Abstract
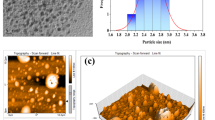
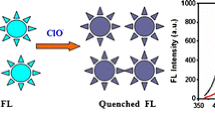
The nitrogen-doped carbon dots (N-CDs) were prepared by using coke powder as carbon source and one-step hydrothermal method. The N-CDs were studied as a fluorescent chemosensor for determining Cr(VI) in water. The selective, sensitive, reproducibility and stability of as-prepared N-CDs were investigated. The morphology, composition and properties of N-CDs were characterized by a series of methods. The fluorescence quenching of N-CDs by Cr(VI) was explored. The experimental results reveal that the obtained N-CDs have great hydrophilicity and strong luminescence properties, which demonstrates the successful do** of nitrogen into the CDs. The surface-active groups and emission wavelength range of CDs increase due to the electronegativity and electron donor effect of do** N atom. Furthermore, the N-CDs exhibit good photochemical properties for the detection of Cr(VI), including a wide linear range from 0.3 to 200 µM (R2=0.9935) and a low detection limit of 0.10 µM at the signal-to-noise ratio of 3 (S/N=3). Moreover, the N-CDs as a sensor was used successfully for Cr (VI) detection in real water samples with recovery rates of 99.9%–110.6%. This sensor also shows highly reproducibility and stability. The N-CDs fluorescent chemical sensor may be a potential candidate for applying in the field of other fluorescent chemical sensing, catalysis, photoelectric devices and other fields.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruchez M, Moronne M, Gin P, et al. Semiconductor Nanocrystals as Fluorescent Biological Labels[J]. Science, 1998, 281(5385): 2013–2016
Chen Q, Song Z, Zhang D, et al. Effect of Size on the Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Cubic CsPbBr3 Quantum Dots[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2019, 56(1): 1–7
Yin X, Li X, Zhu C, et al. Integration of Fluorescence/Photoacoustic Imaging and Targeted Chemo/Photothermal Therapy with Ag2Se@BSA-RGD Nanodots[J]. New J. Chem., 2020, 44(12): 4 850–4 857
Liu H, Kang Y, Meng T, et al. High Photon Absorptivity of Quantum Dot Infrared Photodetectors Achieved by the Surface Plasmon Effect of Metal Nanohole Array[J]. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2020, 15(1): 1–12
Othman HO, Salehnia F, Fakhri N, et al. A Highly Sensitive Fluorescent Immunosensor for Sensitive Detection of Nuclear Matrix Protein 22 as Biomarker for Early Stage Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(48): 28 865–28 871
Kortel M, Mansuriya BD, Vargas Santana N, et al. Graphene Quantum Dots as Flourishing Nanomaterials for Bio-Imaging, Therapy Development, and Micro-Supercapacitors[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11(9): 866
Badıllı U, Mollarasouli F, Bakirhan NK, et al. Role of Quantum Dots in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, and Its Application in Drug Delivery[J]. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2020, 131: 116 013
Gajjela RS, Koenraad PM. Atomic-Scale Characterization of Droplet Epitaxy Quantum Dots[J]. Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(1): 85
Ghosal K, Ghosh A. Carbon Dots: The Next Generation Platform for Biomedical Applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2019, 96: 887–903
Baek SW, Molet P, Choi MJ, et al. Nanostructured Back Reflectors for Efficient Colloidal Quantum-Dot Infrared Optoelectronics[J]. Adv. Mater, 2019, 31(33): 1 901 745
Siddique A, Singh VP, Chatterjee S, et al. Facile Synthesis and Versatile Applications of Amorphous Carbon Dot[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5(3): 10077–10083
Ding L, Peng Z, Shen W, et al. Microwave Synthesis of CdTe/TGA Quantum Dots and Their Thermodynamic Interaction with Bovine Serum Albumin[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2016, 31(6): 1 408–1 414
Ding L, He H, Li S, et al. Preparation of Different Lights Irradiated ZnSe/GSH QDs and Their Interaction with BSA[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2019, 34(4): 858–865
Zhao D, Liu X, Zhang R, et al. Facile One-Pot Synthesis of Multifunctional Protamine Sulfate-Derived Carbon Dots for Antibacterial Applications and Fluorescence Imaging of Bacteria[J]. New J. Chem., 2021, 45(2): 1010–1019
Wang K, Liang L, Xu J, et al. Synthesis and Bacterial Inhibition of Novel Ag2S-N-CQD Composite Material[J]. Chemical Papers, 2020, 74(5): 1 517–1 524
He Z, Huang H, Jiang R, et al. Click Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes: A Novel Method for Preparation of Carboxyl Groups Functionalized Carbon Quantum Dots[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2020, 108: 110 376
Borna S, Sabzi RE, Pirsa S. Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots from Apple Juice and Graphite: Investigation of Fluorescence and Structural Properties and Use as an Electrochemical Sensor for Measuring Letrozole[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2021, 32(8): 10 866–10 879
Qiang R, Yang S, Hou K, et al. Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots with Green Luminescence from Potato Starch[J]. New J. Chem., 2019, 43(27): 10 826–10 833
Zheng Y, Zheng J, Wang J, et al. Facile Preparation of Stable Solid-State Carbon Quantum Dots with Multi-Peak Emission[J]. Nanomaterials, 2020, 10(2): 303
Deng Y, Zhou Y, Ye S, et al. Alcohol Solvent Effect on Fluorescence Properties in the Solvothermal Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2022, 37(1): 23–27
Zhang Z, Zhang J, Chen N, et al. Graphene Quantum Dots: An Emerging Material for Energy-Related Applications and Beyond[J]. Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5(10): 8 869–8 890
Atchudan R, Edison TNJI, Shanmugam M, et al. Sustainable Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots from Banana Peel Waste Using Hydrothermal Process for in vivo Bioimaging[J]. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2021, 126: 114 417
Sun D, Ban R, Zhang PH, et al. Hair Fiber as a Precursor for Synthesizing of Sulfur-and Nitrogen-Co-Doped Carbon Dots with Tunable Luminescence Properties[J]. Carbon, 2013, 64: 424–434
Abazar F, Noorbakhsh A. Chitosan-Carbon Quantum Dots as a New Platform for Highly Sensitive Insulin Impedimetric Aptasensor[J]. Sensors Actuators B: Chem., 2020, 304: 127 281
Han G, Cai J, Liu C, et al. Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor Based on Xylan-Based Ag@CQDs-rGO Nanocomposite for Dopamine Detection[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2021, 541: 148 566
Wang Y, Hu X, Li W, et al. Preparation of Boron Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Rapid Detection of Cr (VI)[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2020, 243: 118 807
Kong L, Chu X, Liu W, et al. Glutathione-Directed Synthesis of Cr (VI) and Temperature-Responsive Fluorescent Copper Nanoclusters and Their Applications in Cellular Imaging[J]. New J. Chem., 2016, 40(5): 4 744–4 750
Ding L, Zhou PJ, Zhan HJ, et al. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of L-Glutathione Capped ZnSe QDs and Its Interaction with BSA by Spectroscopy[J]. J. Lumin., 2013, 142: 167–172
Chen Q, Li X, **e R, et al. Novel Rapid Synthesis of Nanoscale Tungsten Nitride Using Non-Toxic Nitrogen Source[J]. Ceram. Int., 2020, 46(2): 2 580–2 584
Yoshinaga T, Akiu M, Iso Y, et al. Photoluminescence Properties of L-Cysteine-Derived Carbon Dots Prepared in Non-Aqueous and Aqueous Solvents[J]. J. Lumin., 2020, 224: 117 260
Liu H, Xu A, Feng Z, et al. pH-Dependent Fluorescent Quenching of Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots: Towards Hydroxyl[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2020, 260: 114 627
Xue R, Fu L, Dong S, et al. Promoting Chlorella Photosynthesis and Bioresource Production Using Directionally Prepared Carbon Dots with Tunable Emission[J]. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2020, 569: 195–203
Esmaeilzadeh M, Sadjadi S, Salehi Z. Pd Immobilized on Hybrid of Magnetic Graphene Quantum Dots and Cyclodextrin Decorated Chitosan: An Efficient Hydrogenation Catalyst[J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2020, 150: 441–448
Hu C, Liu Y, Yang Y, et al. One-Step Preparation of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots from Oxidized Debris of Graphene Oxide[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013, 1(1): 39–42
Zhao L, Di F, Wang D, et al. Chemiluminescence of Carbon Dots under Strong Alkaline Solutions: A Novel Insight into Carbon Dot Optical Properties[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(7): 2 655–2 658
Zheng M, **e Z, Qu D, et al. On-Off-on Fluorescent Carbon Dot Nanosensor for Recognition of Chromium (VI) and Ascorbic Acid Based on the Inner Filter Effect[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(24): 13 242–13 247
Chandra S, Patra P, Pathan SH, et al. Luminescent S-Doped Carbon Dots: An Emergent Architecture for Multimodal Applications[J]. Jour- nal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013, 1(18): 2 375–2 382
Li M, Ma C, Wang G, et al. Controlling the up-Conversion Photoluminescence Property of Carbon Quantum Dots (CQDs) by Modifying Its Surface Functional Groups for Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance of CQDs/BiVO4 under a Broad-Spectrum Irradiation[J]. Res. Chem. Intermed., 2021, 47(8): 3 469–3 485
Yang G, Wan X, Su Y, et al. Acidophilic S-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots Derived from Cellulose Fibers and Their Fluorescence Sensing Performance for Metal Ions in an Extremely Strong Acid Environment[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(33): 12 841–12 849
Liu W, Diao H, Chang H, et al. Green Synthesis of Carbon Dots from Rose-Heart Radish and Application for Fe3+ Detection and Cell Imaging[J]. Sensors Actuators B: Chem., 2017, 241: 190–198
Zhu J, Chu H, Wang T, et al. Fluorescent Probe Based Nitrogen Doped Carbon Quantum Dots with Solid-State Fluorescence for the Detection of Hg2+ and Fe3+ in Aqueous Solution[J]. Microchem. J., 2020, 158:105 142
Ma Z, Ma Y, Gu M, et al. Carbon Dots Derived from the Maillard Reaction for pH Sensors and Cr (VI) Detection[J]. Nanomaterials, 2020, 10(10): 1 924
Hu G, Ge L, Li Y, et al. Carbon Dots Derived from Flax Straw for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detections of Cobalt, Chromium, and Ascorbic Acid[J]. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2020, 579: 96–108
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering Bu L, Peng J, Peng H, et al. Fluorescent Carbon Dots for the Sensitive Detection of Cr (VI) in Aqueous Media and Their Application in Test Papers[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(98): 95 469–95 475
Feng S, Gao Z, Liu H, et al. Feasibility of Detection Valence Speciation of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) in Environmental Samples by Spectrofluorimetric Method with Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2019, 212: 286–292
Zhang Y, Dong Y, Zheng H, et al. High Quantum Yield Fluorescent Chitosan-Based Carbon Dots for the Turn-on-off-on Detection of Cr (VI) and H2O2[J]. Nano, 2021, 16(09): 2150103
**a L, Li X, Zhang Y, et al. Sustainable and Green Synthesis of Waste-Biomass-Derived Carbon Dots for Parallel and Semi-Quantitative Visual Detection of Cr (VI) and Fe3+[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(4): 1 258
Nordberg GF, Flower B, Nordberg M, et al. Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals[M]. The Netherlands: Academic Press, 2007: 1 385
Funding
Funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China(61904130), the Open Fund of the Fujian Universities and Colleges Engineering Research Center of Modern Facility Agriculture of Fujian University (G2-KF2002), the Opening Project of Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Chemical Materials and Devices, Ministry of Education, Jianghan University (JDGD202017), the Open Fund of the Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory for New Processes of Ironmaking and Steel Making (Wuhan University of Science and Technology) of China (KF-20-5), the Fund of Hangzhou Meishi Technology Co., Ltd of China (2021420112000081), the Key Research and Development Program of Hubei Province (2020BAB084), and the Program (BG20190227001) of High-end Foreign Experts of the State of the State Administration of Foreign Experts Affairs (SAFEA)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, J., Li, S., Ding, L. et al. Preparation of Nitrogen-doped Carbon Dots from Coke Powder as a Fluorescent Chemosensor for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Cr (VI). J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 37, 1096–1104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-022-2639-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-022-2639-3