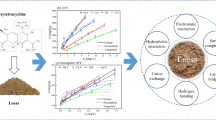
Abstract
Purpose
The contamination of soil with antibiotics has become a hot issue for the environment and global public health. However, there are scarcely any studies on the occurrence forms of antibiotics in saline soil. Occurrence forms of antibiotics are related to bioavailability. Therefore, this study facilitates the evaluation of the ecological risk of antibiotics in saline soil.
Materials and methods
An experiment with artificial antibiotic contamination of soil and salinization simulations was conducted. The changes in the occurrence forms of oxytetracycline (OTC) and sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in saline soil were analyzed by continuous ultrasonic extraction. The factors for occurrence forms, including aging time and particle size fraction, were considered.
Results and discussion
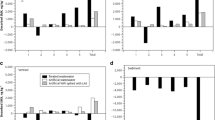
Soil salinization promoted the conversion of OTC and SMX from acid-soluble and bound states to water-soluble and locked states. Oxytetracycline in saline soil was predominantly in the water-soluble and acid-soluble states, accounting for 54.9–83.7% of the total. Sulfamethoxazole as well is accounting for 66.1–82.1%. In addition, the aging process from 7 to 63 days facilitated the conversion of OTC and SMX from the water-soluble, acid-soluble, and bound states to the non-extractable locked states, resulting in reduced bioavailability. Since the content of extractable forms of OTC and SMX in saline clay was high, it favors conversion to a locked state.
Conclusions
Oxytetracycline and sulfamethoxazole in saline soil were mainly in bioavailable states. The aging effect reduced the bioavailability of OTC and SMX in saline soil. Clay had the low proportion of OTC and SMX in the bioavailable state, reducing environmental risks.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Alexander M (2000) Aging, bioavailability, and overestimation of risk from environmental pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 34:4259–4265. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001069+
Bastos MC, Soubrand M, Le Guet T, Le Floch E, Joussein E, Baudu M, Casellas M (2020) Occurrence, fate and environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical compounds in soils amended with organic wastes. Geoderma 375:114498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114498. ISSN: 0016-7061
Bílková Z, Malá J, Hrich K (2019) Fate and behaviour of veterinary sulphonamides under denitrifying conditions. Sci Total Environ 695:133824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133824
Boonsaner M, Hawker D (2010) Accumulation of oxytetracycline and norfloxacin from saline soil by soybeans. Sci Total Environ 408:1731–1737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.12.032
Calace N, Fiorentini F, Petronio B, Pietroletti M (2001) Effects of acid rain on soil humic compounds. Talanta 54:837–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(01)00334-4
Carstens KL, Gross AD, Moorman TB, Coats JR (2013) Sorption and photodegradation processes govern distribution and fate of sulfamethazine in freshwater–sediment microcosms. Environ Sci Technol 47:10877–10883. https://doi.org/10.1021/es402100g
Carvalho IT, Santos L (2016) Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: a review of the European scenario. Environ Int 94:736–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.06.025
Chen H, Gao B, Li H, Ma LQ (2011) Effects of pH and ionic strength on sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin transport in saturated porous media. J Contam Hydrol 126:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2011.06.002
Chen K-L, Liu L-C, Chen W-R (2017) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and sulfapyridine antibiotics in high organic content soils. Environ Pollut 231:1163–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.011
Chen Y, Hu C, Deng D, Li Y, Luo L (2020) Factors affecting sorption behaviors of tetracycline to soils: importance of soil organic carbon, pH and Cd contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 197:110572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110572. ISSN: 0147-6513
Conde-Cid M, Nunez-Delgado A, Fernandez-Sanjurjo MJ, Alvarez-Rodriguez E, Fernandez-Calvino D, Arias-Estevez M (2020) Tetracycline and sulfonamide antibiotics in soils: Presence, fate and environmental risks. Processes 8:1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111479. ISSN: 2227-9717
Cycoń M, Mrozik A, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2019) Antibiotics in the soil environment—degradation and their impact on microbial activity and diversity. Front Microbiol 10:338. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00338
De Liguoro M, Cibin V, Capolongo F, Halling-Sørensen B, Montesissa C (2003) Use of oxytetracycline and tylosin in intensive calf farming: evaluation of transfer to manure and soil. Chemosphere 52:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00284-4
Díaz-Cruz MS, de Alda MJ, Barceló D (2006) Determination of antimicrobials in sludge from infiltration basins at two artificial recharge plants by pressurized liquid extraction–liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1130:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.05.076
Figueroa RA, Leonard A, MacKay AA (2004) Modeling tetracycline antibiotic sorption to clays. Environ Sci Technol 38:476–483. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0342087
Forster M, Laabs V, Lamshoft M, Groeneweg J, Zuhlke S, Spiteller M, Krauss M, Kaupenjohann M, Amelung W (2009) Sequestration of manure-applied sulfadiazine residues in soils. Environ Sci Technol 43:1824–1830. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8026538
Francisco-Marquez M, Soriano-Correa C, Sainz-Díaz CI (2017) Adsorption of sulfonamides on phyllosilicate surfaces by molecular modeling calculations. J Phys Chem C 121:2905–2914. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b12467
Gao J, Pedersen JA (2005) Adsorption of sulfonamide antimicrobial agents to clay minerals. Environ Sci Technol 39:9509–9516. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050644c
Gao Y, Ren L, Ling W, Gong S, Sun B, Zhang Y (2010) Desorption of phenanthrene and pyrene in soils by root exudates. Bioresour Technol 101:1159–1165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.062
Gao Y, Zeng Y, Shen Q, Ling W, Han J (2009) Fractionation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon residues in soils. J Hazard Mater 172:897–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.084
Hacıosmanoğlu GG, Mejías C, Martín J, Santos JL, Aparicio I, Alonso E (2022) Antibiotic adsorption by natural and modified clay minerals as designer adsorbents for wastewater treatment: a comprehensive review. J Environ Manage 317:115397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115397. ISSN: 0301-4797
He Y, Liu C, Tang X-Y, **an Q-S, Zhang J-Q, Guan Z (2019) Biochar impacts on sorption-desorption of oxytetracycline and florfenicol in an alkaline farmland soil as affected by field ageing. Sci Total Environ 671:928–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.414
Heemken OP, Theobald N, Wenclawiak BW (1997) Comparison of ASE and SFE with soxhlet, sonication, and methanolic saponification extractions for the determination of organic micropollutants in marine particulate matter. Anal Chem 69:2171–2180. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac960695f
Hou J, Wan WN, Mao DQ, Wang C, Mu QH, Qin SY, Luo Y (2015) Occurrence and distribution of sulfonamides, tetracyclines, quinolones, macrolides, and nitrofurans in livestock manure and amended soils of Northern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4545–4554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3632-y
Hu Y, Cheng H (2016) Health risk from veterinary antimicrobial use in China’s food animal production and its reduction. Environ Pollut 219:993–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.099
Hu Y, Cheng H (2017) Elevated antimicrobial residues in animal food products call for institutional changes on veterinary drug management and animal food product surveillance in China. Int J Antimicrob Agents 51:165–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.11.016
Huang L, Liu Y, Ferreira JFS, Wang M, Na J, Huang J, Liang Z (2022) Long-term combined effects of tillage and rice cultivation with phosphogypsum or farmyard manure on the concentration of salts, minerals, and heavy metals of saline-sodic paddy fields in Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res 215:105222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.105222
Janssen C, Heijerick D, De Schamphelaere K, Allen H (2003) Environmental risk assessment of metals: tools for incorporating bioavailability. Environ Int 28:793–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00126-5
Ji LL, Wan YQ, Zheng SR, Zhu DQ (2011) Adsorption of tetracycline and sulfamethoxazole on crop residue-derived ashes: implication for the relative importance of black carbon to soil sorption. Environ Sci Technol 45:5580–5586. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200483b
Jiang Y, Liang X, Yuan L, Nan Z, Deng X, Wu Y, Ma F, Diao J (2021) Effect of livestock manure on chlortetracycline sorption behaviour and mechanism in agricultural soil in Northwest China. Chem Eng J 415:129020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129020. ISSN: 1385-8947
Jiang Y, Zhang Q, Deng X, Nan Z, Liang X, Wen H, Huang K, Wu Y (2020) Single and competitive sorption of sulfadiazine and chlortetracycline on loess soil from Northwest China. Environ Pollut 263:114650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114650. ISSN: 0269-7491
Kilislioglu A (2003) The effect of various cations and pH on the adsorption of U(VI) on Amberlite IR-118H resin. Appl Radiat Isot 58:713–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-8043(03)00116-7
Kottler B, Alexander M (2001) Relationship of properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to sequestration in soil. Environ Pollut 113:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00189-5
LeFevre GH, Hozalski RM, Novak PJ (2013) Root exudate enhanced contaminant desorption: an abiotic contribution to the rhizosphere effect. Environ Sci Technol 47:11545–11553. https://doi.org/10.1021/es402446v
Li S, Shi W, Li H, Xu N, Zhang R, Chen X, Sun W, Wen D, He S, Pan J, He Z, Fan Y (2018) Antibiotics in water and sediments of rivers and coastal area of Zhuhai City, Pearl River estuary, south China. Sci Total Environ 636:1009–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.358
Li J, Guo K, Cao Y, Wang S, Song Y, Zhang H (2021) Enhance in mobility of oxytetracycline in a sandy loamy soil caused by the presence of microplastics. Environ Pollut 269:116151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116151
Li Y, Tang H, Hu Y, Wang X, Ai X, Tang L, Matthew C, Cavanagh J, Qiu J (2016a) Enrofloxacin at environmentally relevant concentrations enhances uptake and toxicity of cadmium in the earthworm Eisenia fetida in farm soils. J Hazard Mater 308:312–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.057
Li Y, Wang H, Liu X, Zhao G, Sun Y (2016b) Dissipation kinetics of oxytetracycline, tetracycline, and chlortetracycline residues in soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:13822–13831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6513-8
Li WC (2014) Occurrence, sources, and fate of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environment and soil. Environ Pollut 187:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.01.015
Li Y-W, Wu X-L, Mo C-H, Tai Y-P, Huang X-P, **ang L (2011) Investigation of sulfonamide, tetracycline, and quinolone antibiotics in vegetable farmland soil in the Pearl River Delta area, southern China. J Agric Food Chem 59:7268–7276. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf1047578
Ling W, Ren L, Gao Y, Zhu X, Sun B (2009) Impact of low-molecular-weight organic acids on the availability of phenanthrene and pyrene in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 41:2187–2195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.08.003
Liu L, Song C, Yan Z, Li F (2009) Characterizing the release of different composition of dissolved organic matter in soil under acid rain leaching using three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy. Chemosphere 77:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.06.026
Liu Y, Bao Y, Cai Z, Zhang Z, Cao P, Li X, Zhou Q (2015) The effect of aging on sequestration and bioaccessibility of oxytetracycline in soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10425–10433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4190-7
Liu Y, Chen J (2022) Effect of ageing on biochar properties and pollutant management. Chemosphere 292:133427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133427. ISSN: 0045-6535
Ma LL, Zhang J, Han LS, Li WM, Xu L, Hu F, Li HX (2012) The effects of aging time on the fraction distribution and bioavailability of PAH. Chemosphere 86:1072–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.11.065
Mao X, Yang Y, Guan P, Geng L, Ma L, Di H, Liu W, Li B (2022) Remediation of organic amendments on soil salinization: focusing on the relationship between soil salts and microbial communities. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 239:113616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113616
Massé DI, Saady NMC, Gilbert Y (2014) Potential of biological processes to eliminate antibiotics in livestock manure: an overview. Animals 4:146–163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani4020146
McCarty LS, Mackay D (1993) Enhancing ecotoxicological modeling and assessment. Body residues and modes of toxic action. Environ Sci Technol 27:1718–1728. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00046a001
Northcott GL, Jones KC (2000) Experimental approaches and analytical techniques for determining organic compound bound residues in soil and sediment. Environ Pollut 108:19–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00199-2
Pan B, Wang P, Wu M, Li J, Zhang D, **ao D (2012) Sorption kinetics of ofloxacin in soils and mineral particles. Environ Pollut 171:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.07.037
Pan Z, Yang S, Zhao L, Li X, Weng L, Sun Y, Li Y (2021) Temporal and spatial variability of antibiotics in agricultural soils from Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, northern China. Chemosphere 272:129803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129803
Rath S, Fostier AH, Pereira LA, Dioniso AC, de Oliveira FF, Doretto KM, Maniero Peruchi L, Viera A, de Oliveira Neto OF, Dal Bosco SM, Martínez-Mejía MJ (2019) Sorption behaviors of antimicrobial and antiparasitic veterinary drugs on subtropical soils. Chemosphere 214:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.083
Rey-Salgueiro L, Pontevedra-Pombal X, Álvarez-Casas M, Martínez-Carballo E, García-Falcón MS, Simal-Gándara J (2009) Comparative performance of extraction strategies for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in peats. J Chromatogr A 1216:5235–5241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.05.011
Richnow HH, Seifert R, Hefter J, Kästner M, Mahro B, Michaelis W (1994a) Metabolites of xenobiotica and mineral oil constituents linked to macromolecular organic matter in polluted environments. Org Geochem 22:671–IN10. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-6380(94)90132-5
Sentek V, Braun G, Braun M, Sebesvari Z, Renaud FG, Herbst M, Frindte K, Amelung W (2020) Salinity-independent dissipation of antibiotics from flooded tropical soil: a microcosm study. Sci Rep 10:14088. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70943-w
Shen S, Yang S, Jiang Q, Luo M, Li Y, Yang C, Zhang D (2020) Effect of dissolved organic matter on adsorption of sediments to oxytetracycline: an insight from zeta potential and DLVO theory. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:1697–1709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06787-3
Shimizu A, Takada H, Koike T, Takeshita A, Saha M, Rinawati Nakada N, Murata A, Suzuki T, Suzuki S, Chiem NH, Tuyen BC, Viet PH, Siringan MA, Kwan C, Zakaria MP, Reungsang A (2013) Ubiquitous occurrence of sulfonamides in tropical Asian waters. Sci Total Environ 452–453:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.027
Singh A, Chaurasia D, Khan N, Singh E, Bhargava PC (2023) Efficient mitigation of emerging antibiotics residues from water matrix: Integrated approaches and sustainable technologies. Environ Pollut 328:121552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121552. ISSN: 0269-7491
Song M, Su Y, Jiang L, Peng K, Li J, Liu S, Sun Y, Chen CE, Luo C (2023) Assessing the bioavailability of antibiotics in soil with the diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT). J Hazard Mater 448:130935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.130935
Song Y, **g X, Fleischmann S, Wilke B-M (2002) Comparative study of extraction methods for the determination of PAHs from contaminated soils and sediments. Chemosphere 48:993–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00180-7
Song Y, Wang F, Yang X, Liu C, Kengara FO, ** X, Jiang X (2011) Chemical extraction to assess the bioavailability of chlorobenzenes in soil with different aging periods. J Soils Sediments 11:1345–1354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-011-0414-8
Tan L, Wang F, Liang M, Wang X, Das R, Mao D, Luo Y (2019) Antibiotic resistance genes attenuated with salt accumulation in saline soil. J Hazard Mater 374:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.020
Tao S, Xu F, Liu W, Cui Y, Coveney RM (2006) A chemical extraction method for mimicking bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to wheat grown in soils containing various amounts of organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 40:2219–2224. https://doi.org/10.1021/es051967b
Tessier A, Campbell PG, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac50043a017
Tolls J (2001) Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: a review. Environ Sci Technol 35:3397–3406. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0003021
Wang C, Zhu L, Zhang C (2015) A new speciation scheme of soil polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons for risk assessment. J Soils Sediments 15:1139–1149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1083-9
Wang S, Wang H (2015) Adsorption behavior of antibiotic in soil environment: a critical review. Front Env Sci Eng 9:565–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-015-0801-2
Wang Y, Fang L, Lin L, Luan T, Tam NF (2014) Effects of low molecular-weight organic acids and dehydrogenase activity in rhizosphere sediments of mangrove plants on phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 99:152–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.10.054
Wang Z, Li Q, Li X, Song C, Zhang G (2003) Sustainable agriculture development in saline-alkali soil area of Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Chin Geogr Sci 13:171–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-003-0012-9
Wegst-Uhrich SR, Navarro DA, Zimmerman L, Aga DS (2014) Assessing antibiotic sorption in soil: a literature review and new case studies on sulfonamides and macrolides. Chem Cent J 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-8-5
Wessels J, Ford W, Szymczak W, Schneider S (1998) The complexation of tetracycline and anhydrotetracycline with Mg2+ and Ca2+: a spectroscopic study. J Phys Chem B 102:9323–9331. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9824050
Wu J, Wang JY, Li ZT, Guo SM, Li KJ, Xu PS, Ok YS, Jones DL, Zou JW (2023) Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in agricultural soils: a systematic analysis. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 53:847–864. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2022.2094693
Wu X, Zhu L (2016) Evaluating bioavailability of organic pollutants in soils by sequential ultrasonic extraction procedure. Chemosphere 156:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.113
Wu Y, Williams M, Smith L, Chen D, Kookana R (2012) Dissipation of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim antibiotics from manure-amended soils. J Environ Sci Health B 47:240–249. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2012.636580
**ang L, Wu X-L, Jiang Y-N, Yan Q-Y, Li Y-W, Huang X-P, Cai Q-Y, Mo C-H (2016) Occurrence and risk assessment of tetracycline antibiotics in soil from organic vegetable farms in a subtropical city, South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:13984–13995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6493-8
**e W-Y, Shen Q, Zhao FJ (2018) Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance from animal manures to soil: a review. Eur J Soil Sci 69:181–195. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12494
Xu L, Zhang H, **ong P, Zhu Q, Liao C, Jiang G (2021a) Occurrence, fate, and risk assessment of typical tetracycline antibiotics in the aquatic environment: a review. Sci Total Environ 753:141975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141975
Xu X, Ma W, An B, Zhou K, Mi K, Huo M, Liu H, Wang H, Liu Z, Cheng G, Huang L (2021b) Adsorption/desorption and degradation of doxycycline in three agricultural soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 224:112675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112675. ISSN: 0147-6513
Yang C, Zhao Y, Cao W, **ng M, Xu X, Wang Z, Sun J (2022) Metagenomic analysis reveals antibiotic resistance genes and virulence factors in the saline-alkali soils from the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ Res 214:113823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113823
Yang J-F, Ying G-G, Yang L-H, Zhao J-L, Liu F, Tao R, Yu Z-Q, Pa P (2009) Degradation behavior of sulfadiazine in soils under different conditions. J Environ Sci Health B 44:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601230902728245
Yang L, Bian XG, Yang RP, Zhou CL, Tang BP (2018) Assessment of organic amendments for improving coastal saline soil. Land Degrad Dev 29:3204–3211. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3027
Zhang D, Yang S, Wang Y, Yang C, Chen Y, Wang R, Wang Z, Yuan X, Wang W (2019) Adsorption characteristics of oxytetracycline by different fractions of organic matter in sedimentary soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:5668–5679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4028-1
Zhang H, Lu T, Zhang R, Wang M, Krishnan S, Liu S, Zhou Y, Li D, Qi Z (2020) Effects of clay colloids on ciprofloxacin transport in saturated quartz sand porous media under different solution chemistry conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 199:110754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110754
Zhang J, Sequaris JM, Klumpp E (2013) Effects of natural organic matter on the microporous sorption sites of black carbon in a Yangtze River sediment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6992–6998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1712-z
Zhang HB, Luo YM, Wu LH, Huang YJ, Christie P (2015a) Residues and potential ecological risks of veterinary antibiotics in manures and composts associated with protected vegetable farming. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:5908–5918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3731-9
Zhang Q-q, Ying G-g, Pan C-g, Liu Y-s, Zhao J-l (2015b) Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ Sci Technol 49:6772–6782. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00729
Zhang X, Sarmah AK, Bolan NS, He L, Lin X, Che L, Tang C, Wang H (2016) Effect of aging process on adsorption of diethyl phthalate in soils amended with bamboo biochar. Chemosphere 142:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.037
Zhang W, Zhang L, Zhang K, Wang X, Xue F (2012) Determination of tetracyclines and their epimers in agricultural soil fertilized with swine manure by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Integr Agric 11:1189–1198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(12)60114-2
Zhao Y, Zhang Z, Li Z, Yang B, Li B, Tang X, Lai Y (2023) Comprehensive study on saline-alkali soil amelioration with sediment of irrigation area in Northeast China. Arab J Chem 16:104608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104608. ISSN: 1878-5352
Zhi S, Shen S, Zhou J, Ding G, Zhang K (2020) Systematic analysis of occurrence, density and ecological risks of 45 veterinary antibiotics: focused on family livestock farms in Erhai Lake basin, Yunnan, China. Environ Pollut 267:115539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115539
Zhou X, Wang J, Lu C, Liao Q, Gudda FO, Ling W (2020) Antibiotics in animal manure and manure-based fertilizers: occurrence and ecological risk assessment. Chemosphere 255:127006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127006. ISSN: 0045-6535
Zhou Y, Li W-b, Kumar V, Necibi MC, Mu Y-J, Shi C-z, Chaurasia D, Chauhan S, Chaturvedi P, Sillanpää M (2022) Synthetic organic antibiotics residues as emerging contaminants waste-to-resources processing for a circular economy in China: challenges and perspective. Environ Res 211:113075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113075
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41302206); Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province, China (2023-JC-YB-130); and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, CHD (300102299205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zengyu Liu: methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, and writing, preparation, and revision of original draft. Yuyun Chen: conceptualization, project administration, and funding acquisition. Junqin Zhang: validation and data curation. Fei Wang: writing which included review and editing. Hongli Zhang: writing which included review and editing. Rongrong Yun: writing which included review and editing. Ling Li: writing which included review and editing. Chayma Chilouch: writing which included review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Maria Manuela Abreu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Chen, Y., Zhang, J. et al. Study on the occurrence forms of oxytetracycline and sulfamethoxazole in saline soil and their influencing factors. J Soils Sediments 24, 1639–1651 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-024-03735-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-024-03735-8