Abstract
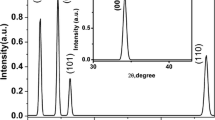
Silver (Ag) and tin (Sn) nanoparticles (NPs) were deposited by thermal evaporation onto heated glass substrates with a good control of size, shape and surface coverage. This process has the advantage of allowing the fabrication of thin-film solar cells with incorporated NPs without vacuum break, since it does not require chemical processes or post-deposition annealing. The X-ray diffraction, TEM and SEM properties are correlated with optical measurements and amorphous silicon hydrogenated (a-Si:H) films deposited on top of both types of NPs show enhanced absorbance in the near-infrared. The results are interpreted with electromagnetic modelling performed with Mie theory. A broad emission in the near-infrared region is considerably increased after covering the Ag nanoparticles with an a-Si:H layer. Such effect may be of interest for possible down-conversion mechanisms in novel photovoltaic devices.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimov YA, Koh WS, Ostrikov K (2009) Enhancement of optical absorption in thin-film solar cells through the excitation of higher-order nanoparticle plasmon modes. Opt Express 17(12):10195–10205
Pillai S, Catchpole KR, Trupke T, Green MA (2007) Surface plasmon enhanced silicon solar cells. J Appl Phys 101(9)
Martin A, Green KE, Yoshihiro H, Wilhelm W (2011) Progress in photovoltaics: Research and applications Prog. Prog Photovolt Res Appl 19:84–92
Stephan Fahr CR, Falk L (2010) Improving the efficiency of thin film tandem solar cells by plasmonic intermediate reflectors. Phot Nano: Fund Appl 8:291–296
Lance K, Kelly EC, Lin Lin Z, Schatz GC (2003) The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 107:668–677
Mendes MJ, Luque A, Tobias I, Marti A (2009) Plasmonic light enhancement in the near-field of metallic nanospheroids for application in intermediate band solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 95:071105
Yuriy A, Akimov WSK (2011) Design of Plasmonic nanoparticles for efficient subwavelength light trap** in thin-film solar cells. Plasmonics 6:155–161
El-Sayed MA (2001) Some interesting properties of metals confined in time and nanometer space of different shapes. Acc Chem Res 34(4):257–264
Nakayama K, Atwater HA (2008) Plasmonic nanoparticle enhanced light absorption in GaAs solar cells Appl. Phys Lett 93:121904
Skrabalak SE, Au L, Li X, **a Y (2007) Facile Synthesis of Ag Nanocubes and Au Nanocages. Nat Protoc 2:2182–2190
Mendes MJ, Hernández E, Galicia IT, Veja AM and Luque A (2010) Embedment of metal nanoparticles in GaAs and Si for plasmonic absorption enhancement in intermediate band solar cells. in 25th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition. 5th World Conf Photovoltaic Energy Convers
Hutter E, Fendler JH (2004) Exploitation of localized surface plasmon resonance. Adv Mater 16(19):1685–1706
Iida T, Ishihara H (2003) Theoretical study of the optical manipulation of semiconductor nanoparticles under an excitonic resonance condition. Phys Rev Lett 90:057403
Chang SS, Park DK (2002) Novel Sn powder preparation by spark processing and luminescence properties Mat. Sci Eng B 95:55
Temple TL, Mahanama GDK, Reehal HS, Bagnall DM (2009) Influence of localized surface plasmon excitation in silver nanoparticles on the performance of silicon solar cells. Sol Energ Mat Sol Cells 93:1978–1985
Kjeldsen MM, Hansen JL, Pedersen TG, Gaiduk P, Larsen AN (2010) Tuning the plasmon resonance of metallic tin nanocrystals in Si-based materials. Appl Phys A 100(1):31–37
Aguas H, Ram SK, Araujo A, Gaspar D, Vicente A, Filonovich SA, Fortunato E, Martins R, Ferreira I (2011) Silicon thin film solar cells on commercial tiles. Energy Environ Sci 4(11):4620–4632
Ohring M (1992) The Materials Science of Thin films. Academic Press 195–247
Scherrer P (1918) Göttinger Nachrichten Gesell 2:98
Refractive Index Database. http://refractiveindex.info. Accessed Nov 2012
Bohren CF, Huffman DR (2004) Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, ISBN: 9780471293408
Sun H, Yu M, Wang G, Sun X, Lian J (2012) Temperature-dependent morphology evolution and surface plasmon absorption of ultrathin gold island films. J Phys Chem C 116:9000–9008
Pillai S, Green MA (2010) Plasmonics for photovoltaics applications. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 94:1481–1486
West PR, Ishii S, Naik NGV, Emani NK, Shalaev VM, Boltasseva A (2010) Searching for better plasmonic materials. Laser & Photon Rev 4(6):1–13
Palik E (1997) Handbook of optical constants of solids (5 volume set). Academic Press, San Diego
Takeuchi K, Adachi S (2009) Optical properties of β-Sn films. J Appl Phys 105(7):073520
Fu Q, Sun (2001) Mie theory for light scattering by a spherical particle in an absorbing medium. Appl Opt 40(9):1354–1361
Boyd GT, Yu ZH, Shen YR (1986) Photoinduced luminescence from the noble metals and its enhancement on roughened surfaces. Phys Rev B 33:7923–7936
Na SH, Park CH (2010) First-principles study of the structural phase transition in Sn. J Kor Phys Soc 56(1):494–497
Adachi S (1989) Optical dispersion relations for GaP, GaAs, GaSb, InP, InAs, InSb, Al x Ga1−x As, and In1−x Ga x As y P1−y . J Appl Phys 66(12):813
Ihm J, Cohen ML (1981) Equilibrium properties and the phase transition of grey and white tin. Phys Rev B 23(4):1576
Kremer F, Luce FP, Fabrim ZE, Sanchez DF, Lang R, Zawislak FC, Fichtner PFP (1981) Tailoring the blue–violet photoluminescence from Sn-implanted SiO2 using a two-step annealing process. J Phys D Appl Phys 45:095304
Yeshchenko OA, Dmitruk IM, Alexeenko AA, Losytskyy MY, Kotko AV, Pinchuk AO (2009) Size-dependent surface-plasmon-enhanced photoluminescence from silver nanoparticles embedded in silica. Phys Rev B 79:235438
Moontragoon P, Vukmirovic N, Ikonic Z, Harrison P (2009) Electronic structure and optical transitions in Sn and SnGe quantum dots in a Si matrix. Microelect Journal 40:483–485
Smitha SL, Nissamudeen KM, Philip D, Gopchandran KG (2008) Studies on surface plasmon resonance and photoluminescence of silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 71(1):186–190
Minissale S (2009) Optical properties of Er-doped Si-based media. Dissertation
Zheng J, Zhou C, Yu M, Liu J (2012) Different sized luminescent gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 4:4073–4083
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Strategic Project PEst-C/CTM/LA0025/2011, project PTDC/CTM/099719/2008 and the colleagues Joana Vaz Pinto and Luis Pereira for the XRD and SEM measurements. M. J. Mendes also acknowledges funding from the EU FP7 Marie Curie Action (FP7-PEOPLE-2010-ITN) through the PROPHET project (Grant No. 264687).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaspar, D., Pimentel, A.C., Mendes, M.J. et al. Ag and Sn Nanoparticles to Enhance the Near-Infrared Absorbance of a-Si:H Thin Films. Plasmonics 9, 1015–1023 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9709-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9709-0