the Shanghai Clinical Research Center for Acupuncture and Moxibustion (No. 20MC1920500)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Fj., Shi, S., Wang, Yq. et al. Protective Mechanism of Electroacupuncture on Peripheral Neurotoxicity Induced by Oxaliplatin in Rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 28, 833–839 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-022-2896-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-022-2896-1