Abstract
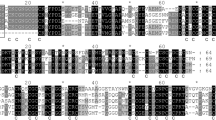
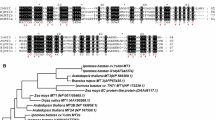
A new gene of metallothionein (MT) family was cloned from garlic (Allium sativum) seedlings using RACE method and designated AsMT2b. The full length of AsMT2b cDNA was 520 bp encoding 80 amino acids. The deduced amino acids of AsMT2b showed that AsMT2b contained the characteristic structure of type 2 MT proteins, but the number and arrangement of the cysteine residues in the N-and C-terminal domains was different from other type 2 MT proteins. Semi-quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR showed that transcript levels of AsMT2b were enhanced only in response to higher concentrations or longer incubation time of Cd. Such an expression pattern of AsMT2b greatly differed from that of other type 2 MT genes. Yeast cells transformed with this gene had improved resistance to Cd. AsMT2b overexpressing Arabidopsis showed stronger Cd tolerance and higher Cd accumulation compared with wild-type plants. These results suggest that AsMT2b should be useful in phytoremediation of Cd-polluted soil in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Margoshes, M., Vallee, B. L., A cadmium protein from equine kidney cortex, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1957, 29: 4813–4814.
Robinson, N. J., Tommey, A. M., Kuske, C. et al., Plant metallothioneins, Biochem. J., 1993, 295: 1–10.
Cobbett, C., Goldsbrough, P. B., Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: Roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2002, 53: 159–182.
Bhalerao, R., Keskitalo, J., Sterky, F. et al., Gene expression in autumn leaves, Plant Physiol., 2003, 131: 430–442.
Liu, P., Goh, C. J., Loh, C. S. et al., Differential expression and characterization of three metallothionein-like genes in Cavendish banana, Physiol. Plant, 2002, 114: 241–250.
Yu, L. H., Umeda, M., Liu, J. Y. et al., A novel MT gene of rice plants is strongly expressed in the node portion of the stem, Gene, 1998, 206: 29–35.
Akashi, K., Nishimura, N., Ishida, Y. et al., Potent hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity of drought-induced type-2 metallothionein in wild watermelon, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2004, 323: 72–78.
Zhou, J., Goldsbrough, P. B., Structure, organization and expression of the metallothionein gene family in Arabidopsis, Mol. Gen. Genet., 1995, 248: 318–328.
Garcia-Hernandez, M., Murphy, A., Taiz, L., Metallothioneins 1 and 2 have distinct but overlap** expression patterns in Arabidopsis, Plant Physiol., 1998, 118: 387–397.
Lee, J., Shim, D., Song, W. Y, et al., Arabidopsis metallothioneins 2a and 3 enhance resistance to cadmium when expressed in Vicia faba guard cells, Plant Mol. Biol., 2004, 54: 805–815.
Giritch, A., Ganal, M., Stephan, U. W. et al., Structure, expression and chromosomal localisation of the metallothionein-like gene family of tomato, Plant Mol. Biol., 1998, 37: 701–714.
Zhang, H. Y., Jiang, Y. N., He, Z. Y. et al., Cadmium accumulation and oxidative burst in garlic (Allium sativum), J. Plant Physiol., 2005, 162: 977–984.
Adams, A., Gottschling, D. E., Kaiser, C. A. et al., Methods in Yeast Genetics: A Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Course Manual, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 1998.
Clough, S. J., Bent, A. F., Floral dip: A simplified method for agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana, Plant J., 1998, 16: 735–743.
Zhang, H. Y., Xu, W. Z., Guo, J. B. et al., Coordinated responses of phytochelatins and metallothioneins to heavy metals in garlic seedlings, Plant Sci., 2005, 169: 1059–1065.
Ma, M., Lau, P. S., Jia, Y. T. et al., The isolation and characterization of type 1 metallothionein (MT) cDNA from a heavy-metal-tolerant plant, Festuca rubra cv. Merlin, Plant Sci., 2003, 164: 51–60.
Kawashima, I., Inokuchi, Y., Chino, M. et al., Isolation of a gene for a metallothionein like protein from soybean, Plant Cell Physiol., 1991, 32: 913–916.
Chang, T. J., Chen, L., Lu, Z. X. et al., Cloning and expression patterns of a metallothionein-like gene htMT2 of Helianthus tube-rosus, Acta Bot. Sin., 2002, 44: 1188–1193.
Brkljacic, J. M., Samardzic, J. T., Timotijevic, G. S. et al., Expression analysis of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) metallothionein-like gene (MT3) under different stress and physiological conditions, J. Plant Physiol., 2004, 161: 741–746.
Mejare, M., Bulow, L., Metal-binding proteins and peptides in bio-remediation and phytoremediation of heavy metals, Trends in Biotech, 2001, 19: 67–73.
Evans, K. M., Gatehouse, J. A., Lindsay, W. P. et al., Expression of the pea metallothionein-like gene PsMT A in Escherichia coli and Arabidopsis thaliana and analysis of trace metal ion accumulation: implications for PsMT A function, Plant Mol. Biol., 1992, 20: 1019–1028.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Xu, W., Dai, W. et al. Functional characterization of cadmium-responsive garlic gene AsMT2b: A new member of metallothionein family. CHINESE SCI BULL 51, 409–416 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0409-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0409-9