Abstract
Background
Which patients with pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) should undergo surgical intervention remains a controversial issue. The aim of this retrospective study was to validate the new European evidence-based guidelines on pancreatic cystic neoplasms (EEBGPCN) for the management of IPMNs.
Methods
One hundred fifty-eight patients with resected IPMNs at National Taiwan University Hospital between January 1994 and December 2016 were enrolled. Clinical information, including new-onset diabetes mellitus (DM) and preoperative CA 19-9 levels, were collected. All patients were stratified into three groups—absolute, relative indications, and conservative approach—according to EEBGPCN. The performance characteristics of EEBGPCN for high-grade dysplasia (HGD)/invasive carcinoma (IC) of IPMNs were calculated.
Results
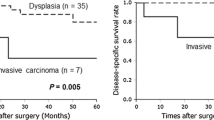
One hundred seven (67.7%) patients with low-grade dysplasia and 51 patients with HGD/IC, including 10 HGD and 41 IC, were analyzed. The missed rate for HGD/IC by EEBGPCN was 1.9% (3/158). The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and accuracy of the absolute or relative indications for resecting IPMN according to EEBGPCN were 94.1%, 28.0%, 38.4%, 90.9%, and 49.4%. Jaundice, enhancing mural nodule < 5 mm, cyst diameter > 40 mm, increased levels of serum CA 19-9, new-onset DM, and main pancreatic duct dilation were associated with HGD/IC.
Conclusions
The missed rate for HGD/IC is low by EEBGPCN. Increased serum CA 19-9 and new-onset DM in EEBGPCN were verified as the indications for the surgical resection of IPMNs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassi C, Sarr MG, Lillemoe KD, Reber HA. Natural History of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms (IPMN): Current Evidence and Implications for Management. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12(4):645-50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-007-0447-x.
Xu MM, Yin S, Siddiqui AA, Salem RR, Schrope B, Sethi A et al. Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of three current guidelines for the evaluation of asymptomatic pancreatic cystic neoplasms. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(35):e7900. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000007900.
Hsiao CY, Yang CY, Wu JM, Kuo TC, Tien YW. Utility of the 2006 Sendai and 2012 Fukuoka guidelines for the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: A single-center experience with 138 surgically treated patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(38):e4922. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000004922.
LaFemina J, Katabi N, Klimstra D, Correa-Gallego C, Gaujoux S, Kingham TP et al. Malignant Progression in IPMN: A Cohort Analysis of Patients Initially Selected for Resection or Observation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(2):440-7. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2702-y.
Falconi M, Crippa S, Chari S, Conlon K, Kim SW, Levy P et al. Quality assessment of the guidelines on cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2015;15(5):463-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2015.05.478.
Sighinolfi M, Quan SY, Lee Y, Ibaseta A, Pham K, Dua MM et al. Fukuoka and AGA Criteria Have Superior Diagnostic Accuracy for Advanced Cystic Neoplasms than Sendai Criteria. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62(3):626-32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4460-y.
Del Chiaro M, Verbeke C, Salvia R, Kloppel G, Werner J, McKay C et al. European experts consensus statement on cystic tumours of the pancreas. Dig Liver Dis. 2013;45(9):703-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2013.01.010.
Tanaka M, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Adsay V, Chari S, Falconi M, Jang JY et al. International consensus guidelines 2012 for the management of IPMN and MCN of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2012;12(3):183-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2012.04.004.
Vege SS, Ziring B, Jain R, Moayyedi P. American gastroenterological association institute guideline on the diagnosis and management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(4):819-22; quize12-3. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2015.01.015.
M. H, L. B, U. H, T. P, C. T, J. K et al. European evidence-based guidelines on pancreatic cystic neoplasms. Gut. 2018;67(5):789-804. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2018-316027.
Basturk O, Hong SM, Wood LD, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J, Biankin AV et al. A Revised Classification System and Recommendations From the Baltimore Consensus Meeting for Neoplastic Precursor Lesions in the Pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39(12):1730-41. https://doi.org/10.1097/pas.0000000000000533.
Tanaka M, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Kamisawa T, Jang JY, Levy P, Ohtsuka T et al. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2017;17(5):738-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2017.07.007.
Yu S, Takasu N, Watanabe T, Fukumoto T, Okazaki S, Tezuka K et al. Validation of the 2012 Fukuoka Consensus Guideline for Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Pancreas From a Single Institution Experience. Pancreas. 2017;46(7):936-42. https://doi.org/10.1097/mpa.0000000000000874.
Srinivasan N, Teo J-Y, Chin Y-K, Hennedige T, Tan DM, Low AS et al. Systematic review of the clinical utility and validity of the Sendai and Fukuoka Consensus Guidelines for the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. HPB (Oxford). 2018;20(6):497-504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpb.2018.01.009.
Zhou W, Xu Y, Rong Y, Wu W, Kuang T, **n B et al. Validation of Sendai and Fukuoka consensus guidelines in predicting malignancy in patients with preoperatively diagnosed mucinous pancreatic cystic neoplasms. J Surg Oncol. 2017;117(3):409-16. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.24882.
Wong J, Weber JA Centeno B, Vignesh S, Harris CL, Klapman JB et al. High-Grade Dysplasia and Adenocarcinoma Are Frequent in Side-Branch Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm Measuring Less than 3 cm on Endoscopic Ultrasound. J Gastrointest Surg. 2013;17(1):78-85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-012-2017-0.
Fritz S, Klauss M, Bergmann F, Hackert T, Hartwig W, Strobel O et al. Small (Sendai Negative) Branch-Duct IPMNs: Not Harmless. Ann Surg. 2012;256(2):313-20. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e31825d355f.
Heckler M, Brieger L, Heger U, Pausch T, Tjaden C, Kaiser J et al. Predictive performance of factors associated with malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia of the pancreas. BJS Open. 2018;2(1):13-24. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs5.38.
Aggarwal G, Rabe KG, Petersen GM, Chari ST. New-onset diabetes in pancreatic cancer: a study in the primary care setting. Pancreatology. 2012;12(2):156-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2012.02.003.
Pannala R, Leibson CL, Rabe KG, Timmons LJ, Ransom J, de Andrade M et al. Temporal association of changes in fasting blood glucose and body mass index with diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(9):2318-25. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2009.253.
Raghavan SR, Ballehaninna UK, Chamberlain RS. The impact of perioperative blood glucose levels on pancreatic cancer prognosis and surgical outcomes: an evidence-based review. Pancreas. 2013;42(8):1210-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182a6db8e.
Khadka R, Tian W, Hao X, Koirala R. Risk factor, early diagnosis and overall survival on outcome of association between pancreatic cancer and diabetes mellitus: Changes and advances, a review. Int J Surg. 2018;52:342-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.02.058.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I-Shiow Jan: contributions to the design of study, interpretation of data, and drafting the manuscript. Ming-Chu Chang, Ching-Yao Yang, Yu-Wen Tien, Yung-Ming Jeng, Chih-Horng Wu, and Bang-Bin Chen: contributions to acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data and assisting in drafting the manuscript. Yu-Ting Chang: contributions to the design of the study, acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data, drafting the manuscript, and final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jan, IS., Chang, MC., Yang, CY. et al. Validation of Indications for Surgery of European Evidence-Based Guidelines for Patients with Pancreatic Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms. J Gastrointest Surg 24, 2536–2543 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-019-04420-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-019-04420-9