Abstract
Purpose
The use of stormwater basins as constructed wetlands for the bioremediation of agricultural runoff waters contaminated with pesticides has great potential. The structure and dynamics of the bacterial community in such system, and its function with respect to contaminant removal, remain to be investigated in detail.
Materials and methods
The bacterial component of sediment collected from a vineyard stormwater basin (in Rouffach, France) that pooled incoming runoff water containing pesticide and copper, was investigated by enumeration of cultivable bacteria on sediment extract solid medium and by liquid enrichment cultures from sediment, in the presence of glyphosate, diuron, 3,4-dichloroaniline and copper. Its structure, as a function of sediment location, depth, rhizospheric status and the presence of contaminants, was studied by temporal temperature gradient electrophoresis. Cultures obtained by enrichment were screened by RISA and RFLP and the ability of different cultures for contaminant mitigation was evaluated by the chrome azurol S method (copper complexation) and HPLC (glyphosate, diuron and 3,4-dichloroaniline degradation). The composition of the mixed cultures with the highest potential with regard to degradation of glyphosate, diuron and 3,4-dichloroaniline and copper complexation were evaluated by sequence analysis of cloned PCR-amplified 16S rRNA gene fragments obtained from enrichment cultures.
Results and discussion
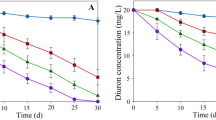
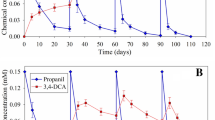
The bacterial community structure of sediment showed differences depending on sampling location, sediment depth and sampling date. Spiking with a cocktail of concentrated glyphosate, diuron, 3,4-dichloroaniline and copper altered the bacterial community structure, but rhizospheric samples were less affected. RISA and RFLP analysis differentiated 98 distinct cultures, 28 of which were able to complex copper, and three, 35 and seven were able to degrade glyphosate, diuron and 3,4-dichloroaniline, respectively. Sequencing of cloned 16S rRNA gene fragments amplified from faster-growing rhizospheric mixed culture 106, selected as the most efficient in complexing copper and degrading glyphosate, diuron and 3,4-dichloroaniline, showed that it consisted of Arthrobacter sp., Pseudomonas putida, Delftia acidovorans and Brevundimonas sp. strains.
Conclusions
The investigated stormwater basin contains bacterial populations specifically adapted to the transformation of diuron, 3,4-dichloroaniline (3,4-DCA) and glyphosate, and to copper complexation. The mixed culture 106 complexed high amounts of copper ions and degraded glyphosate and diuron without accumulation of the major diuron metabolite 3,4-DCA. Our results also suggest that plants may help to stabilise bacterial-driven pesticide mitigation in environments subject to variable conditions such as stormwater basins.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubertot JN, Barbier JM, Carpentier A, Gril JJ, Guichard L, Lucas P, Savary S, Savini I, Voltz, M (2005) Pesticides, agriculture et environnement. Réduire l’utilisation des pesticides et en limiter les impacts environnementaux. Rapport d’expertise scientifique collective. INRA et CEMAGREF, Paris
Banas D, Marin B, Skraber S, Chopin EIB, Zanella A (2010) Copper mobilisation affected by weather conditions in a stormwater detention system receiving runoff waters from vineyard soils (Champagne, France). Environ Pollut 158:476–482
Batisson I, Pesce S, Besse-Hoggan P, Sancelme M, Bohatier J (2007) Isolation and characterization of diuron-degrading bacteria from lotic surface water. Microb Ecol 54:761–770
Bazot S, Lebeau T (2008). Simultaneous mineralization of glyphosate and diuron by a consortium of three bacteria as free- and/or immobilized-cells formulations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:1351–1358
Bazot S, Bois P, Joyeux C, Lebeau T (2007) Mineralization of diuron [3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea] by co-immobilized Arthrobacter sp. and Delftia acidovorans. Biotechnol Lett 29:749–754
Bouldin JL, Farris JL, Moore MT, Smith S Jr, Cooper CM (2006) Hydroponic uptake of atrazine and lambda-cyhalotrin in Juncus effusus and Ludwigia peploides. Chemosphere 65:1049–1057
Bragato C, Brix H, Malagoli M (2006) Accumulation of nutrients and heavy metals in Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steudel and Bolboschoenus maritimus (L.) Palla in a constructed wetland of the Venice lagoon watershed. Environ Pollut 144:967–975
Braid M, Daniels LM, Kitts CL (2003) Removal of PCR inhibitors from soil DNA by chemical flocculation. J Microbiol Meth 52:389–393
Braud A, Hoegy F, Jezequel K, Lebeau T, Schalk IJ (2009) New insights into the metal specificity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyoverdine-iron uptake pathway. Environ Microbiol 11:1079–1091
Calheiros CSC, Duque AF, Moura A, Henriques IS, Correia A, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2009) Changes in the bacterial community structure in two-stage constructed wetlands with different plants for industrial wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 100:3228–3235
Cardinale M, Brusetti L, Quatrini P, Borin S, Puglia AM, Rizzi A, Zanardini E, Sorlini C, Corselli C, Daffonchio D (2004) Comparison of different primer sets for use in automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of complex bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6147–6156
Carter A (2000) How pesticides get into water—and proposed reduction measures. Pestic Outlook 11:149–156
Cullington JE, Walker A (1999) Rapid biodegradation of diuron and other phenylurea herbicides by a soil bacterium. Soil Biol Biochem 31:677–686
Dejonghe W, Berteloot E, Goris J, Boon N, Crul K, Maertens S, Höfte M, De Vos P, Verstraete W, Top EM (2003) Synergistic degradation of linuron by a bacterial consortium and isolation of a single linuron-degrading Variovorax strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1532–1541
Dessai DVG, Nayak GN, Basavaiah N (2009) Grain size, geochemistry, magnetic susceptibility: proxies in identifying sources and factors controlling distribution of metals in a tropical estuary, India. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 85:307–318
Dick RE, Quinn JP (1995) Glyphosate-degrading isolates from environmental samples: occurrence and pathways of degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:545–550
El-Deeb BA, Soltan SM, Ali AM, Ali KA (2000) Detoxification of the herbicide diuron by Pseudomonas sp. Folia Microbiol 45:211–216
El-Fantroussi S (2000) Enrichment and molecular characterization of a bacterial culture that degrades methoxy-methyl urea herbicides and their aniline derivatives. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5110–5115
El-Fantroussi S, Verschuere L, Verstraete W, Top EM (1999) Effect of phenylurea herbicides on soil microbial communities estimated by analysis of 16SrRNA gene fingerprints and community-level physiological profiles. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:982–988
Ellis PA, Camper ND (1982) Aerobic degradation of diuron by aquatic microorganisms. J Environ Sci Health B 17:277–289
Felske A, Akkermans ADL, De Vos WM (1998) Quantification of 16S rRNA in complex bacterial communities by multiple competitive reverse transcription-PCR in temperature gradient gel electrophoresis fingerprints. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4581–4587
Field JA, Reed RL, Sawyer TE, Griffith SM, Wigington PJ (2003) Diuron occurrence and distribution in soil and surface and ground water associated with grass seed production. J Environ Qual 32:171–179
Grégoire C, Elsaesser D, Huguenot D, Lange J, Lebeau T, Merli A, Mosé R, Passeport E, Payraudeau S, Schutz T, Schulz R, Tapia-Padilla G, Tournebize J, Trevisan M, Wanko A (2009) Mitigation of agricultural nonpoint-source pesticide pollution in artificial wetland ecosystems. Environ Chem Lett 7:205–231
Grégoire C, Payraudeau S, Domange N (2010) Use and fate of 17 pesticides applied on a vineyard catchment. Int J Environ Anal Chem 90:406–420
Hernando MD, Ejerhoon M, Fernández-Alba AR, Chisti Y (2003) Combined toxicity effects of MTBE and pesticides measured with Vibrio fischeri and Daphnia magna bioassays. Water Res 37:4091–4098
Heuer H, Hartung K, Wieland G, Kramer I, Smalla K (1999) Polynucleotide probes that target a hypervariable region of 16S-RNA genes to identify bacterial isolates corresponding to bands of community fingerprints. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1045–1049
Huang J, Su Z, Xu Y (2005) The evolution of microbial phosphonate degradative pathways. J Mol Evol 61:682–690
Huguenot D, Bois P, Jézéquel K, Cornu JY, Lebeau T (2010) Selection of low cost materials for the sorption of copper and herbicides as single or mixed compounds in matrices of increasing complexity. J Hazard Mater 182:18–26
IFEN (2007) Les pesticides dans les eaux—données 2005. Les dossiers IFEN 9
Kawai S, Uno B, Tomita M (1991) Determination of glyphosate and its major metabolite aminomethylphosphonic acid by high-performance liquid-chromatography after derivatization with para-toluenesulfonyl chloride. J Chromatogr 540:411–415
Kjelleberg S, Hermansson M (1984) Starvation-induced effects on bacterial surface characteristics. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:497–503
Kotsou M, Mari I, Lasaridi K, Chatzipavlidis I, Balis C, Kyriacou A (2004) The effect of olive oil mill wastewater (OMW) on soil microbial communities and suppressiveness against Rhizoctonia solani. Appl Soil Ecol 26:113–121
Kunito T, Saeki K, Oyaizu H, Matsumoto S (1999) Influences of copper forms on the toxicity to microorganisms in soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 44:174–181
Lebeau T, Bagot D, Jezequel K, Fabre B (2002) Cadmium biosorption by free and immobilised microorganisms cultivated in a liquid soil extract medium: effect of Cd, pH and techniques of culture. Sci Total Environ 291:73–83
Lebeau T, Braud A, Jézéquel K (2008) Performance of bioaugmentation-assisted phytoextraction applied to metal contaminated soils: a review. Environ Pollut 153:497–522
Le Bissonnais Y, Gascuel-Odoux C (2000) L’érosion hydrique des sols cultivés en milieu tempéré. Sol : interface fragile, (Stengel P & Gelin S, eds.), pp. 222. Coédition INRA et Nathan, Paris
Liebens J (2001) Heavy metal contamination of sediments in stormwater management systems: the effect of land use, particle size, and age. Environ Geol 41:341–351
Marugg JD, van Spanje M, Hoekstra WP, Schippers B, Weisbeek PJ (1985) Isolation and analysis of genes involved in siderophore biosynthesis in plant-growth-stimulating Pseudomonas putida WCS358. J Bacteriol 164:563–570
Matamoros V, Jaume Puigagut J, Joan Garcia J, Bayona JM (2007) Behavior of selected priority organic pollutants in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands: a preliminary screening. Chemosphere 69:1374–1380
McGrath SP, Shen ZG, Zhao FJ (1997) Heavy metal uptake and chemical changes in the rhizosphere of Thlaspi caerulescens and Thlaspi ochroleucum grown in contaminated soils. Plant Soil 188:153–159
McKinlay RG, Kasperek K (1999) Obsevations on decontamination of herbicide-polluted water by marsh plant systems. Water Res 33:505–511
Mitchell C, Brodie J, White I (2005) Sediments, nutrients and pesticide residues in event flow conditions in streams of the Mackay Whitsunday Region, Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 1:23–36
Nacamulli C, Bevivino A, Dalmastri C, Tabacchioni S, Chiarini L (1997) Perturbation of maize rhizosphere microflora following seed bacterization with Burkholderia cepacia MCI 7. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 23:183–193
Obojska A, Lejczak B, Kubrak M (1999) Degradation of phosphonates by streptomycete isolates. Appl Microbiol Biotech 51:872–876.
Peruzzo PJ, Porta AA, Roncoa AE (2008) Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in north pampasic region of Argentina. Environ Pollut 156:61–66
Rajkumar M, Ae N, Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2010) H Potential of siderophore-producing bacteria for improving heavy metal phytoextraction. Trends Biotechnol 28:142–149
Ribolzi O, Valles V, Gomez L, Voltz M (2002) Speciation and origin of particulate copper in runoff water from a Mediterranean vineyard catchment. Environ Pollut 117:261–271
Schröder P, Navarro-Aviñó JHA, Goldhirsh AG, DiGregorio S, Komives T, Langergraber G, Lenz A, Maestri E, Memon AR, Ranalli A, Sebastiani L, Smrcek S, Vanek T, Vuilleumier S, Wissing F (2007) Using phytoremediation technologies to upgrade waste water treatment in Europe. Environ Sci Pollut Res 14:440–447
Schulz R (2004) Field studies on exposure, effects, and risk mitigation of aquatic nonpoint-source insecticide pollution: a review. J Environ Qual 33:419–448
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and the determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56
Sleytr K, Tietz A, Langergraber G, Haberl R, Sessitsch A (2009) Diversity of abundant bacteria in subsurface vertical flow constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 35:1021–1025
Stenström J, Svensson K, Johansson M (2001) Reversible transition between active and dormant microbial states in soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 36:93–104
Stottmeister U, Wiessner A, Kuschk P, Kappelmeyer U, Kastner M, Bederski O, Muller RA, Moormann H (2003) Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Adv 22:93–117
Thioulouse J, Chessel D, Doledec S, Olivier JM (1997) ADE-4: a multivariate analysis and graphical display software. Stat Comput 7:75–83
Thompson I, van der Gast CJ, Ciric L, Singer AC (2005) Bioaugmentation for bioremediation: the challenge of strain selection: minireview. Environ Microbiol 7:909–915
Tixier C, Sancelme M, Aït-Aïssa S, Widehem P, Bonnemoy F, Cuer A, Truffaut N, Veschambre H (2002) Biotransformation of phenylurea herbicides by a soil bacterial strain, Arthrobacter sp. N2: structure, ecotoxicity and fate of diuron metabolite with soil fungi. Chemosphere 46:519–526
Travkin VM, Golovleva LA (2003) The degradation of 3,4-dichloroaniline by Pseudomonas fluorescens strain 26-K. Microbiology 72:240–243
Tsui MTK, Chu LM (2003) Aquatic toxicity of glyphosate-based formulations: comparison between different organisms and the effects of environmental factors. Chemosphere 52:1189–1197
Turnbull GA, Cullington JE, Walker A, Morgan JAW (2001a) Identification and characterisation of a diuron-degrading bacterium. Biol Fertil Soils 33:472–476
Turnbull GA, Ousley M, Walker A, Shaw E, Morgan JAW (2001b) Degradation of substituted phenylurea herbicides by Arthrobacter globiformis strain D47 and characterization of a plasmid-associated hydrolase gene, puhA. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2270–2275
Upchurch R, Chiu CY, Everett K, Dyszynski G, Coleman DC, Whitman WB (2008) Differences in the composition and diversity of bacterial communities from agricultural and forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1294–1305
USEPA (1996) Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils and oils, method 3051A. USEPA, Washington, DC
Van Elsas JD, Torsvik V, Hartmann A, Øvreås L, Jansson JK (2007) The bacteria and archaea in soil. Modern soil microbiology, 2nd edn. CRC, United States
Vartapetian BB, Jackson MB (1997) Plant adaptations to anaerobic stress. Ann Bot 79:3–20
Vauterin L, Vauterin P (1992) Computer-aided objective comparison of electrophoresis patterns for grou** and identification of microorganisms. Eur Microbiol 1:37–41
Verstraete W, Wittelbolle L, Heylen K, Vanparys B, de Vos P, van de Wiele T, Boon N (2007) Microbial resource management: the road to go for environmental biotechnology. Eng Life Sci 7:117–126
Viti C, Quaranta D, De Philippis R, Corti G, Agnelli A, Cuniglio R, Giovannetti L (2008) Characterizing cultivable soil microbial communities from copper fungicide-amended olive orchard and vineyard soils. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:309–318
Vroumsia T, Steiman R, Seigle-Murandi F, Benoit-Guyod JL, Khadrani A (1996) Biodegradation of three substituted phenylurea herbicides (chlortoluron, diuron, and isoproturon) by soft fungi. A comparative study. Chemosphere 33:2045–2056
Vymazal J, Kröpfelová L, Svehla J, Chrastný V, Stíchová J (2009) Trace elements in Phragmites australis growing in constructed wetlands for treatment of municipal wastewater. Ecol Eng 35:303–309
Widehem P, Aït-Aïssa S, Tixier C, Sancelme M, Veschambre H, Truffaut N (2002) Isolation, characterization and diuron transformation capacities of a bacterial strain Arthrobacter sp. N2. Chemosphere 46:527–534
Wikström P, Andersson AC, Forsman M (1999) Biomonitoring complex microbial communities using random amplified polymorphic DNA and principle component analysis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 28:131–139
You IS, Bartha R (1982) Metabolism of 3,4-dichloroaniline by Pseudomonas putida. J Agr Food Chem 30:274–277
Zhang G, Niu F, Ma X, Liu W, Dong M, Feng H, An L, Cheng G (2007) Phylogenetic diversity of bacteria isolates from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau permafrost region. Can J Microbiol 53:1000–1010
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the European Union through the project LIFE ENVIRONMENT ArtWET (LIFE 06 ENV/F/000133) “Mitigation of agricultural nonpoint-source pesticides pollution and phytoremediation in artificial wetland ecosystems” (Région Alsace and Conseil Général du Haut-Rhin) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Klara Hilscherova
Paul Bois, David Huguenot and Marie-Paule Norini contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bois, P., Huguenot, D., Norini, MP. et al. Herbicide degradation and copper complexation by bacterial mixed cultures from a vineyard stormwater basin. J Soils Sediments 11, 860–873 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-011-0354-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-011-0354-3