Abstract
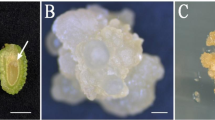
A high-efficiency somatic embryogenesis protocol of Japanese larch (Larix leptolepis Gordon) has been established in our investigation. Calli were induced from immature zygotic embryos of female cones of L. leptolepis and then subcultured regularly on to a modified Gupta and Durzan (DCR) basal medium for 5 years. Embryogenic tissues showed distinct morphological changes during somatic embryo development when they were transferred to a maturation medium supplemented with abscisic acid (ABA) compared with the morphology in a medium lacking ABA. Histological observations indicated that polyembryony was a characteristic feature during early embryogeny and somatic embryos at later stages showed normal histodifferentiation. In addition, histochemical analysis revealed that abundant starch granules and proteins accumulated in mature embryos, indicating that they played important roles in the development and regeneration of normal plantlets from somatic embryos on hormone-free germination media
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cangahuala-Inocente G C, Steine N, Santos M, Guerra M P. 2004. Morphohistological analysis and histochemistry of Feijoa sellowiana somatic embryogenesis. Protoplasma, 224: 33–40
Carman J G. 1990. Embryogenic cells in plat tissue cultures: occurrence and behavior. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol., 26: 746–753
Chrispeels M J, Crawford N M, Schroeder J I. 1999. Proteins for transport of water and mineral nutrients across the membranes of plant cells. Plant Cell, 11: 661–675
Chu C C. 2002. Contributions of Chinese botanists to plant tissue culture in the 20th century. Acta Bot. Sin., 44: 1,075–1,084
Dai R L, Zang W, **ng G S, Wang Y F. 1999. Quantitative stereologic analysis of changes in the metabolize dynamic of protein during somatic embryogenesis in Lycium barbarum L. Acta Agric. Boreali. Sin., 19: 266–269 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Dunstan D I, Dong J Z, Carrier D J, Abrams S R. 1998. Events following ABA treatment of spruce somatic embryos. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol., 34: 159–168
Feher A, Taras P, Pasternak P, Dudits D. 2003. Transition of somatic plant cell to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult., 74: 201–228
Feirer R P, Conkey J H, Verhagen S A. 1989. Triglycerides in embryogenic conifer calli: a comparison with zygotic embryos. Plant Cell Rep., 8: 207–209
Filonova L H, Bozhkov P V, von Arnold S. 2000. Developmental pathway of somatic embryogenesis in Picea abies as revealed by time-lapse tracking. J. Exp. Bot., 51: 249–264
Gorbatenko O, Hakman I. 2001. Desiccation-tolerant somatic embryos of Norway spruce (Picea abies) can be produced in liquid cultures and regenerated into plantlets. Int. J. Plant Sci., 162: 1,211–1,218
Guo Y M, Yang Y G, Guo Y, Guo Z C. 2003. The application and influence of biotechnology in forestry. Acta Agric. Boreali. Sin., 24: 337–344 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Gupta P K, Durzan D J. 1985. Shoot multiplication from mature of Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) and sugar pine (Pinus lambertiana). Plant Cell Rep., 4: 177–179
Gutmann M, von Aderkas P, Label P, Lelu M A. 1996. Effects of abscisic acid on somatic embryo maturation of hybrid larch. J. Exp. Bot., 47: 1,905–1,917
Higgings T J V, Jacobsen J V, Zwar J A. 1982. Gibberellic acid and abscisic acid modulate protein synthesis and mRNA levels in barley aleurone layers. Plant Mol. Biol., 1: 191–215
Jiang B, Yang Y G, Guo Y M, Guo Z C, Chen Y Z. 2004. Recent advances in conifer somatic embryogenesis. Chin. Bull. Bot., 21: 495–505 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Kim Y W, Youn Y, Noh E R, Kim J C. 1999. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryos of Japanese larch (Larix leptolepis). Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult., 55: 95–101
Kong L. 1994. Factors Affecting White Spruce Somatic Embryogenesis and Embryo Conversion. Ph. D. Dissertation. Calgary: University of Calgary
Lewandowski A, Burczyk J, Mejnartowicz L. 1991. Genetic structure and the mating system in an old stand of Polish larch. Silvae Genet., 40: 75–79
Litvay J D, Verma D C, Johnson M A. 1985. Influence of a loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) culture medium and its components on growth and embryogenesis of the wild carrot (Daucus carota L.). Plant Cell Rep., 4: 325–328
Liu C Q, **a X L, Yin W L, Huang L C, Zhou J H. 2006. Shoot regeneration and somatic embryogenesis from needles of redwood (Sequoia sempervirens (D.Don.) Endl.). Plant Cell Rep., 25: 621–628
Merkle S A, Dean J F D. 2000. Forest tree biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 11: 298–302
Mordhorst A P, Toonen M A J, de Vries S C. 1997. Plant embryogenesis. Critical Rev. Plant Sci., 16: 535–576
Oliviusson P, Hakman I. 1995. A tonoplast intrinsic protein (TIP) is present in seeds, roots and somatic embryos of Norway spruce (Picea abies). Physiol. Plant., 95: 288–295
Roberts D R, Flinn B S, Webb D T, Webster F B, Sutton B C S. 1990. Abscisic acid and indole-3-butric acid regulation of maturation and accumulation of storage proteins in somatic embryos of interior spruce. Physiol. Plant., 78: 355–360
Singh H. 1978. Embryology of Gymnosperms. Berlin: Gebruder Borntraeger
Tyerman S D, Bohnert H J, Maurel C, Steudle E, Smith J A C. 1999. Plant aquaporins: their molecular biology, biophysics and significance for plant water relations. J. Exp. Bot., 50: 1,055–1,071
von Aderkas P, Klimaszewska K, Bonga J M. 1990. Diploid and haploid embryogenesis in Larix leptolepis L. decidua, and their reciprocal hybrids. Can. J. For. Res., 20: 9–14
von Aderkas P, Lelu M A, Label P. 2001. Plant growth regulator levels during maturation of larch somatic embryos. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 39: 495–502
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Xx., Lu, Ld., Hao, Hq. et al. High-efficiency somatic embryogenesis and morphohistology and histochemistry of somatic embryo development in Larix leptolepis Gordon. For. Stud. China 9, 182–188 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-007-0029-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-007-0029-8