Summary
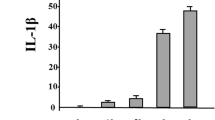
Human interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a proinflammatory cytokine to suppress neutrophil apoptosis, which is a potential therapeutic agent. The modulatory effect of TNFα was investigated in IL-15-induced suppression of human neutrophil apoptosis. TNFα was shown to reverse the ability of IL-15 to delay neutrophil apoptosis within certain time course. Moreover, this reverse effect by TNFα might be associated with a reduction of the expression of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-Xl protein detected by Western blotting. It is concluded that TNFα can be used to modulate IL-15-induced suppression of neutrophil apoptosis within certain time course.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bamford R N, Grant A J, Burton J D et al. The interleukin (IL)-2 receptor beta chain is shared by IL-2 and a cytokine, provisionally designated IL-T, that stimulates T-cell proliferation and the induction of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1994,91:4940–4944
Grabstein K H, Eisenman J, Shanebeck K et al. Cloning of a T cell growth factor that interacts with the beta chain of the interleukin-2 receptor. Science,1994, 264:965–968
Kirman I, Vainer B, Nielsen O H. Interleukin-15 and its role in chronic inflammatory diseases. Inflamm Res, 1998,47:285–289
Waldmann T, Tagaya Y, Bamford R. Interleukin-2, interleukin-15, and their receptors. Int Rev Immunol, 1998,16:205–226
Cassatella M A, McDonald P P. Interleukin-15 and its impact on neutrophil function. Curr Opin Hematol, 2000,7(3):174–177
Williams N S, Klem J, Puzanov I J et al. Natural killer cell differentiation: insights from knockout and transgenic mouse models and in vitro systems. Immunol Rev, 1998,165:47–61
Lodolce J, Burkett P, Koka R et al. Interleukin-15 and the regulation of lymphoid homeostasis. Mol Immunol, 2002,39(9):537–544
Bouchard A, Ratthe C, Girard D. Interleukin-15 delays human neutrophil apoptosis by intracellular events and not via extracellular factors: role of Mcl-1 and decreased activity of caspase-3 and caspase-8. J Leukoc Biol, 2004,75(5):1–8
Pelletier M, Ratthe C, Girard D. Mechanisms involved in interleukin-15-induced suppression of human neutrophil apoptosis: role of the anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 protein and several kinases including Janus kinase-2, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinases-1/2. FEBS Lett, 2002,532(1–2):164–170
Elletier M, Lavastre V, Savoie A et al. Modulation of interleukin-15-induced human neutrophil responses by the plant lectrin Viscum album agglutinin-I. Clin Immunol, 2001,101(2):229–236
Ding Z M, Babensee J E, Simon S I et al. Relative contribution of LFA-1 and Mac-1 to neutrophil adhesion and migration. J Immunol, 1999,163(9):5029–5038
Walsh G M, Dewson G, Wardlaw A J et al. A comparative study of different methods for the assessment of apoptosis and necrosis in human eosinophils. J Immunol Methods, 1998,217(1-2):153–163
Laemelli U K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 1970,227:680–685
Girard D, Paquet M E, Paquin R et al. Differential effects of interleukin-15 (IL-15) and IL-2 on human neutrophils: modulation of phagocytosis, cytoskeleton rearrangement, gene expression, and apoptosis by IL-15. Blood, 1996, 88(8):3176–3184
Weinmann P, Gaehtgens P, Walzog B. Bcl-Xl-and Bax-alpha-mediated regulation of apoptosis of human neutrophils via caspase-3. Blood, 1999,93(9):3106–3115
Oltvai Z N, Milliman C L, Korsmeyer S J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell, 1993, 74(4):609–619
Sedlak T W, Oltvai Z N, Yang E et al. Multiple Bcl-2 family members demonstrate selective dimerizations with Bax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1995,92(17):7834–7838
Gottschalk A R, Boise L H, Thompson C B et al. Identification of immunosuppressant-induced apoptosis in a murine B-cell line and its prevention by bcl-x but not bcl-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1994,91(15):7350–7354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
LIU **, male, born in 1971, Ph.D.
This project was supported by a grant from NIH foundation of USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., **ong, C., Li, C. et al. Modulation of interleukin-15-induced suppression of human neutrophil apoptosis by TNFα. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 27, 354–357 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0402-9
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0402-9