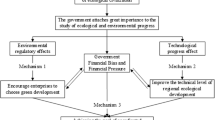
Abstract
Government attention and policy implementation are important for achieving environmental goals. This study uses 257 cities in China from 2013–2019 as the sample and measures local government attention through text mining, thus exploring the carbon emission reduction effect of government attention. Threshold regression is further used to examine the role and nonlinear relationship that environmental policies assume in the effect of government attention on carbon emission reduction. The conclusions are as follows: first, government attention can significantly reduce carbon emissions: with a 1% increase in local government attention to environmental protection, China’s urban CO2 can be reduced by 0.04%. Second, the impact of government attention on carbon emissions is more significant in cities in non-air pollution prevention areas, in non-SO2 and acid rain control areas, with longer tenure of officials, and with female officials serving during the sample period. Third, the effect of government attention on carbon emission reduction can be significantly increased under policy influence, especially when two policies are implemented in concert. Fourth, market incentive policies play a stronger role in the first place, while traditional energy-saving policies have strong sustainability. In general, the study concludes that municipalities should allocate more attention to the environment, and it gives some reasons supporting policy choices.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Some or all data, models, or code that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abid N, Ceci F, Ahmad F (2022) Financial development and green innovation, the ultimate solutions to an environmentally sustainable society: evidence from leading economies. J Clean Prod 369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133223
Adams RB, Ferreira D (2009) Women in the boardroom and their impact on governance and performance. J Financ Econ 94(2):291–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2008.10.007
Adams S, Adedoyin F, Olaniran E et al (2020) Energy consumption, economic policy uncertainty and carbon emissions; causality evidence from resource rich economies. Econ Anal Policy 68:179–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2020.09.012
Ahmad F, Draz MU, Chang WY et al (2020a) More than the resource curse: exploring the nexus of natural resource abundance and environmental quality in northwestern China. Resour Policy 70:101902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101902
Ahmad F, Draz MU, Ozturk I et al (2020b) Looking for asymmetries and nonlinearities: the nexus between renewable energy and environmental degradation in the northwestern provinces of China. J Clean Prod 266:121714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121714
Ahmad F, Draz MU, Chandio AA et al (2021) Investigating the myth of smokeless industry: environmental sustainability in the ASEAN countries and the role of service sector and renewable energy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:55344–55361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14641-8
Ahmad F, Draz MU, Chandio AA et al (2022) Natural resources and environmental quality: exploring the regional variations among Chinese provinces with a novel approach. Resour Policy 77:102745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.102745
Azimi M, Feng F, Zhou C (2020) Environmental policy innovation in China and examining its dynamic relations with air pollution and economic growth using SEM panel data. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07644-4
Balderas Torres A, Lazaro Vargas P, Paavola J (2020) The systemic and governmental agendas in presidential attention to climate change in Mexico 1994-2018. Nat Commun 11(1):455. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14048-7
Bao R, Liu T (2022) How does government attention matter in air pollution control? Evidence from government annual reports. Resour Conserv Recycl 185:106435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106435
Chen J, Li Q, Wang X (2022) Does the government’s environmental attention improve enterprise green innovation?—Evidence from China. Front Environ Sci 10:999492. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.999492
Cohen J (1995) Presidential rhetoric and the public agenda. Am J Polit Sci 39(1):87–107. https://doi.org/10.2307/2111759
Creti A, Nguyen DK (2020) Energy, climate and environment: policies and international coordination. Energy Policy 140:111226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111226
Du BS, Wu ZF (2021) Research on the impact of officer replacement and policy discontinuity on education investment. Soft Sci 35(8):7–13. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKibYlV5Vjs7iy_Rpms2pqwbFRRUtoUImHffreuh8rICZUuCA1-sXE1vSKezEsHUo3XxqyGxPvieO&uniplatform=NZKPT
Du SF, Tang WZ, Song ML (2016) Low-carbon production with low-carbon premium in cap-and-trade regulation. J Clean Prod 134:652–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.012
Flavin P, Franko WW (2017) Government’s unequal attentiveness to citizens’ political priorities. Policy Stud J 45(4):659–687. https://doi.org/10.1111/psj.12184
Frederick V, Withagen C (2012) Is there really a green paradox? J Environ Econ Manag 64(3):342–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2012.08.002
Glaeser LE, Kahn EM (2010) The greenness of cities: carbon dioxide emissions and urban development. J Urban Econ 67(3):404–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jue.2009.11.006
Hansen BE (1999) Threshold effects in non- dynamic panels: estimation, testing and inference. J Econom 93(2):345–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(99)00025-1
He DH, Kong FB (2019) Political potential in the implementation of public policies in China -- based on the analysis of rural forest reform policies in recent 20 years. Soc SciChina 4(4-25):204 https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKibYlV5Vjs7iLik5jEcCI09uHa3oBxtWoOcTXFxnVLvv6K6eZQeNgr8-oglZANOESkeFStYEnn2H&uniplatform=NZKPT
Hou XS, Yang RD (2016) The government's will to develop cities and the spatial promotion of regional urbanization in China -- a study based on the perspective of the government work report. Econ Rev (6):9–22. https://doi.org/10.19361/j.er.2016.06.02
Huang S, Ding Y, Failler P (2022) Does the government’s environmental attention affect ambient pollution? Empirical research on Chinese cities. Sustainability 14:3242. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14063242
Iqbal W, Tang YM, Ma LJ et al (2021) Energy policy paradox on environmental performance: the moderating role of renewable energy patents. J Environ Manag 297(2021):113230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113230
Jaffe AB, Newell RG, Stavins RN (2005) A tale of two market failures: technology and environmental policy. Ecol Econ 54(2-3):164–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.12.027
Ji X, Wu GW, Lin J et al (2022) Reconsider policy allocation strategies: a review of environmental policy instruments and application of the CGE model. J Environ Manag 323(2022):116176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116176
Jones B, Baumgartner F, Talbert J (1993) The destruction of issue monopolies in congress. AmPolitical Sci Rev 87(3):657–671. https://doi.org/10.2307/2938742
Kelso A (2017) The politics of parliamentary procedure: an analysis of Queen’s speech debates in the House of Commons. Br Politics 12(2):267–288. https://doi.org/10.1057/bp.2015.49
Li YH, Kong L (2019) Develo** solar and wind power generation technology to accelerate China’s energy transformation. Bull Chin Acad Sci 34(4):426–433. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKibYlV5Vjs7iLik5jEcCI09uHa3oBxtWoOHZJUxee1UcqdjclAW7r-JVzwY1eq-gUwov-TgJfaER&uniplatform=NZKPT
Liu CY, Shang YH (2017) Economic and social influencing factors of haze pollution degree and their spatio-temporal difference analysis--an empirical test based on panel data of 30 large and medium-sized cities. Econ Manag Rev 33(1):75–82. https://doi.org/10.13962/j.cnki.37-1486/f.2017.01.009
Lu WX, Wu HC, Yang SJ et al (2022) Effect of environmental regulation policy synergy on carbon emissions in China under consideration of the mediating role of industrial structure. J Environ Manag 322:116053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116053
Ma YR, Ji Q, Fan Y (2016) Spatial linkage analysis of the impact of regional economic activities on PM2.5 pollution in China. J Clean Prod 139(15):1157–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.152
Neves SA, Marques AC, Patrício M (2020) Determinants of CO2 emissions in European Union countries: does environmental regulation reduce environmental pollution? Econ Anal Policy 68:114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2020.09.005
Parmesan C, Yohe G (2003) A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature 421:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01286
Pinkse J, Gasbarro F (2019) Managing physical impacts of climate change: an attentional perspective on corporate adaptation. Bus Soc 58(2):333–368. https://doi.org/10.1177/0007650316648688
Qin YR (2022) Does environmental policy stringency reduce CO2 emissions? Evidence from high-polluted economies. J Clean Prod 341:130648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130648
Reguera AN, Fuentes DP, Laffarga J (2017) Does board gender diversity influence financial performance? Evidence from Spain. J Bus Ethics 141:337–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-015-2735-9
Ren L, Matsumoto KI (2020) Effects of socioeconomic and natural factors on air pollution in China: a spatial panel data analysis. Sci Total Environ 740:140155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140155
Ren SG, Li XL, Yuan BL (2018) The effects of three types of environmental regulation on ecoefficiency: a cross-region analysis in China. J Clean Prod 173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.113
Schreifels JJ, Fu Y, Wilson EJ (2012) Sulfur dioxide control in China: policy evolution during the 10th and 11th five-year plans and lessons for the future. Energy Policy 48:779–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.06.015
Shi YD (2014) Outstanding contradictions faced by China's energy policy and future strategic transformation. Dev Res 2:7–10 https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=bdl6HUpjFL1SgOr4xNNfY89vnRubHJ720KZOUPMToUhhmkDkOWCWSi5Nnp5ogM6OOsFA-beNCnuDYhg1W38-fZtTO3ppLx4yJ5aVepqio4viD24kQW0OrQ==&uniplatform=NZKPT
Simon HA (1976) Administrative behavior: a study of decision-making processes in administrative organizations[M], 3rd edn. Free Press, New York
Smulders S, Tsur Y, Zemel A (2012) Announcing climate policy: can a green paradox arise without scarcity? J Environ Econ Manag 64(3):364–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2012.02.007
Stavins RN (1996) Correlated uncertainty and policy instrument choice. J Environ Econ Manag 30(2):218e232 https://ideas.repec.org/a/eee/jeeman/v30y1996i2p218-232.html
Tao P (2019) On the basic view and localization of political attention research. J ShangHai Administration College 20(6):63–71 https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=bdl6HUpjFL0NErCAM-BJW0Mj93qMsMUoXJHl4QzSVS1iQVKHRuZG8R755jrOk56r02vAfoikPTLfMKOa0mZCHbC3ADYw-U44GCzvQW2r_C1Wy6UjbnRT7CZFcwrHXOrl&uniplatform=NZKPT
Tian J, Zhang S, Wei X et al (2022) The impact of government environmental attention on public health: implications for corporate sustainable development. Front Environ Sci 10:973477. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.973477
Tosun J (2012) Environmental monitoring and enforcement in Europe: a review of empirical research. Environ Policy Governance 22(6):437–448. https://doi.org/10.1002/eet.1582
Wang JF (2013) Paying attention to the attention in democratic governance commenting on re-conceiving decision-making in democratic politics attention, choice, and public policy. Public Adm 5:144 https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDHIS2&filename=GGXZ201305009&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=osANsS7rAnXylkGJTg6GPevH9Hc5BWLuW9CyvZkQqcHIPbYVmVxP6ayQIJWJaMbP
Wang L, Wang H, Dong Z et al (2021) The air pollution effect of government economic growth expectations: evidence from China’ s cities based on green technology. Environ Sci Pollut R 28(22):27639–27654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12536-2
Wang XB, Xu XX (2014) Official ability and economic development: evidence from the individual effect of provincial officials. Southern Econ (6):1–24. https://doi.org/10.19592/j.cnki.scje.2014.06.002
Wu H, Xu L, Ren S et al (2020) How do energy consumption and environmental regulation affect carbon emissions in China? New evidence from a dynamic threshold panel model. Resour Policy 67:101678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101678
Xu B, Chen YF, Shen XB (2019) Clean energy development, carbon dioxide emission reduction and regional economic growth. Econ Res J 54(7):188–202 https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKibYlV5Vjs7iLik5jEcCI09uHa3oBxtWoHGwy9XepWzL80GIlbuDYn2rvrgANvITNEEkVx5Vg6gF&uniplatform=NZKPT
Yang J, Zheng X (2020) Government annual report: decision usefulness, information accessibility and policy communication efficiency-observations from 19 Chinese cities. Policy Stud:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/01442872.2020.1724277
Ye KH, Guo ZH, Zhang WR et al (2022) Heterogeneous environmental policy tools for expressway construction projects: A crossregional analysis in China. Environ Impact Assess Rev 97:106907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106907
Yue L, Cao YX, Wang Y (2022) Regional carbon emission reduction effect of energy policy. Resour Sci 44(6):1105–1118. https://doi.org/10.18402/resci.2022.06.00
Zeng JJ, Tong WS (2018) How do energy policies affect the development of industrial green economy. China Popul Resour Environ 28(12):19–28 https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2019&filename=ZGRZ201812003&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=173CxpLuCZu7cTpmNxOM2NsQitlPg0F4wVzjnv71jl6q9jj9FSDrnVgfCdrDo80I
Zeng J, Liu T, Feiock R et al (2019) The impacts of China’ s provincial energy policies on major air pollutants: a spatial econometric analysis. Energy Policy 132:392–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.05.052
Zhang KX (2021) Research on the inverted U-shaped relationship between local government attention and environmental policy execution. Public Manag Rev 3(4):132–161 https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKibYlV5Vjs7iJTKGjg9uTdeTsOI_ra5_XUHKq-zk00djZLEc9R-o-V8AApvlJBJ8F-awwU-xF6oB&uniplatform=NZKPT
Zhang X, Xu F (2022) The impact of environmental regulation on green technological innovation -- analysis of regional heterogeneity based on the perspective of government intervention. Urban Issues (9):55–64. https://doi.org/10.13239/j.bjsshkxy.cswt.220906
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Zhang W et al (2019) Energy and resource conservation and air pollution abatement in China’s iron and steel industry. Resour Conserv Recycl 147:67–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.04.018
Zhao X, Yin H, Zhao Y (2015) Impact of environmental regulations on the efficiency and CO2 emissions of power plants in China. Appl Energy 149:238–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.03.112
Zhao LX, Yang CX, Su B et al (2020a) Research on a single policy or policy mix in carbon emissions reduction. J Clean Prod 267:122030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122030
Zhao X, Shang Y, Song M (2020b) Industrial structure distortion and urban ecological efficiency from the perspective of green entrepreneurial ecosystems. Socio Econ Plann Sci 72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2019.100757
Zheng S, Yi H, Li H (2015) The impacts of provincial energy and environmental policies on air pollution control in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 49:386–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.088
Zheng SM, He YJ, Zou K (2021) Climate policy synergy: mechanism and effect. China Popul Resour Environ 31(8):1–12 https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/
Funding
2022 The Excellent Postgraduate Innovation Star Project of Gansu Provincial Department of Education “Regional Carbon Reduction Effect and Mechanism Analysis of Energy Policy” (2022CXZX-020).
2022 Excellent Graduate Innovation Project for Basic Research Business Fees in Central Universities: A Study on the Impact of Foreign Investment Technology Spillovers on Local Enterprise Innovation under the Background of “Double Circulation” - Based on the Perspective of Enterprise Linkage (22lzujbkyxs023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Yuxuan Cao, Li Yue, and **anqiao Gao. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Yuxuan Cao, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This work does not involve any hazards, such as the use of animal or human subjects. There is no plagiarism in our research or any data, articles, or theories of others.
Consent to participate
All of the authors of the paper have participated in certain substantive aspects of this study, and they are acknowledged or listed as contributors.
Consent for publication
This paper has not been and will not be submitted simultaneously to other journals. The paper is an entirely original work conducted by us without copying or plagiarism issues. The information reported in the paper is accurate to the best of our knowledge. A single study was not split into several parts to increase the quantity of submissions and be submitted to various journals or to one journal over time. We consent to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• 1% increase in local government attention to environmental protection, China’s urban CO2 can be reduced by 0.04%.
• Heterogeneity in regional pollution levels and key characteristics of officials was examined.
• Based on the research idea of “government concern-policy implementation-target performance,” a threshold regression is used to explore the policies and their synergistic effects.
• Exploring the policies in detail, allowing for comparisons of differences within the same class of policies.
• Examining the nonlinear relationship between government attention and carbon emission reduction under the influence of different policies.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, ., Yue, L. & Gao, X. Exploring the carbon emission reduction effect of local government attention: an analysis based on an environmental policy perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 107634–107649 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29851-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29851-5