Abstract
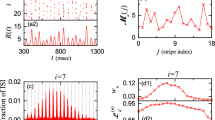
We investigate population and individual firing behaviors in sparsely synchronized rhythms (SSRs) in a spiking neural network of the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG). The main encoding granule cells (GCs) are grouped into lamellar clusters. In each GC cluster, there is one inhibitory (I) basket cell (BC) along with excitatory (E) GCs, and they form the E-I loop. Winner-take-all competition, leading to sparse activation of the GCs, occurs in each GC cluster. Such sparsity has been thought to enhance pattern separation performed in the DG. During the winner-take-all competition, SSRs are found to appear in each population of the GCs and the BCs through interaction of excitation of the GCs with inhibition of the BCs. Sparsely synchronized spiking stripes appear successively with the population frequency \(f_p~ (= 13.1\) Hz) in the raster plots of spikes. We also note that excitatory hilar mossy cells (MCs) control the firing activity of the GC-BC loop by providing excitation to both the GCs and the BCs. SSR also appears in the population of MCs via interaction with the GCs (i.e., GC-MC loop). Population behaviors in the SSRs are quantitatively characterized in terms of the synchronization measures. In addition, we investigate individual firing activity of GCs, BCs, and MCs in the SSRs. Individual GCs exhibit random spike skip**, leading to a multi-peaked inter-spike-interval histogram, which is well characterized in terms of the random phase-locking degree. In this case, population-averaged mean-firing-rate (MFR) \(<\!f_i^{(\text {GC})}\!>\) is less than the population frequency \(f_p\). On the other hand, both BCs and MCs show “intrastripe” burstings within stripes, together with random spike skip**. Thus, the population-averaged MFR \(\langle f_i^{(X)} \rangle\) (\(X=\) MC and BC) is larger than \(f_p\), in contrast to the case of the GCs. MC loss may occur during epileptogenesis. With decreasing the fraction of the MCs, changes in the population and individual firings in the SSRs are also studied. Finally, quantitative association between the population/individual firing behaviors in the SSRs and the winner-take-all competition is discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
29 March 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-023-09949-9
References
Almeida LD, Idiart M, Lisman JE (2009) A second function of gamma frequency oscillations: An E%-max winner-take-all mechanism selects which cells fire. J Neurosci 29:7497–7503
Amaral DG, Witter MP (1989) The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: a review of anatomical data. Neuroscience 31:571–591
Amaral DG, Ishizuka N, Claiborne B (1990) Neurons, numbers and the hippocampal network. Prog Brain Res 83:1–11
Amaral DG, Scharfman HE, Lavenex P (2007) The dentate gyrus: fundamental neuroanatomical organization (dentate gyrus for dummies). Prog Brain Res 163:3–22
Andersen P, Bliss TVP, Skrede KK (1971) Lamellar organization of hippocampal excitatory pathways. Exp Brain Res 13:222–238
Andersen P, Soleng AF, Raastad M (2000) The hippocampal lamella hypothesis revisited. Brain Res 886:165–171
Bakker A, Kirwan CB, Miller M, Stark CEL (2008) Pattern separation in the human hippocampal CA3 and dentate gyrus. Science 319:1640–1642
Barranca VJ, Huang H, Kawakita G (2019) Network structure and input integration in competing firing rate models for decision-making. J Comput Neurosci 46:145–168
Bartos M, Vida I, Frotscher M, Geiger JR, Jonas P (2001) Rapid signaling at inhibitory synapses in a dentate gyrus interneuron network. J Neurosci 21:2687–2698
Beck H, Goussakov IV, Lie A, Helmstaedter C, Elger CE (2000) Synaptic plasticity in the human dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 20:7080–7086
Bielczyk NZ, Piskała K, Płomecka M, Radziński P, Todorova L, Foryś U, (2019) Time-delay model of perceptual decision making in cortical networks. PLoS One 14:e0211885
Brunel N, Hakim V (2008) Sparsely synchronized neuronal oscillations. Chaos 18:015113
Brunel N, Wang XJ (2003) What determines the frequency of fast network oscillations with irregular neural discharges? I. Synaptic dynamics and excitation-inhibition balance. J Neurophysiol 90:415–430
Buckmaster PS, Jongen-Rêlo AL (1999) Highly specific neuron loss preserves lateral inhibitory circuits in the dentate gyrus of kainite-induced epileptic rats. J Neurosci 19:9519–9529
Buckmaster PS, Wenzel HJ, Kunkel DD, Schwartzkroin PA (1996) Axon arbors and synaptic connections of hippocampal mossy cells in the rat in vivo. J Comp Neurol 366:271–292
Buckmaster PS, Yamawaki R, Zhang GF (2002) Axon arbors and synaptic connections of a vulnerable population of interneurons in the dentate gyrus in vivo. J Comp Neurol 445:360–373
Chavlis S, Petrantonakis PC, Poirazi P (2017) Dendrites of dentate gyrus granule cells contribute to pattern separation by controlling sparsity. Hippocampus 27:89–110
Chiang PH, Wu PY, Kuo TW, Liu YC, Chan CF, Chien TC, Cheng JK, Huang YY, Chiu CD, Lien CC (2012) GABA is depolarizing in hippocampal dentate granule cells of the adolescent and adult rats. J Neurosci 32:62–67
Coultrip R, Granger R, Lynch G (1992) A cortical model of winner-take-all competition via lateral inhibition. Neural Netw 5:47–54
Csicsvari J, Hirase H, Czurko A, Mamiya A, Buzsáki G (1999) Oscillatory coupling of hippocampal pyramidal cells and interneurons in the behaving rat. J Neurosci 19:274–287
Csicsvari J, Jamieson B, Wise K, Buzsáki G (2003) Mechanisms of gamma oscillations in the hippocampus of the behaving rat. Neuron 37:311–322
Destexhe A, Paré D (1999) Impact of network activity on the integrative properties of neocortical pyramidal neurons in vivo. J Neurophysiol 81:1531–1547
Dijk van MT, Fenton AA (2018) On how the dentate gyrus contributes to memory discrimination. Neuron 98:832–845
Dudek SM, Alexander GM, Farris S (2016) Rediscovering area CA2: unique properties and functions. Nat Rev Nurosci 17:89–102
Espinoza C, Guzman SJ, Zhang X, Jonas P (2018) Parvalbumin+ interneurons obey unique connectivity rules and establish a powerful lateral inhibition microcircuit in dentate gyrus. Nat Commun 9:4605
Ewell LA, Jones MV (2010) Frequency-tuned distribution of inhibition in the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 30:12597–12607
Fellous J, Sejnowski TJ (2000) Cholinergic induction of oscillations in the hippocampal slice in the slow (0.5-2 Hz), theta (5–12 Hz) and gamma (35–70 Hz) bands. Hippocampus 10:187–197
Fernández-Ruiz A, Oliva A, Soula M, Rocha-Almeida F, Nagy GA, Martin-Vazquez G, Buzsáki G (2021) Gamma rhythm communication between entorhinal cortex and dentate gyrus neuronal assemblies. Science 372:eabf3119
Geiger JRP, Lübke J, Roth A, Frotscher M, Jonas P (1997) Submillisecond AMPA receptor-mediated signaling at a principal neuron-interneuron synapse. Neuron 18:1009–1023
Geisler C, Brunel N, Wang XJ (2005) Contributions of intrinsic membrane dynamics to fast network oscillations with irregular neuronal discharges. J Neurophysiol 94:4344–4361
Gerstner W, Kistler W (2002) Spiking Neuron Models. Cambridge University Press, New York
Gluck MA, Myers CE (2001) Gateway to memory: an introduction to neural network modeling of the hippocampus in learning and memory. MIT Press, Cambridge
Hafting T, Fyhn M, Molden S, Moser MB, Moser EI (2005) Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex. Nature 436:801–806
Hasenstaub A, Shu Y, Haider B, Kraushaar U, Duque A, McCormick D (2005) Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials carry synchronized frequency information in active cortical networks. Neuron 47:423–435
Hosp JA, Strüber M, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Vida I, Jonas P, Bartos M (2014) Morpho-physiological criteria divide dentate gyrus interneurons into classes. Hippocampus 24:189–203
Houghton C (2017) Dentate gyrus and hilar region revisited. Behav Brain Sci 39:28–29
Hsiao YT, Zheng C, Colgin LL (2016) Slow gamma rhythms in CA3 are entrained by slow gamma activity in the dentate gyrus. J Neurophysiol 116:2594–2603
Jahr CE, Stevens CF (1990) Voltage dependence of NMDA-activated macroscopic conductances predicted by single-channel kinetics. J Neurosci 10:3178–3182
**de S, Zsiros V, Jiang Z, Nakao K, Pickel J, Kohno K, Belforte JE, Nakazawa K (2012) Hilar mossy cell degeneration causes transient dentate granule cell hyperexcitability and impaired pattern separation. Neuron 76:1189–1200
**de S, Zsiros V, Nakazawa K (2013) Hilar mossy cell circuitry controlling dentate granule cell excitability. Front Neural Circuit 7:14
Kassab R, Alexandre F (2018) Pattern separation in the hippocampus: distinct circuits under different conditions. Brain Struct Funct 223:2785–2808
Kim SY, Lim W (2014) Realistic thermodynamic and statistical-mechanical measures for neural synchronization. J Neurosci Meth 226:161–170
Kim SY, Lim W (2018) Effect of inhibitory spike-timing-dependent plasticity on fast sparsely synchronized rhythms in a small-world neuronal network. Neural Netw 106:50–66
Kim SY, Lim W (2021) Effect of diverse recoding of granule cells on optokinetic response in a cerebellar ring network with synaptic plasticity. Neural Netw 134:173–204
Kim SY, Lim W (2021) Influence of various temporal recoding on Pavlovian eyeblink conditioning in the cerebellum. Cogn Neurodyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-021-09673-2
Kim SY, Lim W (2021) Equalization effect in interpopulation spike-timing-dependent plasticity in two inhibitory and excitatory populations. In: Lintas A, Enrico P, Pan X, Wang R, Villa A (eds) Advances in cognitive neurodynamics (VII). Springer, Singapore, p 8
Kim SY, Lim W (2021d) Dynamical origin for winner-take-all competition in a biological network of the hippocampal dentate gyrus. bioRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.5.12.443925
Kneisler TB, Dingledine R (1995) Spontaneous and synaptic input from granule cells and the perforant path to dentate basket cells in the rat hippocampus. Hippocampus 5:151–164
Knierim JJ, Neunuebel JP (2016) Tracking the flow of hippocampal computation: Pattern separation, pattern completion, and attractor dynamics. Neurobiol Learn Mem 129:38–49
Krueppel R, Remy S, Beck H (2011) Dendritic integration in hippocampal dentate granule cells. Neuron 71:512–528
Larimer P, Strowbridge BW (2008) Nonrandom local circuits in the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 28:12212–12223
Leutgeb JK, Leutgeb S, Moser MB, Moser EI (2007) Pattern separation in the dentate gyrus and CA3 of the hippocampus. Science 315:961–966
Lübke J, Frotscher M, Spruston N (1998) Specialized electrophysiological properties of anatomically identified neurons in the hilar region of the rat fascia dentata. J Neurophysiol 79:1518–1534
Marr D (1971) Simple memory: a theory for archicortex. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 262:23–81
McNaughton B, Morris R (1987) Hippocampal synaptic enhancement and information storage within a distributed memory system. Trends Neurosci 10:408–415
McNaughton BL, Barnes CA, Mizumori SJY, Green EJ, Sharp PE (1991) Contribution of granule cells to spatial representations in hippocampal circuits: A puzzle. In: Morrell F (ed) Kindling and synaptic plasticity: the legacy of Graham Goddar. Springer-Verlag, Boston, pp 110–123
Morgan RJ, Santhakumar V, Soletsz I (2007) Modeling the dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res 163:639–658
Myers CE, Scharfman HE (2009) A role for hilar cells in pattern separation in the dentate gyrus: A computational approach. Hippocampus 19:321–337
Myers CE, Scharfman HE (2011) Pattern separation in the dentate gyrus: A role for the CA3 backprojection. Hippocampus 21:1190–1215
Myers CE, Bermudez-Hernandez K, Scharfman HE (2013) The influence of ectopic migration of granule cells into the hilus on dentate gyrus-CA3 function. PLoS ONE 8:e68208
Nitz D, McNaughton B (2004) Differential modulation of CA1 and dentate gyrus interneurons during exploration of novel environments. J Neurophysiol 91:863–872
Nomura T, Fukuda T, Aika Y, Heizmann CW, Emson PC, Kobayashi T, Kosaka T (1997) Distribution of nonprincipal neurons in the rat hippocampus, with special reference to their dorsoventral difference. Brain Res 751:64–80
Nomura T, Fukuda T, Aika Y, Heizmann CW, Emson PC, Kobayashi T, Kosaka T (1997) Laminar distribution of non-principal neurons in the rat hippocampus, with special reference to their compositional difference among layers. Brain Res 764:197–204
O’Reilly RC, McClelland JC (1994) Hippocampal conjunctive encoding, storage, and recall: Avoiding a tradeoff. Hippocampus 4:661–682
Pearson K (1895) Notes on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc R Soc Lond 58:240–242
Petrantonakis PC, Poirazi P (2014) A compressed sensing perspective of hippocampal function. Front Syst Neurosci 8:141
Petrantonakis PC, Poirazi P (2015) Dentate gyrus circuitry features improve performance of sparse approximation algorithms. PLoS One 10:e0117023
Press WH, teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP, (1992) Nemerical receipes in C: the art of scientific computing, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York
Rangel LM, Chiba AA, Quinn LK (2015) Theta and beta oscillatory dynamics in the dentate gyrus reveal a shift in network processing state during cue encounters. Front Syst Neurosci 9:96
Ratzliff AH, Santhakumar V, Howard A, Soltesz I (2002) Mossy cells in epilepsy: rigor mortis or vigor mortis? Trends Neurosci 25:140–144
Ratzliff ADH, Howard AL, Santhakumar V, Osapay I, Soltesz I (2004) Rapid deletion of mossy cells does not result in a hyperexcitable dentate gyrus: Implications for epileptogenesis. J Neurosci 24:2259–2269
Rojas-Líbano D, Kay LM (2008) Olfactory system gamma oscillations: the physiological dissection of a cognitive neural system. Cogn Neurodyn 2:179–194
Rolls ET (1989) Functions of neuronal networks in the hippocampus and neocortex in memory. In: Byrne JH, Berry WO (eds) Neural models of plasticity: experimental and theoretical approaches. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 240–265
Rolls ET (1989) The representation and storage of information in neural networks in the primate cerebral cortex and hippocampus. In: Durbin R, Miall C, Mitchison G (eds) Comput Neuron. Addition-Wesley, Wokingham, pp 125–159
Rolls ET (1989) Functions of neuronal networks in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex in memory. In: Cotterill R (ed) Models Brain Function. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 15–33
Rolls ET (2016) Pattern separation, completion, and categorization in the hippocampus and neocortex. Neurobiol Learn Mem 129:4–28
Roux NL, Amar M, Baux G, Fossier P (2006) Homeostatic control of the excitation-inhibition balance in cortical layer 5 pyramidal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 24:3507–3518
Santhakumar V, Bender R, Frotscher M, Ross ST, Hollrigel GS, Toth Z, Soltesz I (2000) Granule cell hyperexcitability in the early post-traumatic rat dentate gyrus: the “irritable mossy cell” hypothesis. J Physiol 524:117–134
Santhakumar V, Aradi I, Soltesz I (2005) Role of mossy fiber sprouting and mossy cell loss in hyperexcitability: A network model of the dentate gyrus incorporating cell types and axonal topography. J Neurophysiol 93:437–453
Santoro A (2013) Reassessing pattern separation in the dentate gyrus. Front Behav Neurosci 7:96
Savanthrapadian S, Meyer T, Elgueta C, Booker SA, Vida I, Bartos M (2014) Synaptic properties of SOM- and CCK-expressing cells in dentate gyrus interneuron networks. J Neurosci 34:8197–8209
Scharfman HE (1991) Dentate hilar cells with dendrites in the molecular layer have lower thresholds for synaptic activation by perforant path than granule cells. J Neurosci 11:1660–1673
Scharfman HE (2018) Advances in understanding hilar mossy cells of the dentate gyrus. Cell Tissue Res 373:643–652
Scharfman HE, Myers CE (2013) Hilar mossy cells of the dentate gyrus: A historical perspective. Front Neural Circuit 6:106
Scharfman HE, Myers CE (2016) Corruption of the dentate gyrus by “dominant” granule cells: Implications for dentate gyrus function in health and disease. Neurobiol Learn Mem 129:69–82
Schmidt B, Marrone DF, Markus EJ (2012) Disambiguating the similar: the dentate gyrus and pattern separation. Behav Brain Res 226:56–65
Schmidt-Hieber C, Bischofberger J (2010) Fast sodium channel gating supports localized and efficient axonal action potential initiation. J Neurosci 30:10233–10242
Schmidt-Hieber C, Jonas P, Bischofberger J (2007) Subthreshold dendritic signal processing and coincidence detection in dentate gyrus granule cells. J Neurosci 27:8430–8441
Shimazaki H, Shinomoto S (2010) Kernel bandwidth optimization in spike rate estimation. J Comput Neurosci 29:171–182
Sloviter RS (1991) Permanently altered hippocampal structure, excitability, and inhibition after experimental status epilepticus in the rat: the “dormant basket cell” hypothesis and its possible relevance to temporal lobe epilepsy. Hippocampus 1:41–66
Sloviter RS (1994) The functional organization of the hippocampal dentate gyrus and its relevance to the pathogenesis of temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol 35:640–654
Sloviter RS, Lømo T (2012) Updating the lamellar hypothesis of hippocampal organization. Front Neural Circuit 6:102
Solages De C, Szapiro G, Brunel N, Hakim V, Isope P, Buisseret P, Rousseau C, Barbour B, Lna C (2008) High-frequency organization and synchrony of activity in the purkinje cell layer of the cerebellum. Neuron 58:775–788
Squire L (1987) Memory and Brain. Oxford University Press, New York
Su L, Chang CJ, Lynch N (2019) Spike-based winner-take-all computation: Fundamental limits and order-optimal circuits. Neural Comput 31:2523–2561
Trapp P, Echeveste R, Gros C (2018) E-I balance naturally emerges from continuous Hebbian learning in autonomous neural networks. Sci Rep 8:8939
Treves A, Rolls ET (1991) What determines the capacity of autoassociative memories in the brain? Network 2:371–397
Treves A, Rolls ET (1992) Computational constraints suggest the need for two distinct input systems to the hippocampal CA3 network. Hippocampus 2:189–199
Treves A, Rolls ET (1994) Computational analysis of the role of the hippocampus in memory. Hippocampus 4:374–391
Wang XJ (2010) Neurophysiological and computational principles of fscortical rhythms in cognition. Physiol Rev 90:1195–1268
Wang Y, Zhang X, **n Q, Hung W, Florman J, Huo J, Xu T, **e Y, Alkema MJ, Zhen M, Wen Q (2020) Flexible motor sequence generation during stereotyped escape responses. eLife 9: e56942
West MJ, Slomianka L, Gundersen HJ (1991) Unbiased stereological estimation of the total number of neurons in the subdivisions of the rat hippocampus using the optical fractionator. Anat Rec 231:482–497
Willshaw D, Buckingham J (1990) An assessment of Marr’s theory of the hippocampus as a temporary memory store. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 329:205–215
Yassa MA, Stark CEL (2011) Pattern separation in the hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 34:515–525
Yim MY, Hanuschkin A, Wolfart J (2015) Intrinsic rescaling of granule cells restores pattern separation ability of a dentate gyrus network model during epileptic hyperexcitability. Hippocampus 25:297–308
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (Grant No. 20162007688).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SY., Lim, W. Population and individual firing behaviors in sparsely synchronized rhythms in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Cogn Neurodyn 16, 643–665 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-021-09728-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-021-09728-4