Abstract
Objective
Diagnosis of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) requires the evaluation of renal biopsy specimens. However, renal biopsy is an invasive procedure and is not frequently performed for various reasons. Thus, recognized noninvasive biomarkers for predicting IgAN progression are urgently needed.
Methods
In the present study, we included 86 IgAN patients with renal biopsy from June 2015 to May 2016 and had their plasma interleukin-7 (IL-7) level measured with ELISA. The association between the plasma IL-7 level and clinico-pathological characteristics was analyzed. Immunohistochemical staining was used to assay the in situ expression of IL-7 in vivo. Western blotting was performed to examine the production of extracellular matrix, p-mTOR and the markers of autophagy under the treatment of IL-7 after TGF-β1 stimulation in renal tubular epithelial cells.
Results
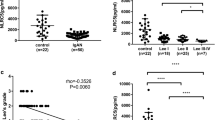
IL-7 was significantly decreased in patients with IgAN compared to healthy subjects (2.3077 vs. 8.6294 pg/mL, P<0.0001). There was a significant difference in the plasma IL-7 level between tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis T0 and T2 classes (P=0.0064). A lower plasma IL-7 value in patients at the time of biopsy indicated a poor renal outcome. In addition, IL-7 was over-expressed in renal tubular epithelial cells and significantly attenuated transforming growth factor βl-induced extracellular matrix production by suppression of cellular autophagy via activation of mTOR1 signaling.
Conclusion
These results suggested that IL-7 might be a noninvasive biomarker for predicating IgAN. It protected renal proximal tubular epithelial cells from cellular fibrosis by inhibiting autophagy via mTORl signaling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wyatt RJ, Julian BA. IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med, 2013,368(25):2402–2414
Working Group of the International IgA Nephropathy Network and the Renal Pathology Society, Cattran DC, Coppo R, et al. The Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy: rationale, clinicopathological correlations, and classification. Kidney Int, 2009,76(5):534–545
van Roon JA, Verweij MC, Wijk MW, et al. Increased intraarticular interleukin-7 in rheumatoid arthritis patients stimulates cell contact-dependent activation of CD4(+) T cells and macrophages. Arthritis Rheum, 2005,52(6):1700–1710
Harrison C. Autoimmune disease: Targeting IL-7 reverses type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2012, 11(8):599
Ben-David H, Sharabi A, Parameswaran R, et al. A tolerogenic peptide down-regulates mature B cells in bone marrow of lupus-afflicted mice by inhibition of interleukin-7, leading to apoptosis. Immunology, 2009, 128(2):245–252
Lundström W, Fewkes NM, Mackall CL. IL-7 in human health and disease. Semin Immunol, 2012,24(3):218–224
Zhai SB, Zhao LY, Zhang Y, et al. Interleukin-7 stimulation inhibits nephrin activation and induces podocyte injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 507(1–4):100–105
Penaranda C, Kuswanto W, Hofmann J, et al. IL-7 receptor blockade reverses autoimmune diabetes by promoting inhibition of effector/memory T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012,109(31):12 668–12 673
Venet F, Demaret J, Blaise BJ, et al. IL-7 Restores T lymphocyte immunometabolic failure in septic shock patients through mTOR activation. J Immunol, 2017,199(5):1606–1615
Allgäuer A, Schreiner E, Ferrazzi F, et al. IL-7 Abrogates the immunosuppressive function of human double-negative T cells by activating Akt/mTOR signaling. J Immunol, 2015,195(7):3139–3148
Aylett CH, Sauer E, Imseng S, et al. Architecture of human mTOR complex 1. Science, 2016,351(6268):48–52
Dunlop EA, Tee AR. mTOR and autophagy: a dynamic relationship governed by nutrients and energy. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2014,36:121–129
Germain N, Viltart O, Loyens A, et al. Interleukin-7 plasma levels in human differentiate anorexia nervosa, constitutional thinness and healthy obesity. PloS One, 2016,11(9):e0161890
De Benedetti F, Massa M, Pignatti P, et al. Elevated circulating interleukin-7 levels in patients with systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol, 1995,22(8): 1581–1585
Neuhaus TJ, Shah V, Callard RE, et al. T-lymphocyte activation insteroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 1995,10(8):1348–1352
Pellegrini M, Calzascia T, Elford AR, et al. Adjuvant IL-7 antagonizes multiple cellular and molecular inhibitory networks to enhance immunotherapies. Nat Med, 2009,15(5):528–536
Zhang W, Du JY, Yu Q, et al. Interleukin-7 produced by intestinal epithelial cells in response to Citrobacter rodentium infection plays a major role in innate immunity against this pathogen. Infect Immun, 2015,83(8):3213–3223
Higgins DF, Kimura K, Bernhardt WM, et al. Hypoxia promotes fibrogenesis in vivo via HIF-1 stimulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest, 2007,117(12):3810–3820
Kawai T, Masaki T, Doi S, et al. PPAR-gamma agonist attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis and inflammation through reduction of TGF-beta. Lab Invest, 2009,89(1): 47–58
Hsieh PF, Liu SF, Lee TC, et al. The role of IL-7 in renal proximal tubule epithelial cells fibrosis. Mol Immunol, 2012,50(1–2):74–82
Huang M, Sharma S, Zhu L, et al. IL-7 inhibits fibroblast TGF-beta production and signaling in pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest, 2002,109(7):931–937
Jiang L, Xu L, Mao J, et al. Rheb/mTORC1 signaling promotes kidney fibroblast activation and fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2013,24(7):1114–1126
Lieberthal W, Levine JS. The role of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2009,20(12):2493–2502
Novalic Z, van der Wal AM, Leonhard WN, et al. Dose-dependent effects of sirolimus on mTOR signaling and polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2012, 23(5):842–853
Wang S, Wilkes MC, Leof EB, et al. Noncanonical TGF-beta pathways, mTORC1 and Abl, in renal interstitial fibrogenesis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2010,298(1):F142–149
Baisantry A, Bhayana S, Rong S, et al. Autophagy induces prosenescent changes in proximal tubular S3 segments. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016,27(6):1609–1616
Ding Y, Kim Sl, Lee SY, et al. Autophagy regulates TGF-beta expression and suppresses kidney fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2014,25(12):2835–2846
Zhu J, Zhang W, Zhang L, et al. IL-7 suppresses macrophage autophagy and promotes liver pathology in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice. J Cell Mol, 2018,22(7):3353–3363
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by grants from Huazhong University of Science and Technology Research Funds for Self-dependent Innovation (No. 2017KFYXJJ101), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81703058, No. 81970591, and No. 82000656).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Yj., Lin, Xp., Li, Xq. et al. Interleukin-7 Is Associated with Clinical and Pathological Activities in Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy and Protects the Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelium from Cellular Fibrosis. CURR MED SCI 41, 880–887 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-021-2409-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-021-2409-z